Introduction to RPC 简单实现 part 1
文档来自这里,这文章的年龄都快和我一样了
看到了就顺手写点感悟
前置概念IDL,RPC
IDL
IDL是interface definition language的缩写,即接口定义语言,描述了接口是如何定义的。写一个IDL
就像是在写一个C的头文件,里面附带了点额外的关键字和结构。
IDL是一种属性编程语言,因此它可以比C更详细地描述参数、函数和接口。
RPC
RPC Remote Procedure Call 远程过程调用,请看这里
是用于创建分布式应用的强大科技,RPC的框架管理着大部分关于网络协议和网络通信的细节,这使得使用rpc框架的人
只需要去关注应用接口的细节而不需要去关注网络通信。
通过 RPC,客户端可以连接到在另一个平台上运行的服务器。
例如:理论上,服务器可以为Linux编写,客户端可以为Win32编写。现实情况要复杂一些。
独立应用程序
首先写一个简单的helloworld,后续我们会将其迁移到rpc框架之中
Hello Lonely World
// File Standalone.cpp
#include <iostream>
// Future server function.
//未来的服务器函数
void Output(const char* szOutput)
{
std::cout << szOutput << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
// Future client call.
//未来的客户端调用
Output("Hello Lonely World!");
}
简单的程序简单的输出
IDL文件
现在,写一个简单的IDL文件,来定义我们helloworld的接口
Hello IDL world
// File Example1.idl
[
// A unique identifier that distinguishes this
// interface from other interfaces.
// 独特的标识符来区分接口
uuid(00000001-EAF3-4A7A-A0F2-BCE4C30DA77E),
// This is version 1.0 of this interface.
version(1.0),
// This interface will use an implicit binding
// handle named hExample1Binding.
// 该接口将使用名为 hExample1Binding 的隐式绑定句柄。
implicit_handle(handle_t hExample1Binding)
]
interface Example1 // The interface is named Example1
//接口名为Example1
{
// A function that takes a zero-terminated string.
// 一个接受以0为结束的字符串的函数
void Output(
[in, string] const char* szOutput);
}
这里就是IDL使用的属性编程,上面的示例定义了一个具有通用唯一标识符(uuid)和版本(version)的接口,名为Example1。
接口Example1定义了一个函数Output,该函数接受一个名为 szOutput 的 const char* 参数作为以零结尾字符串的输入 (in)。
这里的隐式绑定接口后面再讨论,
下一步
为了能够在我们的程序中使用idl,我们要通过一个名为midl.exe的编译器运行它,它将产生一个客户端的代理和服务端的存根(翻译的依托)
代理和存根稍后将使用您最喜欢的编译器(在我的例子中为 cl.exe)进行编译。
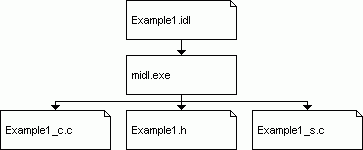
这里做一下补充
midl是如何生成的,首先去原页面下载他的src文件,然后进入目录下的Example1去编译,具体的编译过程如下:
- 打开 Developer Command Prompt for Visual Studio:
在开始菜单中找到 "Visual Studio 20XX"(其中 XX 是你安装的 Visual Studio 版本号),然后找到 "Developer Command Prompt for VS20XX"(或相似的命名)。
这个命令提示符窗口已经配置好了用于 Visual Studio 的环境变量和工具。
导航到包含 MIDL 文件的目录:
-
使用 cd 命令切换到包含你的 MIDL 文件的目录。
-
运行 MIDL 编译器:
midl Example1.idl
然后就会生成这些东西:

How May I Serve You?
现在要在我们的程序中使用生成的文件
hello server world server端程序
// File Example1Server.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Example1.h"
// Server function.
void Output(const char* szOutput)
{
std::cout << szOutput << std::endl;
}
// Naive security callback.
RPC_STATUS CALLBACK SecurityCallback(RPC_IF_HANDLE /*hInterface*/, void* /*pBindingHandle*/)
{
return RPC_S_OK; // Always allow anyone.
}
int main()
{
RPC_STATUS status;
// Uses the protocol combined with the endpoint for receiving
// remote procedure calls.
status = RpcServerUseProtseqEp(
reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>("ncacn_ip_tcp"), // Use TCP/IP protocol.
RPC_C_PROTSEQ_MAX_REQS_DEFAULT, // Backlog queue length for TCP/IP.
reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>("4747"), // TCP/IP port to use.
NULL); // No security.
if (status)
exit(status);
// Registers the Example1 interface.
status = RpcServerRegisterIf2(
Example1_v1_0_s_ifspec, // Interface to register.
NULL, // Use the MIDL generated entry-point vector.
NULL, // Use the MIDL generated entry-point vector.
RPC_IF_ALLOW_CALLBACKS_WITH_NO_AUTH, // Forces use of security callback.
RPC_C_LISTEN_MAX_CALLS_DEFAULT, // Use default number of concurrent calls.
(unsigned)-1, // Infinite max size of incoming data blocks.
SecurityCallback); // Naive security callback.
if (status)
exit(status);
// Start to listen for remote procedure
// calls for all registered interfaces.
// This call will not return until
// RpcMgmtStopServerListening is called.
status = RpcServerListen(
1, // Recommended minimum number of threads.
RPC_C_LISTEN_MAX_CALLS_DEFAULT, // Recommended maximum number of threads.
FALSE); // Start listening now.
if (status)
exit(status);
}
// Memory allocation function for RPC.
// The runtime uses these two functions for allocating/deallocating
// enough memory to pass the string to the server.
void* __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t size)
{
return malloc(size);
}
// Memory deallocation function for RPC.
void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void* p)
{
free(p);
}
client程序
// File Example1Client.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Example1.h"
int main()
{
RPC_STATUS status;
unsigned char* szStringBinding = NULL;
// Creates a string binding handle.
// This function is nothing more than a printf.
// Connection is not done here.
status = RpcStringBindingCompose(
NULL, // UUID to bind to.
reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>("ncacn_ip_tcp"),// Use TCP/IP protocol.
reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>("localhost"), // TCP/IP network address to use.
reinterpret_cast<unsigned char*>("4747"), // TCP/IP port to use.
NULL, // Protocol dependent network options to use.
&szStringBinding); // String binding output.
if (status)
exit(status);
// Validates the format of the string binding handle and converts
// it to a binding handle.
// Connection is not done here either.
status = RpcBindingFromStringBinding(
szStringBinding, // The string binding to validate.
&hExample1Binding); // Put the result in the implicit binding
// handle defined in the IDL file.
if (status)
exit(status);
RpcTryExcept
{
// Calls the RPC function. The hExample1Binding binding handle
// is used implicitly.
// Connection is done here.
Output("Hello RPC World!");
}
RpcExcept(1)
{
std::cerr << "Runtime reported exception " << RpcExceptionCode()
<< std::endl;
}
RpcEndExcept
// Free the memory allocated by a string.
status = RpcStringFree(
&szStringBinding); // String to be freed.
if (status)
exit(status);
// Releases binding handle resources and disconnects from the server.
status = RpcBindingFree(
&hExample1Binding); // Frees the implicit binding handle defined in the IDL file.
if (status)
exit(status);
}
// Memory allocation function for RPC.
// The runtime uses these two functions for allocating/deallocating
// enough memory to pass the string to the server.
void* __RPC_USER midl_user_allocate(size_t size)
{
return malloc(size);
}
// Memory deallocation function for RPC.
void __RPC_USER midl_user_free(void* p)
{
free(p);
}
服务器端有一些注册接口的函数
客户端有一些连接服务的函数,其他的都是相同的
把这些东西扔到一起
现在要进行程序的链接了
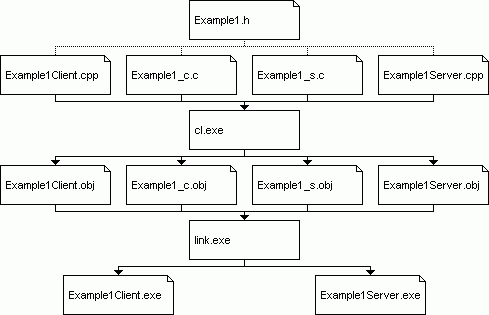
简要的说一下步骤:
- 打开 Developer Command Prompt for Visual Studio:
在开始菜单中找到 "Visual Studio 20XX"(其中 XX 是你安装的 Visual Studio 版本号),然后找到 "Developer Command Prompt for VS20XX"(或类似的命名)。
这个命令提示符窗口已经配置好了用于 Visual Studio 的环境变量和工具。
2. 导航到包含目标文件的目录:
使用 cd 命令切换到包含你的目标文件的目录。
3. 运行 cl.exe 连接目标文件:
使用 cl.exe 连接目标文件并生成可执行文件。以下是一个示例命令:
cl /c YourSourceFile.cpp
link也差不多
link Example1Client.obj Example1_c.obj /OUT:Example1Client.exe Rpcrt4.lib
link Example1Server.obj Example1_s.obj /OUT:Example1Server.exe Rpcrt4.lib
附录以下机翻
本节介绍一些在编写 RPC 应用程序时有用的技术。
调试和RPC
如果您在调试时遇到麻烦,并且问题似乎出在 MIDL 生成的文件中,那么真正的问题很可能出在客户端或服务器中。我有时会遇到指针问题,但在后续文章中,我将更彻底地描述这些事情。
隐式和显式句柄
使用 RPC 时,绑定句柄可以是隐式的(如本文的示例)或显式的。我总是使用显式句柄,因为有时会连接到多个服务器,而这不适用于隐式句柄。要使用显式句柄,您必须更改 IDL 文件、服务器和客户端:
// File Example1Explicit.idl
[
// A unique identifier that distinguishes this
// interface from other interfaces.
uuid(00000002-EAF3-4A7A-A0F2-BCE4C30DA77E),
// This is version 1.0 of this interface.
version(1.0),
// This interface will use explicit binding handle.
explicit_handle
]
interface Example1Explicit // The interface is named Example1Explicit
{
// A function that takes a binding handle and a zero-terminated string.
void Output(
[in] handle_t hBinding,
[in, string] const char* szOutput);
}
// File Example1ExplicitServer.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Example1Explicit.h"
// Server function.
void Output(handle_t hBinding, const char* szOutput)
{
std::cout << szOutput << std::endl;
}
// main - same as before.
// File Example1ExplicitClient.cpp
#include "Example1Explicit.h"
int main()
{
// Call to RpcStringBindingCompose - same as before.
handle_t hExample1ExplicitBinding = NULL;
// Validates the format of the string binding handle and converts
// it to a binding handle.
// Connection is not done here either.
status = RpcBindingFromStringBinding(
szStringBinding, // The string binding to validate.
&hExample1ExplicitBinding); // Put the result in the explicit binding handle.
if (status)
exit(status);
RpcTryExcept
{
// Calls the RPC function. The hExample1ExplicitBinding binding handle
// is used explicitly.
// Connection is done here.
Output(hExample1ExplicitBinding, "Hello RPC World!");
}
RpcExcept(1)
{
std::cerr << "Runtime reported exception " << RpcExceptionCode()
<< std::endl;
}
RpcEndExcept
// Call to RpcStringFree - same as before.
// Releases binding handle resources and disconnects from the server.
status = RpcBindingFree(
&hExample1ExplicitBinding); // Frees the binding handle.
if (status)
exit(status);
}
还有一个叫 的东西auto_handle,但我从来没有用过。它以某种方式关心自动连接到服务器。
应用程序配置文件 (ACF)
在这个例子中,我直接在IDL文件中使用了implicit_handleand explicit_handle,但那是一个微软的扩展。人们通常需要使用包含这些的单独的应用程序配置文件。zip 文件中的示例代码确实使用了单独的 ACF 文件,但我觉得在文章中编写它只会让您更加困惑。
不要摆弄生成的文件
您不应该摆弄生成的文件来编译它们,它们(应该)是正确的。如果您认为midl.exe的开关不正确,请检查它们。另一方面,编译它们时,您可能会收到很多警告,但是当将警告级别降低到 2 时,它们就会保持沉默。
关闭服务器
示例服务器将一直运行,直到通过某种方式关闭它为止。这不是最好的方法,另一种更好的方法是调用该RpcMgmtStopServerListening函数。但你会怎么称呼它呢?您可以在接口中添加另一个Shutdown将调用的函数(可能名为?),RpcMgmtStopServerListening或者您可以在调用之前在服务器中创建另一个线程,该线程将在一分钟左右后RpcServerListen调用。RpcMgmtStopServerListening在另一篇文章中对此进行了更多介绍。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY