1.javabean对象
@MyAnnotation(value="hi") public class Person extends Creature<String> implements Comparable<String>,MyInterface{ private String name; int age; public int id; public Person(){} @MyAnnotation(value="abc") private Person(String name){ this.name = name; } Person(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } @MyAnnotation private String show(String nation){ System.out.println("我的国籍是:" + nation); return nation; } public String display(String interests,int age) throws NullPointerException,ClassCastException{ return interests + age; } @Override public void info() { System.out.println("我是一个人"); } @Override public int compareTo(String o) { return 0; } private static void showDesc(){ System.out.println("我是一个可爱的人"); } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", id=" + id + '}'; } }
2.自定义注解
@Target({TYPE, FIELD, METHOD, PARAMETER, CONSTRUCTOR, LOCAL_VARIABLE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyAnnotation { String value() default "hello"; }
3.接口
public interface MyInterface { void info(); }
4.父类
public class Creature<T> implements Serializable { private char gender; public double weight; private void breath(){ System.out.println("生物呼吸"); } public void eat(){ System.out.println("生物吃东西"); } }
5.开始测试
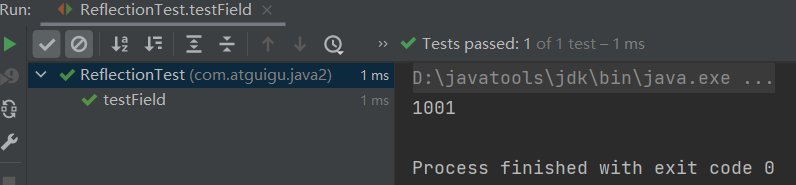
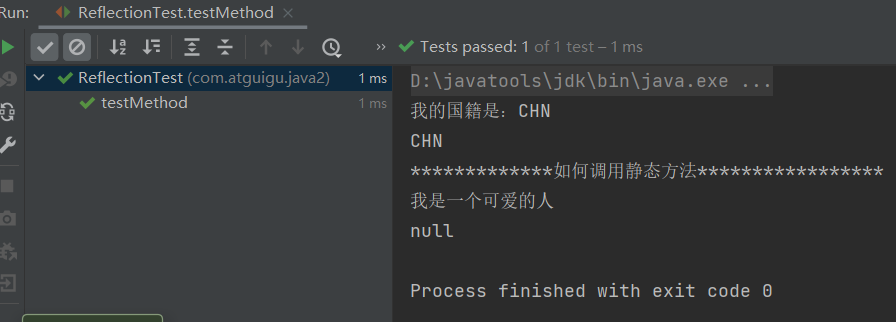
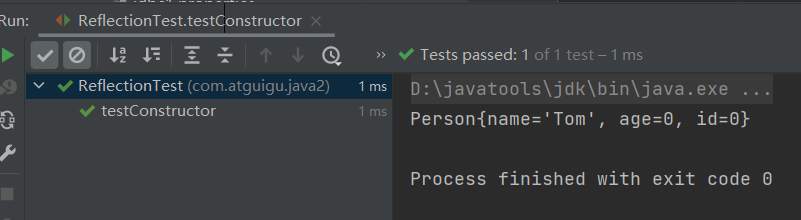
/** * 调用运行时类中指定的结构:属性、方法、构造器 * */ public class ReflectionTest { /* 不需要掌握 */ @Test public void testField() throws Exception { Class clazz = Person.class; //创建运行时类的对象 Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance(); //获取指定的属性:要求运行时类中属性声明为public //通常不采用此方法 Field id = clazz.getField("id"); /* 设置当前属性的值 set():参数1:指明设置哪个对象的属性 参数2:将此属性值设置为多少 */ id.set(p,1001); /* 获取当前属性的值 get():参数1:获取哪个对象的当前属性值 */ int pId = (int) id.get(p); System.out.println(pId); } /* 如何操作运行时类中的指定的属性 -- 需要掌握 */ @Test public void testField1() throws Exception { Class clazz = Person.class; //创建运行时类的对象 Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance(); //1. getDeclaredField(String fieldName):获取运行时类中指定变量名的属性 Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name"); //2.保证当前属性是可访问的 name.setAccessible(true); //3.获取、设置指定对象的此属性值 name.set(p,"Tom"); System.out.println(name.get(p)); } /* 如何操作运行时类中的指定的方法 -- 需要掌握 */ @Test public void testMethod() throws Exception { Class clazz = Person.class; //创建运行时类的对象 Person p = (Person) clazz.newInstance(); /* 1.获取指定的某个方法 getDeclaredMethod():参数1 :指明获取的方法的名称 参数2:指明获取的方法的形参列表 */ Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show", String.class); //2.保证当前方法是可访问的 show.setAccessible(true); /* 3. 调用方法的invoke():参数1:方法的调用者 参数2:给方法形参赋值的实参 invoke()的返回值即为对应类中调用的方法的返回值。 */ Object returnValue = show.invoke(p,"CHN"); //String nation = p.show("CHN"); System.out.println(returnValue); System.out.println("*************如何调用静态方法*****************"); // private static void showDesc() Method showDesc = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showDesc"); showDesc.setAccessible(true); //如果调用的运行时类中的方法没有返回值,则此invoke()返回null // Object returnVal = showDesc.invoke(null); Object returnVal = showDesc.invoke(Person.class); System.out.println(returnVal);//null } /* 如何调用运行时类中的指定的构造器 */ @Test public void testConstructor() throws Exception { Class clazz = Person.class; //private Person(String name) /* 1.获取指定的构造器 getDeclaredConstructor():参数:指明构造器的参数列表 */ Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class); //2.保证此构造器是可访问的 constructor.setAccessible(true); //3.调用此构造器创建运行时类的对象 Person per = (Person) constructor.newInstance("Tom"); System.out.println(per); } }

6.测试Filed
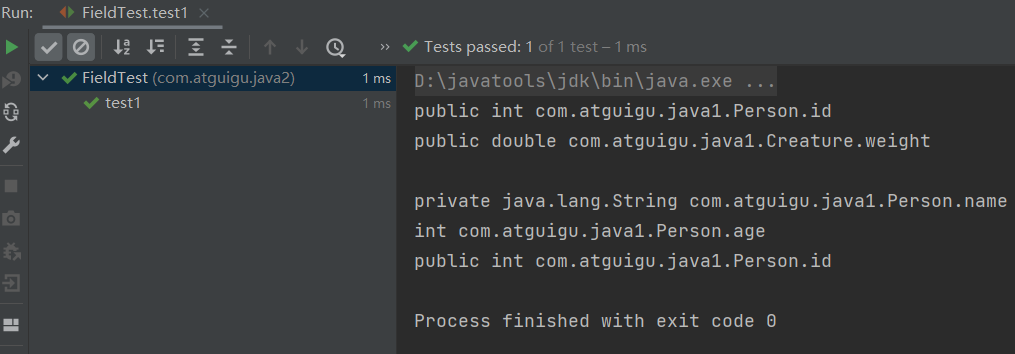
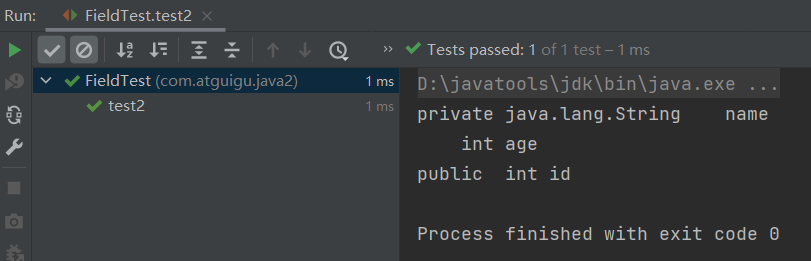
public class FieldTest { @Test public void test1(){ Class clazz = Person.class; //获取属性结构 //getFields():获取当前运行时类及其父类中声明为public访问权限的属性 Field[] fields = clazz.getFields(); for(Field f : fields){ System.out.println(f); } System.out.println(); //getDeclaredFields():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有属性。(不包含父类中声明的属性) Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); for(Field f : declaredFields){ System.out.println(f); } } //权限修饰符 数据类型 变量名 @Test public void test2(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields(); for(Field f : declaredFields){ //1.权限修饰符 int modifier = f.getModifiers(); System.out.print(Modifier.toString(modifier) + "\t"); //2.数据类型 Class type = f.getType(); System.out.print(type.getName() + "\t"); //3.变量名 String fName = f.getName(); System.out.print(fName); System.out.println(); } } }
7.测试Method
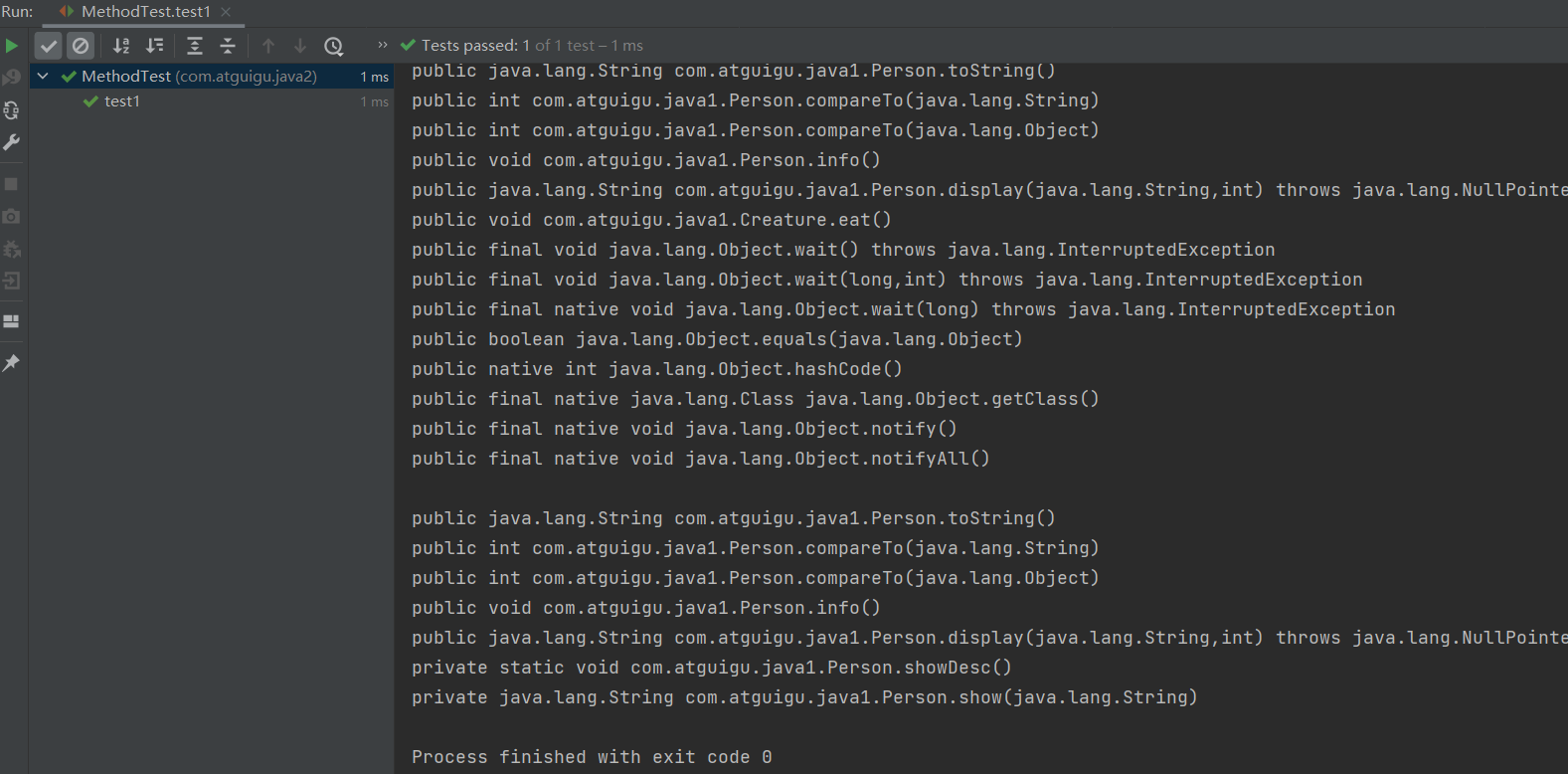
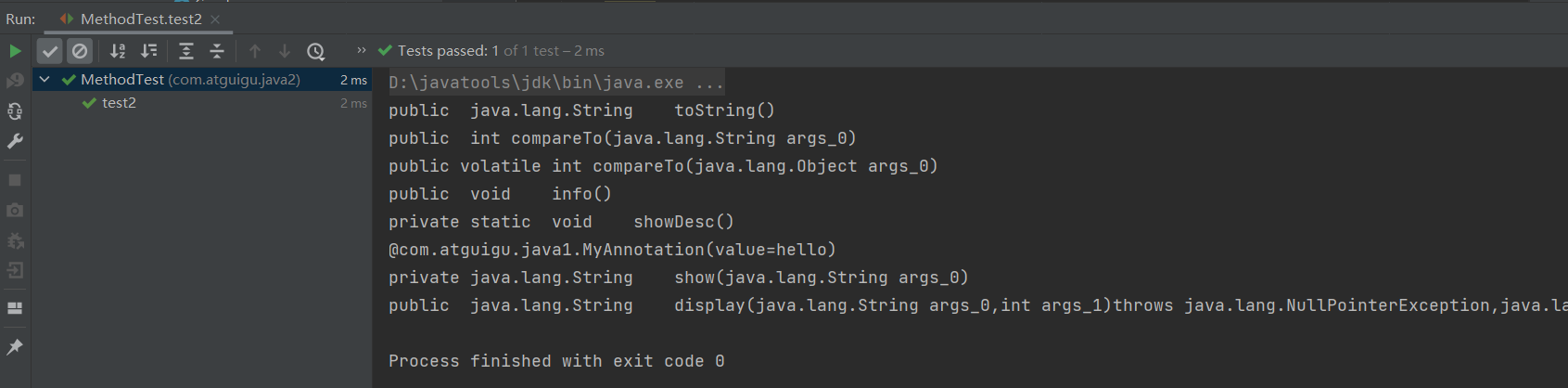
public class MethodTest { @Test public void test1(){ Class clazz = Person.class; //getMethods():获取当前运行时类及其所有父类中声明为public权限的方法 Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); for(Method m : methods){ System.out.println(m); } System.out.println(); //getDeclaredMethods():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有方法。(不包含父类中声明的方法) Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods(); for(Method m : declaredMethods){ System.out.println(m); } } /* @Xxxx 权限修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型1 形参名1,...) throws XxxException{} */ @Test public void test2(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods(); for(Method m : declaredMethods){ //1.获取方法声明的注解 Annotation[] annos = m.getAnnotations(); for(Annotation a : annos){ System.out.println(a); } //2.权限修饰符 System.out.print(Modifier.toString(m.getModifiers()) + "\t"); //3.返回值类型 System.out.print(m.getReturnType().getName() + "\t"); //4.方法名 System.out.print(m.getName()); System.out.print("("); //5.形参列表 Class[] parameterTypes = m.getParameterTypes(); if(!(parameterTypes == null && parameterTypes.length == 0)){ for(int i = 0;i < parameterTypes.length;i++){ if(i == parameterTypes.length - 1){ System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName() + " args_" + i); break; } System.out.print(parameterTypes[i].getName() + " args_" + i + ","); } } System.out.print(")"); //6.抛出的异常 Class[] exceptionTypes = m.getExceptionTypes(); if(exceptionTypes.length > 0){ System.out.print("throws "); for(int i = 0;i < exceptionTypes.length;i++){ if(i == exceptionTypes.length - 1){ System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName()); break; } System.out.print(exceptionTypes[i].getName() + ","); } } System.out.println(); } } }
8.测试其他
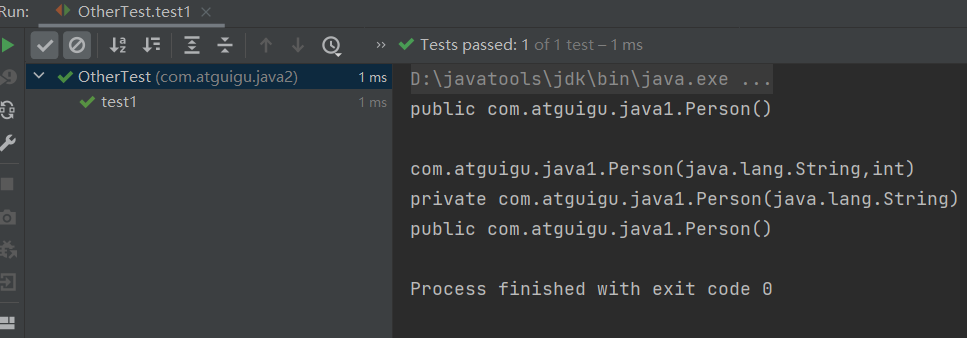
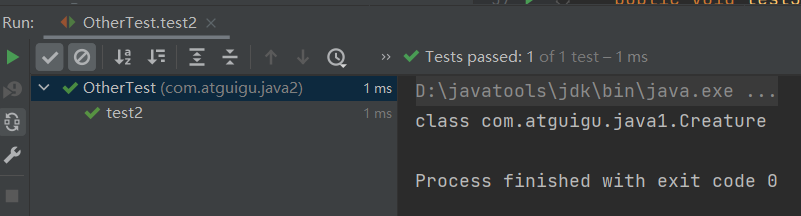
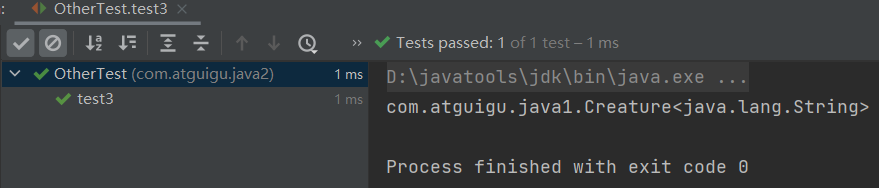
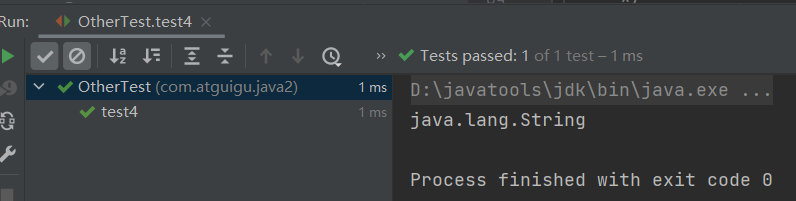
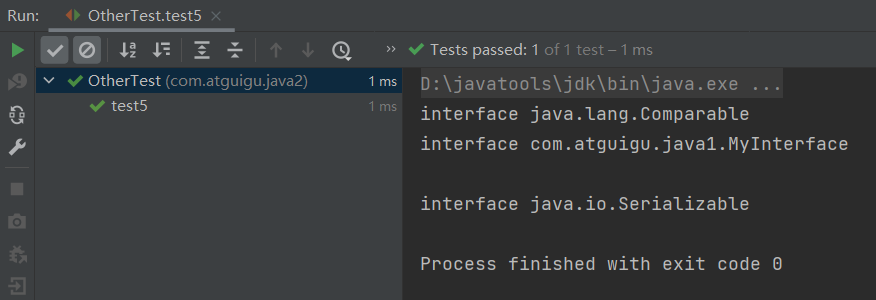
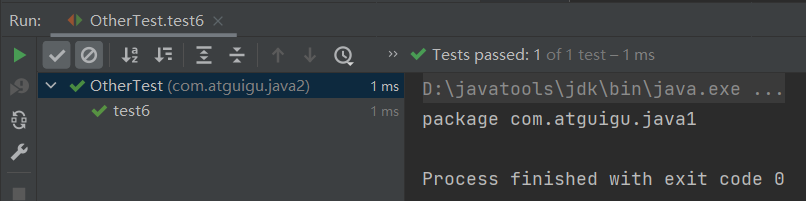
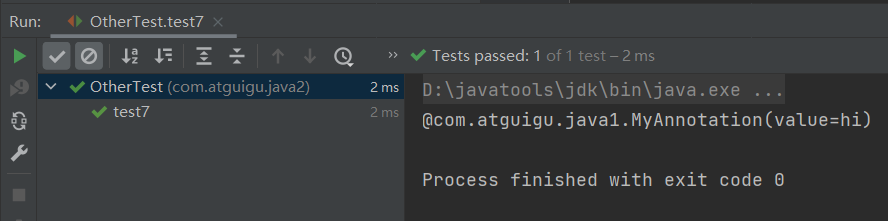
public class OtherTest { /* 获取构造器结构 */ @Test public void test1(){ Class clazz = Person.class; //getConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明为public的构造器 Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors(); for(Constructor c : constructors){ System.out.println(c); } System.out.println(); //getDeclaredConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有的构造器 Constructor[] declaredConstructors = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors(); for(Constructor c : declaredConstructors){ System.out.println(c); } } /* 获取运行时类的父类 */ @Test public void test2(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Class superclass = clazz.getSuperclass(); System.out.println(superclass); } /* 获取运行时类的带泛型的父类 */ @Test public void test3(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass(); System.out.println(genericSuperclass); } /* 获取运行时类的带泛型的父类的泛型 代码:逻辑性代码 vs 功能性代码 */ @Test public void test4(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Type genericSuperclass = clazz.getGenericSuperclass(); ParameterizedType paramType = (ParameterizedType) genericSuperclass; //获取泛型类型 Type[] actualTypeArguments = paramType.getActualTypeArguments(); // System.out.println(actualTypeArguments[0].getTypeName()); System.out.println(((Class)actualTypeArguments[0]).getName()); } /* 获取运行时类实现的接口 */ @Test public void test5(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Class[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces(); for(Class c : interfaces){ System.out.println(c); } System.out.println(); //获取运行时类的父类实现的接口 Class[] interfaces1 = clazz.getSuperclass().getInterfaces(); for(Class c : interfaces1){ System.out.println(c); } } /* 获取运行时类所在的包 */ @Test public void test6(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Package pack = clazz.getPackage(); System.out.println(pack); } /* 获取运行时类声明的注解 */ @Test public void test7(){ Class clazz = Person.class; Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations(); for(Annotation annos : annotations){ System.out.println(annos); } } }