mybatis一级缓存与二级缓存的原理
实现原理
-
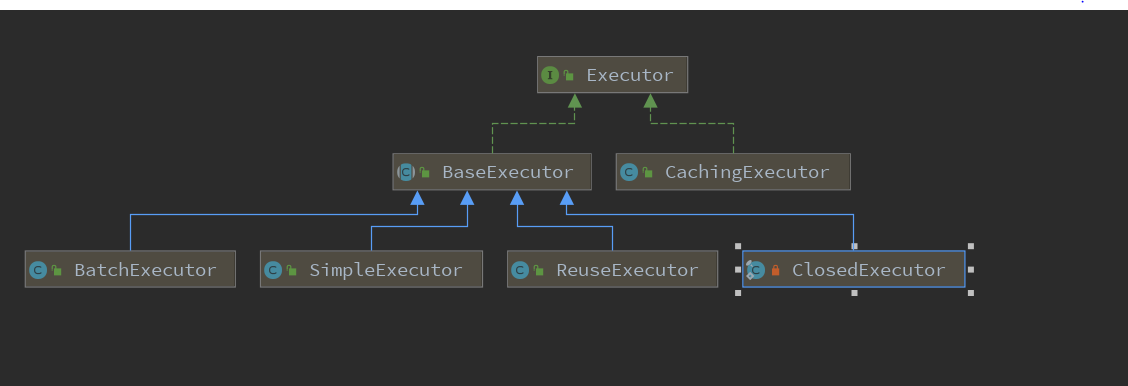
mybatis中的缓存是在mybatis框架中的Executor中来实现的,我们来看一下Executor的继承图
-
通过以上类图我们可以发现Executor接口下有两大实现类BaseExecutor与CachingExecutor
-
BaseExecutor(用来存储我们的一级缓存)
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; //会先去localCache中去查找我们的数据
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); //如不存在则会去数据库中查找
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
- CachingExecutor(是装饰器模式的实现,用来查询我们的二级缓存)
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache(); //在MappedStatement中去获取二级缓存的类型。
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key); //通过tcm来查询缓存,而tcm是CachingExecutor中的变量TransactionalCacheManager
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); //delegate为CachingExecutor中保存的BaseExecutor的引用,若二级缓存不存在回去调用BaseExecutor的方法。
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
- 当我们开启二级缓存后Mybatis会使用CachingExecutor去装饰我们的BaseExecutor,所以会先查询二级缓存后再去查询一级缓存。
Configuration中的newExecutor方法
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { //判断Executor的类型
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) { //如果二级缓存开启则使用CachingExecutor去装饰我们的executor;
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
一级缓存与二级缓存的作用范围
- 一级缓存(由于一级缓存是存在BaseExecutor中的,而Executor又作为创建SqlSession的参数,因此一级缓存具有和sqlsession一样的生命周期)
这是在SqlSessionFactory中调用openSession()中调用的方法
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); //新建一个Executor作为参数传给DefaultSqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
- 二级缓存(使用CachingExecutor来装饰)
//CachingExecutor中的query方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache(); //由此可见我们的二级缓存并不是储存在CachingExecutor中的,而是从MappedStatement中去获取。因此mybatis的二级缓存的生命周期为mapper级别的
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E> query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}


