IOC容器的创建
一、IOC容器创建方式
Ioc容器的创建时通过ApplicationContext接口的相关实现类进行的。
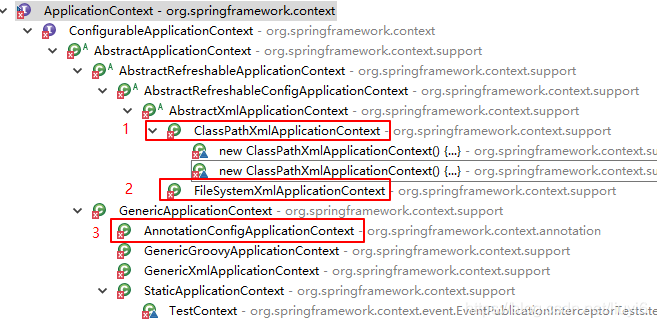
如上图所示:有三种创建IOC容器的方式。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从项目的根目录下加载配置文件
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从磁盘中的加载配置文件
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:当使用注解配置容器对象时使用此类进行注解读取,创建容器。
二、IOC容器创建入口
1、Java中IOC容器创建
Java中通过如下代码进行配置文件读取:
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xml路径");
创建ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象的过程中,调用refresh方法完成容器的创建与初始化。
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
//容器的创建与初始化
refresh();
}
}
2、Web中IOC容器创建
web项目中,Spring启动是在web.xml配置监听器,如下所示:
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
ContextLoaderListener类实现了Tomcat容器的ServletContextListener接口,与其他Servlet监听一样,重写了两个方法:contextInitialized()方法进行web容器初始化,contextDestroyed()方法进行容器销毁。
//初始化
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
//销毁
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
初始化的过程中调用ContextLoader中的initWebApplicationContext()方法,代码如下:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//判断ServletContext是否已经存在WebApplication,如果存在则抛出异常
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
//抛出异常...
}
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
if (this.context == null) {
//创建WebApplicationContext
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
//得到根上下文的父上下文,然后设置到根上下文,一般的web项目parent为空
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
//从web.xml加载参数,初始化根上下文WebApplicationContext,创建bean工厂和bean对象
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" +WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]");
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
//异常处理...
}
这个方法中ServletContext是由web容器监听器(ContextLoaderListener)提供。首先判断servlectContext中是否已经存在根上下文,如果存在,则抛出异常;否则通过createWebApplicationContext方法创建新的根上下文。然后通过loadParentContext()方法为其设置父上下文。再通过configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext为根上下文构建bean工厂和bean对象。最后把上下文存入servletContext,并且存入currentContextPerThread。至此初始化过程完毕,接下来可以获取WebApplicationContext,进而用getBean("bean name")得到bean。
2.1、创建上下文
下面首先针对createWebApplicationContext进行分析,createWebApplicationContext方法用于创建跟上下文,其代码如下:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
//从web.xml配置的contextClass参数中获取上下文类名,如果contextClass为空,则使用默认的。
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
//根上下文必须是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext的子类,否则抛出异常
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
//根据类名创建类
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
determineContextClass方法用于返回根上下文的类名,代码如下:
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
//从web.xml获得参数contextClass,在一般的web项目中,此参数为null
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
//获得根上下文WebApplicationContext的默认实现类的类名,defaultStrategies是Properties类型,在CotnextLoader类开头static语句块中初始化
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
Properties类型的初始化静态代码块:
static {
try {
//获取当前包下面的ContextLoader.properties文件
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
2.2、初始化根上下文
初始化上下文的方法configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext代码如下:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
//设置应用程序上下文Id
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
//获取环境中配置的属性
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//容器的创建与初始化
wac.refresh();
}
综上,对Web中创建IOC容器的流程总结的序列图如下:
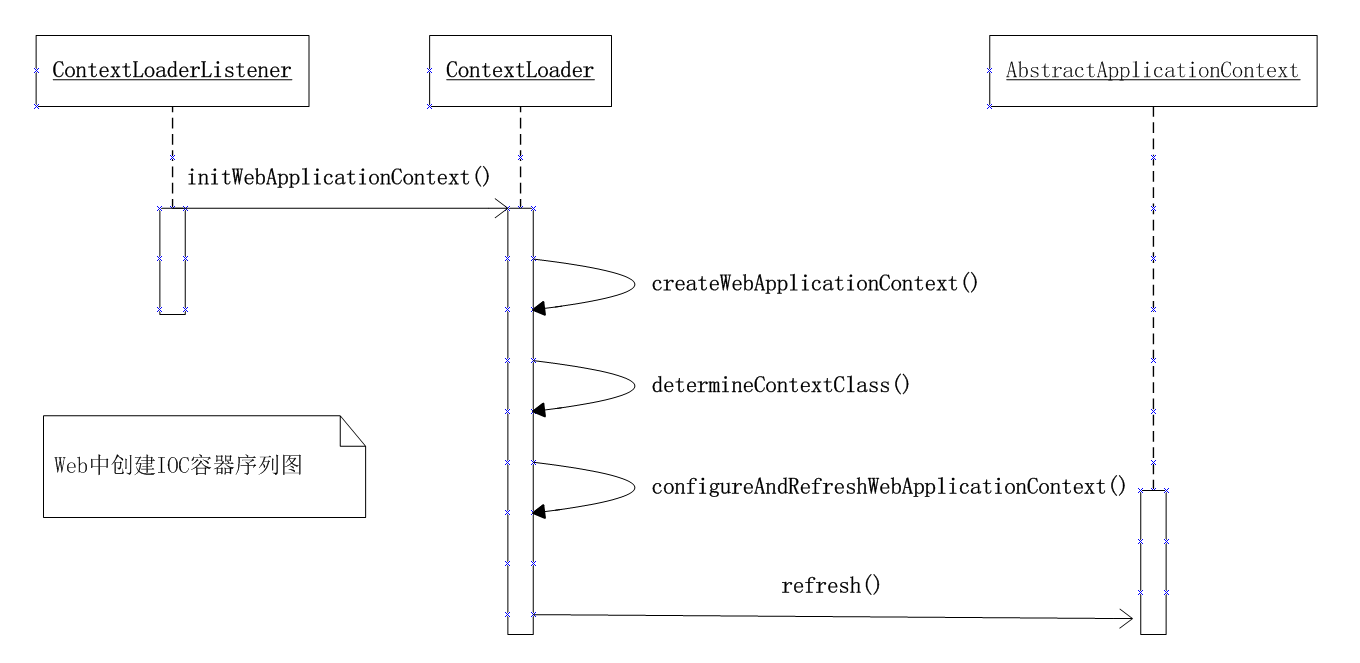
3、refresh方法
从上面的分析看到,无论是Java或Web,最后的容器创建于初始化都会进入refresh方法中,下面对refresh进行分析,refresh方法在AbstractApplicationContext类中实现,其代码如下:
// 完成IoC容器的创建及初始化工作
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor)
// 1: 刷新预处理
prepareRefresh();
// 2:
// a) 创建IoC容器(DefaultListableBeanFactory)
// b) 加载解析XML文件(最终存储到Document对象中)
// c) 读取Document对象,并完成BeanDefinition的加载和注册工作
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 3: 对IoC容器进行一些预处理(设置一些公共属性)
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 4:post-processing对BeanDefinition处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 5: 调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器对BeanDefinition处理
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 6: 注册BeanPostProcessor后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 7: 初始化一些消息源(比如处理国际化的i18n等消息源)
initMessageSource();
// 8: 初始化应用事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 9: 初始化一些特殊的bean
onRefresh();
// 10: 注册一些监听器
registerListeners();
// 11: 实例化剩余的单例bean(非懒加载方式)
// 1)、bean的实例化(创建)
// 2)、bean的属性填充
// 3)、bean的初始化(实现InitializingBean接口的类,在bean标签中的init-method属性)
// 注意事项:Bean的IoC、DI和AOP都是发生在此步骤
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// STEP 12: 完成刷新时,需要发布对应的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - "
+ "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
destroyBeans();
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
refresh方法是初始化Spring容器的核心代码,共分为12个步骤,具体功能如代码所示,将在后续文章中将对refresh中的步骤进行说明。



