二十、网络ifconfig 、ip 、netstat、ss之二
ip 网络层协议
ip地址 点分十进制分为4段,范围 0-255
ip分类
A 占据1段,最左侧一段第一位固定为0
0 000 0000 - 0 111 1111
0 - 127:其中0为网络,127 本地主机内部通信。
网络数: 2^7-2=126个
每个网络中的主机数: 2^24-2=16777216 (1677736)
默认子网掩码: 255.0.0.0
私网地址: 10.0.0.0/8 (8:网络段全为1,有8位)
B 占据2段,最左侧一段第一位固定为10
10 00 0000 - 10 11 1111
128 - 191
网络数:2^(6+8)=2^14=16384个
每个网络中的主机数: 2^16-2=65534
默认子网掩码:255.255.0.0
私网地址: 172.16.0.0/16 - 172.31.0.0/16 (网络变化位第2位)
C 占据3段,最左侧一段第一位固定为110
110 0 0000 - 110 1 1111
192 - 223
网络数:2^(5+8+8)=2^21=2097152个
每个网络中的主机数: 2^8-2=62
默认子网掩码:255.255.255.0
私网地址: 192.168.0.0/24 - 192.168.255.0/24 (网络变化位第3位)
D 占据4段,最左侧一段第一位固定为1110 (做组播)
1110 0000 - 1110 1111
224 - 239
网络数:2^(4+8+8+8)=2^28=268435456个
E类 240 - 255
子网掩码:计算ip地址所在的网络
网络相同,本地通信
网络不同,跨网络通信借助路由器(网络层、数据链路层、物理层)
IP地址与子网掩码 与运算,1和任何数运算都得任何数,0和任何数运算都得0;
例如:IP:145.239.123.0 MASK 224.239.234.123 网络?
IP地址的二进制 1001 0001 . 1110 1111 . 0111 1011 . 0000 0000
MASK的二进制 1110 0000 . 1110 1111 . 1110 1010 . 0111 1011
网络的二进制 1000 0000 . 1110 1111 . 0110 1010 . 0000 0000
网络地址: 128.239.106.0
路由配置:在未梢网络中,路由器一般指的是默认网关
主机路由: 目标是主机
网络路由: 目标是网络
默认网关:目标无论为主机或是网络
路由选择:选择匹配精度越高,匹配结果越少
主机路由 > 网络路由 > 默认网关
0.0.0.0
网关: 到达本地的路由信息
目标: 到达任意网络或主机的路由信息
网络接口命名
centos6 根据MAC,eth[0,1,2,...] 在重启后可能会改变
centos7 根据插口/根据PCI-E总线的槽 ,重启后不变
网络属性配置: 让CentOS主机能够接入至网络中
1、配置IP
2、配置路由ROUTE
3、配置DNS服务
主DNS服务器
次DNS服务器
第三DNS服务器
配置方式
静态指定:
1、命令行配置: 配置在内核中的内存地址中,下次重启失效
1)ifcfg家族:ifconfig ,route , netstat
ip家族 : object{link,addr ,route } ,ss ,tc
2)cnetos7 : nmcli , nmtui
2、编辑配置文件配置: 永久有效
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-NAME
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-NAME
3、图形接口配置
system-config-network-tui(setup)
nmtui
动态分配: DHCP
命令行配置
ifcfg家族:ifconfig,route,netstat
ip家族:ip,ss
特点
1、netstat和ss使用基本相似
1)ss响应比netstat快
2)ss选项 -m,memory。 -o 。 state TCP-STATE [EXPRESSION]
2、ip和ifcfg家族,实现的功能查看IP,设置IP,查看ROUTE,设定ROUTE.基本相似。
1)ip比ifcfg多出就像 yum 比rpm命令多出:查看时支持Glob通配字符的使用,
ip支持过滤功能 scope SCOPE_NA, label LABEL , dev NAME , to PREFIX ,primary or secondary
3、ip命令不修改网卡地址,ifconfig修改网卡地址。ip命令给网卡添加辅助地址,可有别名
二、命令行配置
2.1、ifcfg家庭:ifconfig,route,netstat
ifconfig命令
网络属性显示和配置
ifconfig [options...] [interface] [up|down]
-a 显示所有接口
[-]promise 启用混杂模式
metric N 到达目标的开销值
ifconfig interface address [up|down]
address: ip/mask 或 ip netmask MASK
例如 1.1.1.1/8或1.1.1.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
# ifconfig IFACE address
# ifconfig IFACE address up | down
route命令
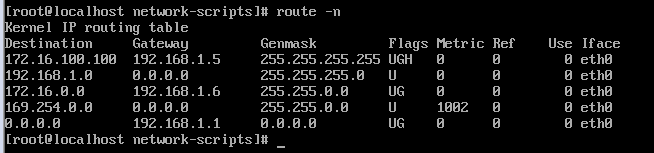
route -n 显示内核中的路由表
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface Destination 到达的目标:主机、网络、默认,最终到达主机 Gateway 网关 Genmask 目标的掩码 Flags 标识位 Metric 开销,到达目标的开销 Iface 报文离开本主机经过的网卡
route add|del [-host|-net ] address gw GW dev interface
添加:route add [-host|-net] address [gw GW] [[dev] interface]
添加主机路由:
route add -host ip/32 gw GW dev interface
route add -host ip netmask MASK gw GW dev interface
添加网络路由:
route add -net ip/mask gw GW dev interface
route add -net ip netmask MASK gw GW dev interface
删除: route del -host|-net address
删除主机路由
route del -host address
删除网络路由
route del -net address
默认路由: -net 0.0.0.0 mask 0.0.0.0
route add|del default gw GW dev IFACE
dig命令
dig -t A FQDN
dig -x IP
host命令
host -t A FQDN
host -t PTR IP
netstat命令
1、network connection:
netstat OPTIONS
-t tcp连接 -u udp连接 -w raw裸套接字 -n numeric不反解IP -a all所有t,u,.. -l listen监听,等待别人访问 -p program和Pid -e user和inode
2、routing tables:
netstat OPTIONS
-r 显示内核中的路由表
-n numeric
3、interface statistics
netstat OPTIONS
-i 显示所有接口
-I<dev> 显示指定接口
1、查看IP: ifconfig interface
1)查看激活 [root@localhost ~]# ifconfig eth0 lo 2)查看所有 [root@localhost ~]# ifconfig -a eth0 lo 3)查看指定 [root@localhost ~]# ifconfig lo lo
2、配置IP: ifconfig interface { ip/mask | ip netmask MASK }
3、查看路由: route -n
4、配置路由: route add -host | -net { ip/mask | ip netmask MASK} gw GW dev interface
6、配置DNS: /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver DNS_SERVER_IP1
nameserver DNS_SERVER_IP2
nameserver DNS_SERVER_IP3
测试DNS服务器
正解: FQDN -->IP
dig -t A FQDN
host -t A FQDN
反解: IP --> FQDN
dig -x IP
host -t PTR IP
7、网络状态查看: netstat option , options: -t tcp,-u udp,-r raw,-n numeric,-a all,-l listen,-p program,-e extend,
裸套接字:不经过传输层,由应用层直接调用IP实现数据传输
numeric: netstat命令默认将Ip反解为字母,-n选项关闭此特性
extend: user,inode扩展信息
program:PID和名字
8、查看内核中的路由表: route -nr
9、查看接口数据: netstat -i查看所有接口数据 , netstat -I<dev>查看由dev指定接口的数据
三、ip家庭:ip,ss
3.1、显示ip命令由哪个程序包生成
1)、rpm -qf `which --skip-alias ip`
2)、rpm -q --whatprovides /sbin/ip
3)、yum whatprovides /sbin/ip
4)、dnf whatprovides /sbin/ip
3.2、显示程序包生成的内容:rpm -ql iproute
3.3、命令行
获取命令帮助:
ip [ OPTIONS ] OBJECT { COMMAND | help }
语法格式: ip OBJECT
OBJECT := { link | addr | route }
3.3.1、ip link SUB_CMD 管理网络设备(二层)
a)
SUB_CMD: = { set | show }
set ,设备启动或禁止
show , 显示设备的属性
获取帮助: ip link help
b)、ip link show [ dev IFACE | up ]
显示所有接口: ip link show
显示指定接口: ip link show [ dev IFACE(接口) ]
显示处于激活状态的接口: ip link show [ up ]
接口属性状态介绍:
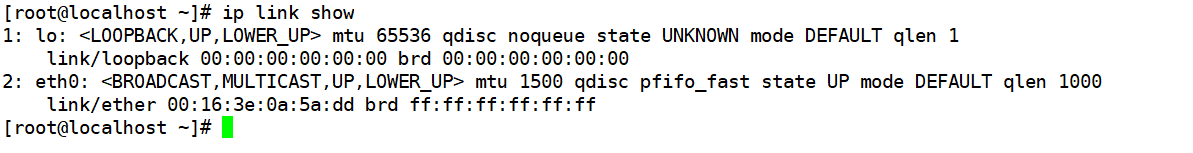
1)网卡名: eth0 2)设备支持的功能: <BROADCAST(广播), MULTICAST(组播或多播), UP(当前网卡的状态), LOWER_UP> 3) 设备的特性: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UNKNOWN qlen 1000 4) 设备的地址: link/ether 00:0c:29:cf:cd:ae brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff mtu 1500: 以太网的MTU值最大为1500字节 (最大协议传输单元) qdisc pfifo_fast :流控算法或实现的机制 state UNKNOWN 网卡当前的状态 qlen 1000 传输队列长度 link/ether 00:0c:29:cf:cd:ae 当前网卡的MAC地址 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff 当前网卡的广播地址
c ) 、ip link set dev IFACE [ up | down ]
IFACE 网卡接口名
激活接口: ip link set dev IFACE up
关闭接口: ip link set dev IFACE down
使用ip link 管理设备示例
1、显示所有接口
2、显示指定设备
3、显示启用的设备
4、禁用某个设备
5、激活某个设备
3.3.2、ip addr SUB_CMD 管理接口地址
a)、SUB_CMD:
add | del 添加或删除地址
show | flush 显示或删除地址,支持显示的过滤功能
获取帮助: ip addr help
ip addr (add | del ) address dev IFACE [ broadcast ADDRESS ] [ label LABEL ] [ scope {*global*|site|link|host} ]
默认在网卡在添加多个地址,并非修改网卡地址
broadcast ADDRESS 添加地址时设定广播地址
label LABEL 添加地址,给出别名
scope SCOPE 设定作用域级别
address: ip/mask
ip addr (show|flush) [ dev IFACE ] [ scope {global|site|link|host} ] [ to PREFIX ] [ label PATTERN ] [ primary | secondary ] 显示、查询 或清空
global 默认(全局可用)。
link 只响应ping此接口的主机(相当于绑定在该地址接口上) 。
host 只响应当前主机Ping对此接口(只在本机内部可用)。
ip addr 管理接口地址使用示例
1、设定接口辅助地址
2、以别名添加接口辅助地址
3、以级别添加接口辅助地址
4、显示接口的地址
5、显示别名的地址
6、显示前缀的地址
7、显示主地址
8、清空设备的地址
9、清空别名的地址
10、清空主地址
11、清空所有从地址
12、清空前缀地址
3.3.3、ip route SUB_CMD 管理路由
SUB_CMD:
add | del 添加或删除地址
show | flush 显示或删除地址,支持显示的过滤功能
添加路由: ip route add TARGET via GW dev IFACE [ src ADDRESS ]
TARGET:
主机路由: IP (不需要加mask)
网络路由:NETWORK/MASK
删除路由 :ip route del address
ip route show|flush [ dev NAME ] [ src PREFIX ] [ via PREFIX ] 显示、查询 或清空
使用示例
1、查看路由表
2、添加路由条目
3、删除路由条目
4、清空via
5、清空src
6、清空dev
四、ss命令--网络状态查看
用法基本同netstat(进程数几十个到100个不明显,但进程数多后却比netstat高效)
-t tcp查看tcp协议的连接 -u ucp -w raw裸套接字 -a all -l listen -n numeric 数字格式 -e extend,usr,inode -p pid/progranm, -m memory -o options 显示计时器信息
state TCP-STAT [EXPRESSION]
建立套接字有一组套接字,源ip和源端口,目标ip和目标端口
源端口: 源ip对应的端口
目标端口: 目标ip对应的端口
TCP-STATE
TCP FINITE STATE MACHINE (tcp有限状态机)
LISTEN SYC-SENT SYC-RECV ESTABLISHED :已建立的连接 FIN_WAIT_1 FIN_WAIT_2 CLOSED
使用示例
1、查看tcp状态的所有连接 :ss -tan
2、查看udp状态的所有连接 :ss -uan
3、查看tcp处于监听状态的连接 : ss -tnl
4、查看udp处于监听状态的连接 : ss -unl
5、查看tcp/udp处于监听状态的连接 : ss -tunl
6、查看tcp/udp扩展信息 : ss -tunle
7、查看每个程序的pid和程序名 :ss -tunlp
8、查看处于ESTABLISHED状态的连接
五、编辑配置文件配置网络属性
1)、/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-IFACE配置IP、MASK 、GW、DNS
2)、/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-IFACE配置route (默认是不存在的,需自己创建)
3)、配置DNS服务器
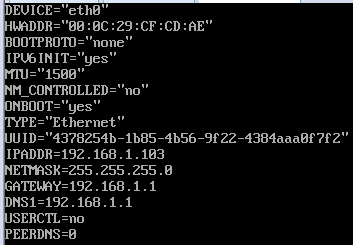
5.1、配置文件内容/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-IFACE (重点)
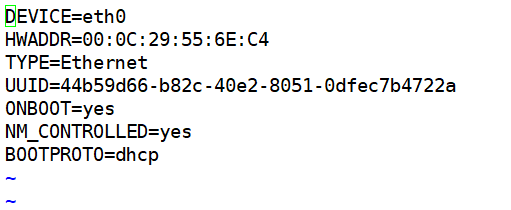
DEVICE: 此配置文件应用到的设备,此名称应该和IFACE保持一致 HWADDR: 此配置文件应用到的网络设备的MAC地址 BOOTPROTO: 激活此设备时使用的地址配置协议,启动此设备命令的协议(static|none|dhcp|bootp) NM_CONTROLLED :NM NetworkManager的简写,此网卡是否接受NM控制---取代network脚本控制网络服务,不建议CentOS6使用NM ONBOOT :系统引导时,是否激活此设备 TYPE : 接口类型,Enthernet,Bridge UUID : 设备的唯一标识
如果BOOTPROTO=static 需要配置以下内容
IPADDR 主地址
NETMASK 掩码
GATEWAY 默认网关
DNS1 DNS服务器 {优先级高于/etc/resolv.conf(因为直接配置在网络接口上),普通用户不能修改/etc/resolv.conf}
DNS2
DNS3
USERCTL :普通用户是否可控制
PEERDNS :如果BOOTPROTO的值为dhcp,是否允许dhcp服务器分配的DNS服务器指向信息直接覆盖resolv.conf
5.2、使用示例: 当前所在网络 192.168.1.1/24
1)、进入/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/目录,编辑ifcfg-eth0文件
2)、用:wq或ZZ退出编辑,重启网络,使之生效
3)、查看路由表
4)、查看DNS解析表 :cat /etc/resolv.conf
5.3、配置/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-IFACE
5.3.1、两种风格格式:(两种风格不能写在一起)
a)、address via GW
b)、每三行定义一条路由
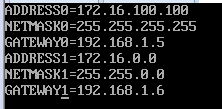
ADDRESS#= address (#代表0~n)
NETMASK#=mask
GATEWAY#=GW
5.3.2、风格一:
1)、进入/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/目录,编辑route-eth0文件
2)、重启网络服务
3)、查看路由表
1)、进入/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/目录,编辑route-eth0文件
2)、重启网络服务
3)、查看路由表
六、图形接口配置
1、进入图形界面 # system-config-network-tui (setup)
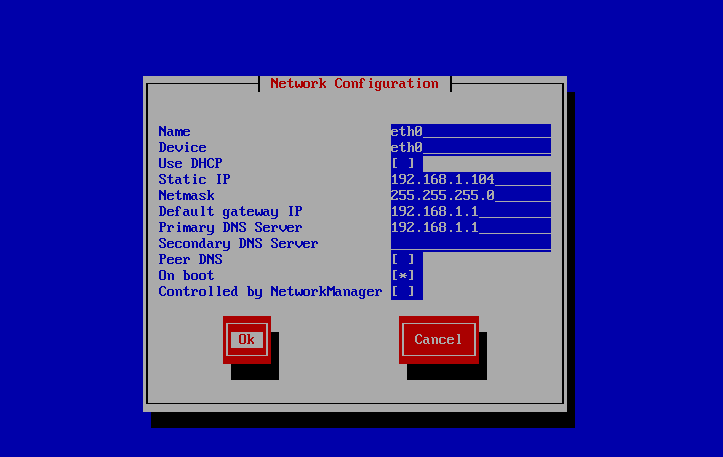
2、配置IP及路由信息
[ * ] 代表ture
NAME: 网卡名
DEVICE:设备名
Use DHCP: 是否使用DHCP, BOOTPROTO={dhcp|bootp|none|static}
Static IP:静态IP地址 , IPADDR
NETMASK: 掩码
DEFAULT GATEWAY IP: 默认网关, GATEWAY
primary dns server: 主DNS服务器 DNS1
secondary dns serve: 从DNS服务器 DNS2
在配置文件中支持配置3个DNS, DNS3
PEERDNS: BOOTPROTO为DHCP时是否将DHCP分配的DNS服务器及domain search覆盖至resolv.conf文件中
ONBOOT: 系统引导时,是否自动激活
CONTROL MANAGER: NM_CONTROLLED 是否由network manager脚本代为管理网络服务,centos6不建议使用
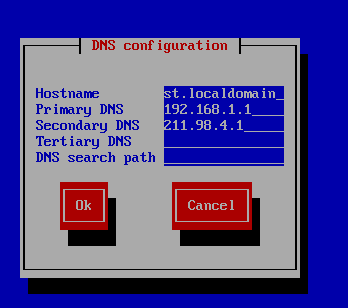
3、配置DNS
HOSTNAME:设定主机名,/etc/sysconfig/network文件中设定
Primary DNS:第一个DNS nameserver DNS_SERVER_IP1
Secondary DNS:第二个DNS nameserver DNS_SERVER_IP2
Tertiary DNS: DNS3
DNS searchpath:DNS搜索域。当只有域名时,自动补全
4、退出,重启服务
5、查看路由表
6、查看ip地址
补充
1、给网卡配置多个地址(ip命令默认给单个网卡配置多个附加的地址)
2、主机名配置
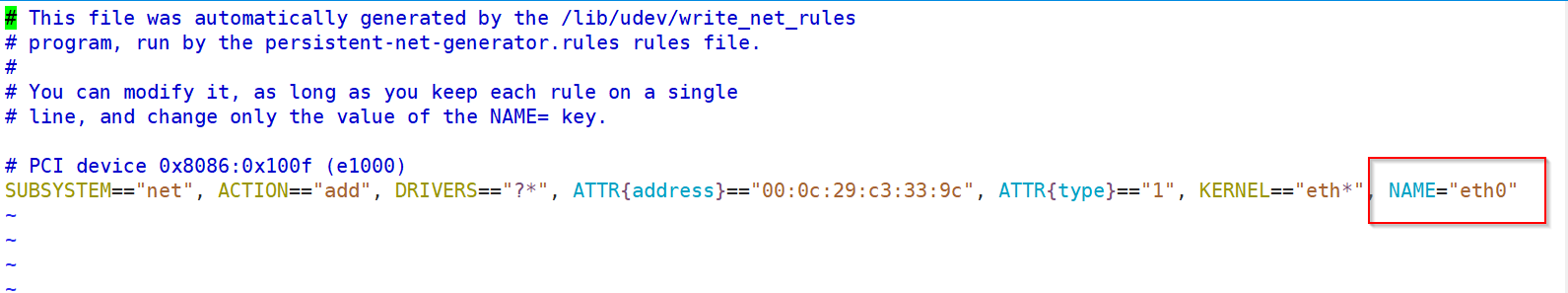
3、网络接口识别命名相关的配置文件
把eth0改为eth1(CentOS 6 )
3)卸掉网卡:modprobe -r e1000
4)再重新装载 :modprobe e1000
5)最后修改配置文件名字(对调文件名)





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号