Note - Ruby
Based on RubyMonk。
因为神秘原因网站挂掉了,所以弄一下,顺便捡起已经生锈的 Ruby。
推荐的在线编译器:Link。
闲话:这样的话肯定 interaction 会少,可以多手动运行一下代码。以及有些代码可能会调整,但语法内容是一样的。以及本来想用英语写的,因为 Ruby 真的很 English,算了还是用中文吧。
Introduction To Ruby Objects
Introduction to Objects
Ruby 的特性,(几乎)万物皆对象。self 即 main,是对象。
1.next 为 2,也是个对象。
More Objects and Methods
在面向对象编程中,method 方法是对象的一部分。方法允许对象执行一个动作。
1.methods 就是 1 的所有方法,即可以执行的动作。
但是方法也是对象(?),所以 1.methods.methods 就是 1 的所有方法的方法。注意到里面有 sort。意味着我们可以对其排序:1.methods.sort。
更多例子:
['rock', 'paper', 'scissors'].index('paper') 查找 'paper' 在列表中的下标,从 \(0\) 开始。
2.between?(1, 3) 检查 2 是否在 1 和 3 的中间。
Syntactic Sugar for Special Methods
猜猜 \(1 + 2\) 怎么写?1.+(2)。显然太反人类了,所以有语法糖。Ruby 在其语法规则中对常用运算符做了例外处理,因此不必使用句点在对象上调用它们,直接写 1 + 2 即可。
Introduction to Strings
Introduction to Strings
类似于 Python,单双引号都可以,基本等价。
字符串长度类似 C++,s.length 就是 s 字符串的长度。
String Basics
字符串插值,用于字符串格式化输出,即 #{string_name}。
name = "liuzimingc"
puts "My name is #{name}."
输出 My name is liuzimingc. 。
单双引号的一个小区别,"\n" 是换行,'\n' 是普通的 \n 字符串。
一些方法:
a.include?(b)检查 a 中是否包含 b。a.start_with?(b)检查 a 是否以 b 。a.end_with?(b)检查 a 是否以 b 结尾。a.index(b)得到 a 中 b 的最早出现位置。不存在则为空。a.upcase得到 a 全转大写的结果。a.swapcase得到 a 大小写互换的结果。
Advanced String Operations
a.split(b)把 a 按 b 分隔开。a + b&a.concat(b)a 连接 b,生成了新的字符串,效率较低。a << ba 连接 b,直接把 b 加在了 a 之后。a.sub(b, c)把 a 中的第一个 b 换成 c。a.sub(regex, b)功能同上,匹配换成了正则表达式。a.gsub(b, c)把 a 中的所有 b 换成 c(global)。a.match(regex)查找 a 中第一个符合 regex 的字符串。a.match(regex, pos)查找 a 中从第 \(pos\) 位开始第一个符合 regex 的字符串。
Conditions and Loops: Control Structures in Ruby
Boolean Expressions in Ruby
== > < >= <= || && !
就讲了这个。和 C++ 一样。
The if..else construct
if-else 语句。
if (conditional-expression)
# code if condition is true
else
# code if condition is false
end
if-elsif-else 语句。
if (condition-expression1)
# code if above condition is true
elsif (condition-expression2)
# code if above condition is true
elsif (condition-expression3)
# code if above condition is true
...
else
# code if all the conditions are false
end
Exercise.
给出一个人的 BMI。根据
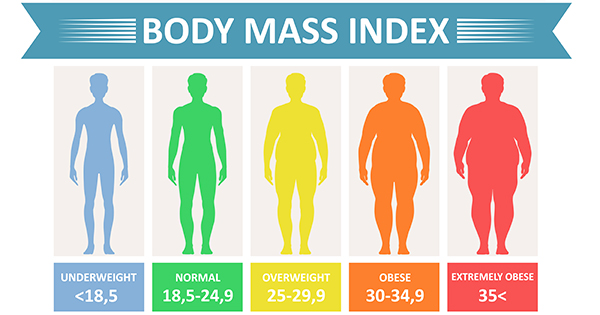
计算输出结果。
Solution.
按上述格式来就行。
BMI = 114514 if BMI < 18.5 puts "underweight" elsif BMI < 25 puts "normal" elsif BMI < 30 puts "overweight" elsif BMI < 35 puts "obese" else puts "extremely obese" end # 这个图取等有点迷,大概这样就行
以及 unless x 就是 if !x。除了 false 和 nil 以外的对象都是 true。
if 0
puts "Hey, 0 is considered to be a truth in Ruby"
end
Loops in Ruby
无限循环(C++ 中的 while (true)):
loop do
# do something
end
执行 \(n\) 次:
n.times do
# do something
end
从 \(1\) 加到 \(100\) 的两种写法:
i = 1
sum = 0
loop do
sum += i
i += 1
if i > 100
break # 注意 break
end
end
puts sum
i = 1
sum = 0
100.times do
sum += i
i += 1
end
puts sum
Conditions and Loops: Control Structures in Ruby
Introduction to Arrays
创建空数组:[] 或 Array.new。
创建数组:直接写 [A, B, ..., Z]。如 [1, 3.14, "interesting"]。
按下标访问,如果是非负数就是正序,从 \(0\) 开始;负数则是倒序,从 \(-1\) 开始。下面两个输出一样:
puts [1, 2, 3, 4, 5][-1]
puts [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].last
添加元素:用 << 或者 push。观察输出:
list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
list << 6
puts list
list.push(7)
puts list
Basic Array Operations
用 map 或者 collect 改变数组的值。如:
puts [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].map { |i| i + 1 }
输出是:
2
3
4
5
6
用 select 选出满足条件的元素。
puts [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].select { |number| number % 2 == 0 } # the output is obvious
用 delete 删除元素。如 [1, 2, 3].delete(3) 就是删除 \(3\) 这个元素。
用 delete_if 删除满足条件的元素。下面的代码和上面的输出一样:
puts [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].delete_if { |number| number % 2 == 1 } # the output is the same
Iteration
存在 for 循环,但是很少用。
array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
for i in array
puts i
end
更常见的是 each 循环,Array#each 方法接受一个块,数组的每个元素依次传递到该块。
array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
array.each do |i|
puts i
end
Exercise.
把数组里的偶数变成其两倍放到另一个数组中。
Solution.
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] b = [] a.each do |i| if i % 2 == 0 b << i * 2 end end puts b
Hashes in Ruby
Introduction to Ruby Hashes
用 {} 创建哈希表,形如:
student_ages = {
"kami" => 10,
"ZuoLe" => 12,
"Bob" => 14
}
用 [] 访问或者修改,和 C++ map 一样。
student_ages = {
"kami" => 10,
"ZuoLe" => 12,
"Bob" => 14
}
student_ages["Bob"] = -1 # has dropped out,显然你也可以 student_ages.delete("Bob")
student_ages["liuzimingc"] = 14 # a new student
Hashes, in and out.
一样可以使用 each 遍历哈希表。但是块里面要传两个值,key 和 value。
restaurant_menu = { "Ramen" => 3, "Dal Makhani" => 4, "Coffee" => 2 }
restaurant_menu.each do | item, price |
puts "#{item}: $#{price}"
end
单独拿出 keys & values 也很简单。
restaurant_menu = { "Ramen" => 3, "Dal Makhani" => 4, "Coffee" => 2 }
puts restaurant_menu.keys
puts restaurant_menu.values # obvious
Posted by liuzimingc


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号