14 网络编程
14 网络编程
14.1 引入
【1】网络编程
把分布在不同地理区域的计算机与专门的外部设备用通信线路互连成一个规模大、功能强的网络系统,从而使众多的计算机可以方便的互相传递信息、共享硬件、软件、数据信息等资源。
设备之间在网络中进行数据的传输,发送/接收数据。
网络:两台或者两台以上的计算机构成网络。
【2】通信两个重要的要素:IP+PORT
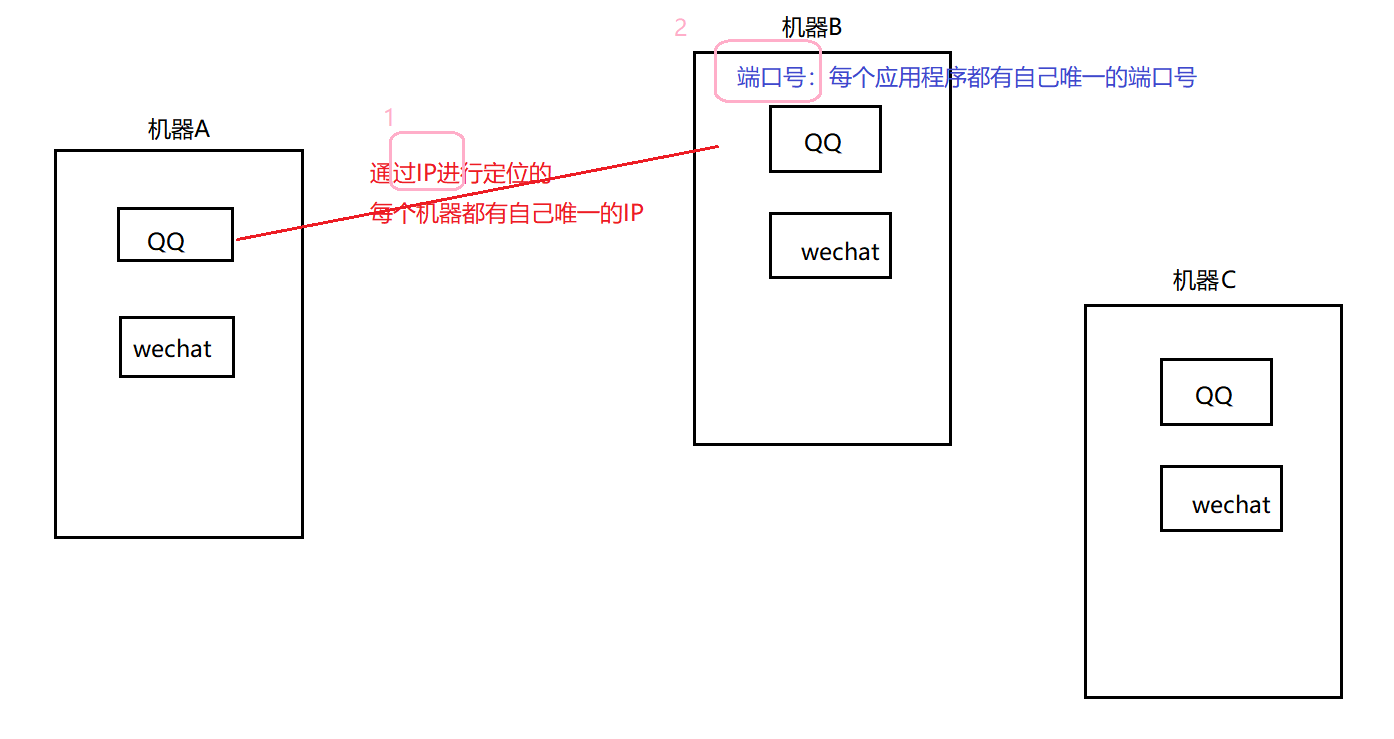
以上图片来自网络
域名:www.baidu.com -》 DNS服务器解析 -》 IP地址
【3】设备之间进行传输的时候,必须遵循一定的规则 -》 通信协议

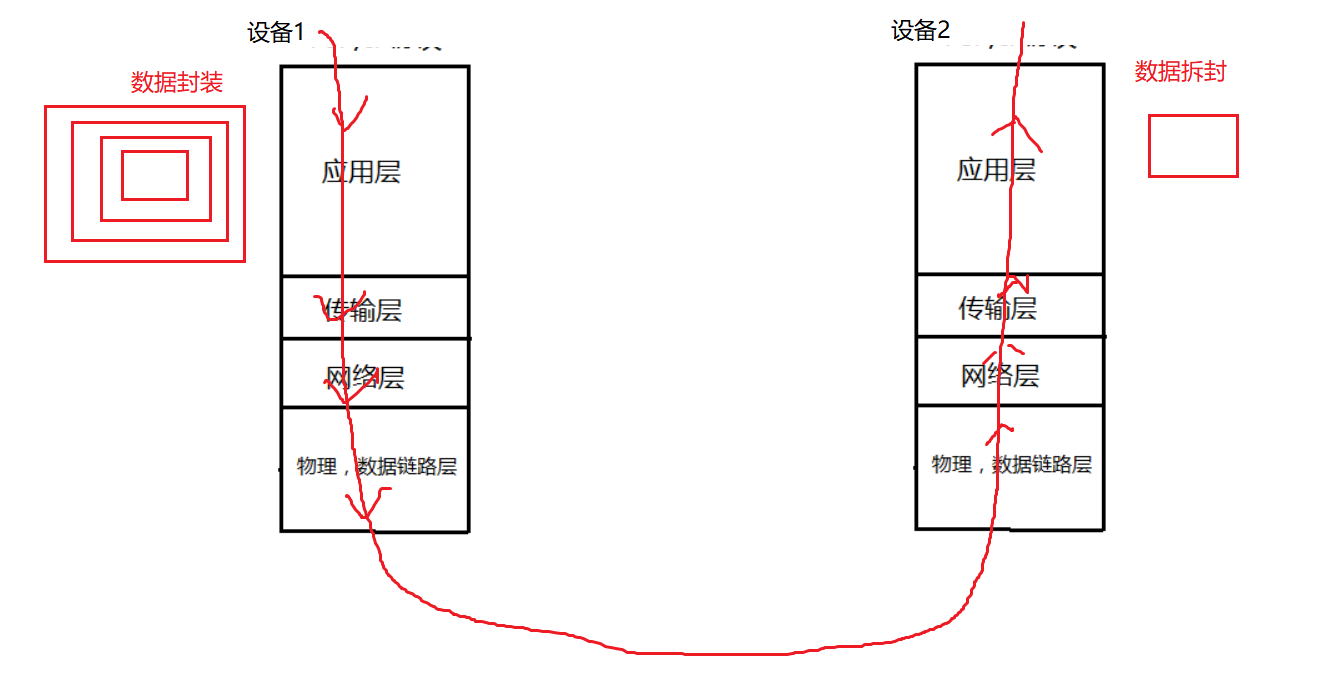
以上图片来自网络
【4】TCP协议:可靠的
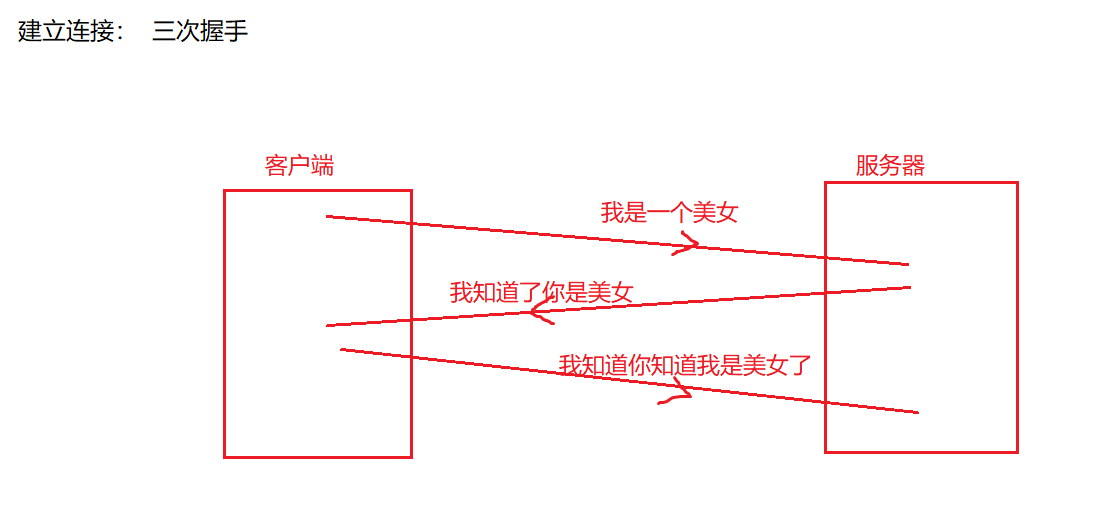
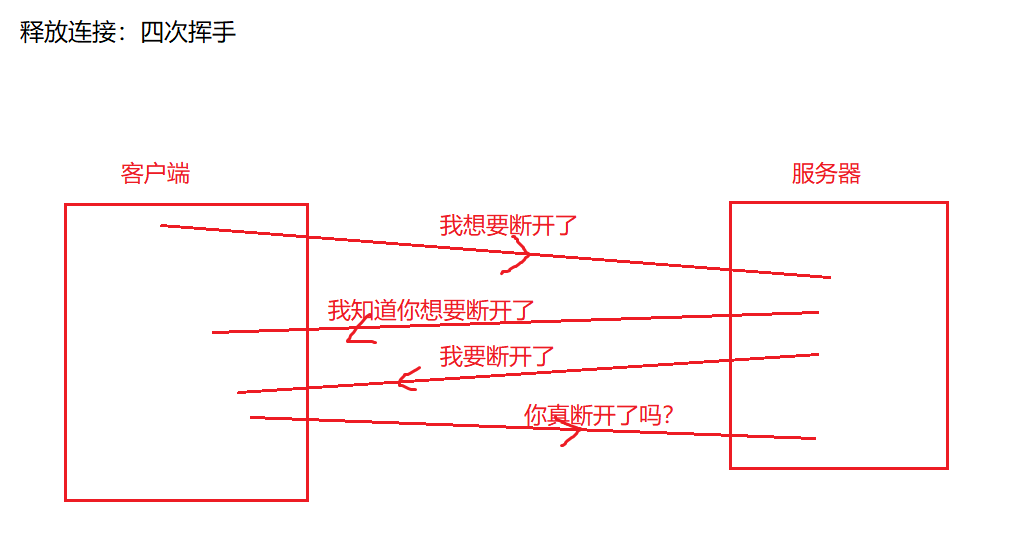
以上图片来自网络
【5】UDP协议:不可靠的
以上图片来自网络
14.2 InetAddress、InetSocketAddress两个类
前情提要:File -》 封装盘符一个文件
【1】InetAddress封装了IP
package com.liweixiao.test01;
import java.net.Inet6Address;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/13
* @description:
*/
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
//InetAddress ia = new InetAddress()不能直接创建对象,因为InetAddress()被default修饰
InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.199.217");
System.out.println(ia);
InetAddress ia2 = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");//localhost指代本机的IP地址
System.out.println(ia2);
InetAddress ia3 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println(ia3);
InetAddress ia4 = InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-7VCF8QNA");
System.out.println(ia4);
InetAddress ia5 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
System.out.println(ia5);//www.baidu.com/14.215.177.38
System.out.println(ia5.getHostName());//www.baidu.com
System.out.println(ia5.getHostAddress());//14.215.177.38
}
}
【2】InetSocketAddress封装了IP、端口号
package com.liweixiao.test01;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/13
* @description:
*/
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress("192.168.189.40", 8080);
System.out.println(isa);
System.out.println(isa.getHostName());
System.out.println(isa.getPort());
InetAddress ia = isa.getAddress();
System.out.println(ia.getHostName());
System.out.println(ia.getHostAddress());
}
}
14.3 网络通信的原理-套接字
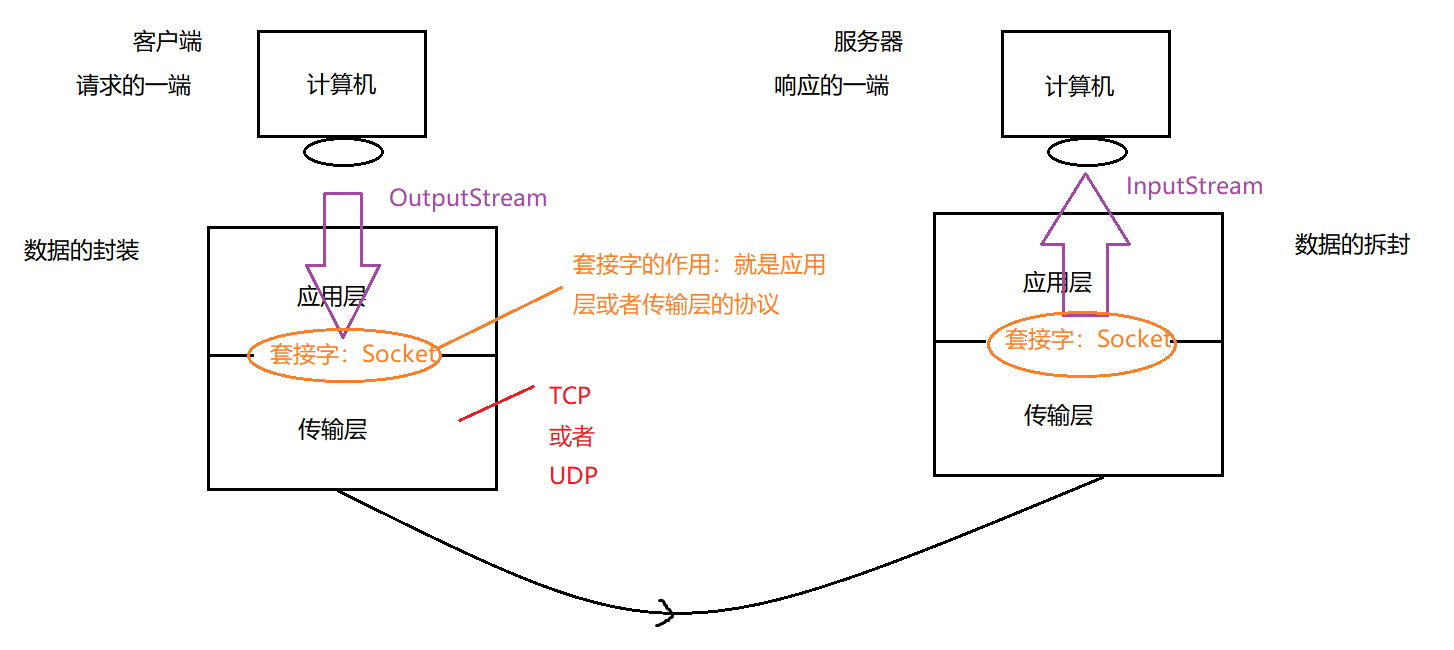
以上图片来自网络
14.4 基于TCP的网络编程
功能:模拟网站的登录,客户端录入账号密码,然后服务器端进行验证。
14.4.1 功能分解1:单向通信
功能:客户端发送一句话到服务器
【客户端】
package com.liweixiao.test012;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:客户端
*/
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的IP和端口号
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.0.209",8888);
//2.对于程序员,向外发送数据 -》 输出流
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
//利用OutputStream可以向外发送数据,但不能直接发送String方法,外面套了一个处理流DataOutputStream
dos.writeUTF("你好");
//3.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
dos.close();
os.close();
s.close();
}
}
【服务端】
package com.liweixiao.test012;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:服务器
*/
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的端口号
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
//2.等着客户端发来的信息
Socket s = ss.accept();//阻塞方法,等待接收客户端的数据,什么时候接收到数据什么时候程序继续向下执行
//accept()返回值是一个Socket,这个Socket是客户端的Socket
//接到这个Socket后,客户端和服务器才真正产生了连接,可以通信了
//3.操作流 -》 输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
//4.读取内容
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("客户端发来的数据为:"+str);
//5.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
dis.close();
is.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}
【测试】
(1)先开启服务器,再开启客户端
如果先开客户端,出错。Connection refused: connect
14.4.2 功能分解2:双向通信
【服务器端】
package com.liweixiao.test012;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:服务器
*/
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的端口号
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
//2.等着客户端发来的信息
Socket s = ss.accept();//阻塞方法,等待接收客户端的数据,什么时候接收到数据什么时候程序继续向下执行
//accept()返回值是一个Socket,这个Socket是客户端的Socket
//接到这个Socket后,客户端和服务器才真正产生了连接,可以通信了
//3.操作流 -》 输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
//4.读取内容
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("客户端发来的数据为:"+str);
///向客户端再输入一句话
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("你好,我是服务端,我接收到你的请求了");
//5.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
dos.close();
os.close();
dis.close();
is.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}
【客户端】
package com.liweixiao.test012;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:客户端
*/
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的IP和端口号
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.0.209",8888);
//2.对于程序员,向外发送数据 -》 输出流
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
//利用OutputStream可以向外发送数据,但不能直接发送String方法,外面套了一个处理流DataOutputStream
dos.writeUTF("你好");
//接收服务器端的回话
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
String str = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("服务器端对我说:"+str);
//3.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
dis.close();
is.close();
dos.close();
os.close();
s.close();
}
}
注意:关闭防火墙。
14.4.3 功能分解3:对象流传送
【封装的User类】
ObjectInputStream、ObjectOutputStream对象流传输的自定义对象,需要序列化
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/16
* @description:
*/
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 800522082945314117L;
//属性
private String name;//账号
private String pwd;//密码
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
//构造器
public User(String name, String pwd) {
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
}
【客户端】
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:客户端
*/
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的IP和端口号
Socket s = new Socket("192.168.0.209",8888);
//录入用户的账号和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请录入您的账号:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.print("请录入您的密码:");
String pwd = sc.next();
User user = new User(name, pwd);
//2.对于程序员,向外发送数据 -》 输出流
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
//接收服务器端的回话
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
boolean b = dis.readBoolean();
if(b){
System.out.println("恭喜,登录成功");
}else {
System.out.println("对不起,登录失败");
}
//3.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
dis.close();
is.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
s.close();
}
}
【服务器端】
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:服务器
*/
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的端口号
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
//2.等着客户端发来的信息
Socket s = ss.accept();//阻塞方法,等待接收客户端的数据,什么时候接收到数据什么时候程序继续向下执行
//accept()返回值是一个Socket,这个Socket是客户端的Socket
//接到这个Socket后,客户端和服务器才真正产生了连接,可以通信了
//3.操作流 -》 输入流
InputStream is = s.getInputStream();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
//4.读取内容
User user = (User) (ois.readObject());
//对对象进行验证
boolean flag=false;
if(user.getName().equals("娜娜") && user.getPwd().equals("123123")){
flag=true;
}
///向客户端输出
OutputStream os = s.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeBoolean(flag);
//5.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
dos.close();
os.close();
ois.close();
is.close();
s.close();
ss.close();
}
}
14.4.4 功能分解4:加入完整的处理异常方式
【服务器端】
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:服务器
*/
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的端口号
ServerSocket ss = null;
Socket s=null;
InputStream is=null;
ObjectInputStream ois=null;
OutputStream os=null;
DataOutputStream dos=null;
try {
ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
//2.等着客户端发来的信息
s = ss.accept();//阻塞方法,等待接收客户端的数据,什么时候接收到数据什么时候程序继续向下执行
//accept()返回值是一个Socket,这个Socket是客户端的Socket
//接到这个Socket后,客户端和服务器才真正产生了连接,可以通信了
//3.操作流 -》 输入流
is = s.getInputStream();
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
//4.读取内容
User user = (User) (ois.readObject());
//对对象进行验证
boolean flag=false;
if(user.getName().equals("娜娜") && user.getPwd().equals("123123")){
flag=true;
}
///向客户端输出
os = s.getOutputStream();
dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeBoolean(flag);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {//5.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
try {
if(dos != null){
dos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(os != null){
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(ois != null){
ois.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(s != null){
s.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(ss != null){
ss.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
【客户端】
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:客户端
*/
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的IP和端口号
Socket s = null;
OutputStream os=null;
ObjectOutputStream oos=null;
InputStream is=null;
DataInputStream dis=null;
try {
s = new Socket("LAPTOP-7VCF8QNA",8888);
//录入用户的账号和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请录入您的账号:");
String name = sc.next();
System.out.print("请录入您的密码:");
String pwd = sc.next();
User user = new User(name, pwd);
//2.对于程序员,向外发送数据 -》 输出流
os = s.getOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
//接收服务器端的回话
is = s.getInputStream();
dis = new DataInputStream(is);
boolean b = dis.readBoolean();
if(b){
System.out.println("恭喜,登录成功");
}else {
System.out.println("对不起,登录失败");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally{
//3.关闭流 + 关闭网络资源
try {
if(dis != null){
dis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(oos != null){
oos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(os != null){
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(s != null){
s.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
14.4.5 功能分解5:多线程接收用户请求
遗留问题:服务器针对一个请求服务,之后服务器就关闭了(程序自然结束了)。
需要解决:服务器必须一直监听,一直开着,等待客户端的请求。
在当前代码中,客户端不用动了。
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description:线程,专门处理客户端的请求
*/
public class ServerThread extends Thread{
InputStream is=null;
ObjectInputStream ois=null;
OutputStream os=null;
DataOutputStream dos=null;
Socket s=null;
public ServerThread(Socket s){
this.s=s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try{
//accept()返回值是一个Socket,这个Socket是客户端的Socket
//接到这个Socket后,客户端和服务器才真正产生了连接,可以通信了
//3.操作流 -》 输入流
is = s.getInputStream();
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
//4.读取内容
User user = (User) (ois.readObject());
//对对象进行验证
boolean flag=false;
if(user.getName().equals("娜娜") && user.getPwd().equals("123123")){
flag=true;
}
///向客户端输出
os = s.getOutputStream();
dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeBoolean(flag);
}catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
if(dos != null){
dos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(os != null){
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(ois != null){
ois.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(is != null){
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
package com.liweixiao.test03;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/15
* @description:服务器
*/
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("服务器启动了");
//1.创建套接字,指定服务器的端口号
ServerSocket ss = null;
Socket s=null;
int count=0;//定义计数器,统计客户端的请求
try {
ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
while (true){//加入死循环,服务器一直监听客户端是否发送数据
s = ss.accept();//阻塞方法,等待接收客户端的数据,什么时候接收到数据什么时候程序继续向下执行
//每次过来的客户端的请求,靠线程处理:
new ServerThread(s).start();
count++;
System.out.println("当前是第"+count+"位用户访问服务器,对应的用户是"+s.getInetAddress());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
14.5 基于UDP的网络编程
【TCP】
客户端:Socket;使用流:输出流OutputStream、DataOutputStream、ObjectOutputStream
服务器端:ServerSocket获取Socket;使用流:输入流InputStream、DataInputStream、ObjectInputStream
客户端和服务器端地位不平等。服务器先启动,等待客户端。
【UDP】
发送方:DatagramSocket 发送:数据包DatagramPacket
接收方:DatagramSocket 接收:数据包DatagramPacket
发送方和接收方的地位是平等的。
UDP案例,完成网站的咨询聊天。
14.5.1 功能分解1:单向通信
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.*;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description:发送方
*/
public class TestSend {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("学生上线。。。");
//1.准备套接字
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//2.准备数据包
String str="你好";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
//数据包需要四个参数:1.发送数据转换为字节数组,2.字节数组的长度,3.封装接收方的IP,4.指定接收方的端口号
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999);
//发送
ds.send(dp);
//关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description://接收方
*/
public class TestReceive {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("老师上线。。。");
//1.创建套接字
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
//2.有一个空的数据包,打算用来接收 对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
//3.接收对方的数据包,放入我们的dp数据包中
ds.receive(dp);//接收完后dp里面就填充内容了
//4.取出数据
byte[] data = dp.getData();
String s=new String(data,0,dp.getLength());//dp.getLength()数组包中的有效长度
System.out.println("学生对我说:"+s);
//5.关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
14.5.2 功能分解2:双向通信
【发送方】
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description:发送方
*/
public class TestSend {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("学生上线。。。");
//1.准备套接字
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//2.准备数据包
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("学生:");
//String str="老师,你好";
String str=sc.next();
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
//数据包需要四个参数:1.发送数据转换为字节数组,2.字节数组的长度,3.封装接收方的IP,4.指定接收方的端口号
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999);
//发送
ds.send(dp);
//接收老师发送回来的信息
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
ds.receive(dp2);
byte[] data = dp2.getData();
String s=new String(data,0,dp2.getLength());//dp.getLength()数组包中的有效长度
System.out.println("老师对我说:"+s);
//关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
【接收方】
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description://接收方
*/
public class TestReceive {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("老师上线。。。");
//1.创建套接字
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
//2.有一个空的数据包,打算用来接收 对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
//3.接收对方的数据包,放入我们的dp数据包中
ds.receive(dp);//接收完后dp里面就填充内容了
//4.取出数据
byte[] data = dp.getData();
String s=new String(data,0,dp.getLength());//dp.getLength()数组包中的有效长度
System.out.println("学生对我说:"+s);
//老师进行回复
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("老师:");
String str=sc.next();
//String str="同学,你也好";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
//封装数据,指定学生的IP和端口号
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 8888);
ds.send(dp2);
//5.关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
14.5.3 功能分解3:加入完整的异常处理方式
【发送方】
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description:发送方
*/
public class TestSend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("学生上线。。。");
//1.准备套接字
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
ds = new DatagramSocket(8888);
//2.准备数据包
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("学生:");
//String str="老师,你好";
String str=sc.next();
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
//数据包需要四个参数:1.发送数据转换为字节数组,2.字节数组的长度,3.封装接收方的IP,4.指定接收方的端口号
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999);
//发送
ds.send(dp);
//接收老师发送回来的信息
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
ds.receive(dp2);
byte[] data = dp2.getData();
String s=new String(data,0,dp2.getLength());//dp.getLength()数组包中的有效长度
System.out.println("老师对我说:"+s);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
}
【接收方】
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.SocketException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description://接收方
*/
public class TestReceive {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("老师上线。。。");
//1.创建套接字
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
//2.有一个空的数据包,打算用来接收 对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
//3.接收对方的数据包,放入我们的dp数据包中
ds.receive(dp);//接收完后dp里面就填充内容了
//4.取出数据
byte[] data = dp.getData();
String s=new String(data,0,dp.getLength());//dp.getLength()数组包中的有效长度
System.out.println("学生对我说:"+s);
//老师进行回复
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("老师:");
String str=sc.next();
//String str="同学,你也好";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
//封装数据,指定学生的IP和端口号
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 8888);
ds.send(dp2);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//5.关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
}
14.5.4 功能分解4:正常通信
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description:发送方
*/
public class TestSend {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("学生上线。。。");
//1.准备套接字
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
ds = new DatagramSocket(8888);
while (true){
//2.准备数据包
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("学生:");
//String str="老师,你好";
String str=sc.next();
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
//数据包需要四个参数:1.发送数据转换为字节数组,2.字节数组的长度,3.封装接收方的IP,4.指定接收方的端口号
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 9999);
//发送
ds.send(dp);
if(str.equals("byebye")){
System.out.println("学生下线");
break;
}
//接收老师发送回来的信息
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
ds.receive(dp2);
byte[] data = dp2.getData();
String s=new String(data,0,dp2.getLength());//dp.getLength()数组包中的有效长度
System.out.println("老师对我说:"+s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
}
【接收方】
package com.liweixiao.test04;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.SocketException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author:LiWeixiao
* @date:2023/2/20
* @description://接收方
*/
public class TestReceive {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("老师上线。。。");
//1.创建套接字
DatagramSocket ds = null;
try {
ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
while (true){
//2.有一个空的数据包,打算用来接收 对方传过来的数据包
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(b, b.length);
//3.接收对方的数据包,放入我们的dp数据包中
ds.receive(dp);//接收完后dp里面就填充内容了
//4.取出数据
byte[] data = dp.getData();
String s=new String(data,0,dp.getLength());//dp.getLength()数组包中的有效长度
System.out.println("学生对我说:"+s);
if(s.equals("byebye")){
System.out.println("学生已经下线,老师也下线");
break;
}
//老师进行回复
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("老师:");
String str=sc.next();
//String str="同学,你也好";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
//封装数据,指定学生的IP和端口号
DatagramPacket dp2 = new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, InetAddress.getByName("localhost"), 8888);
ds.send(dp2);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//5.关闭资源
ds.close();
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号