1.3种中断方式
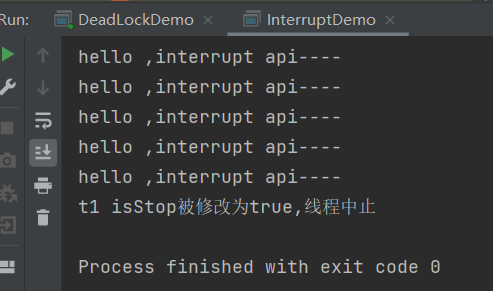
public class InterruptDemo { static volatile boolean isStop = false; static AtomicBoolean atomicBoolean = new AtomicBoolean(false); public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " isStop被修改为true,线程中止"); break; } System.out.println("hello ,interrupt api----"); } }, "t1"); t1.start(); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new Thread(() -> { t1.interrupt(); }, "t2").start(); // t1.interrupt(); } private static void m1_volatile() { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { if (isStop) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " isStop被修改为true,线程中止"); break; } System.out.println("hello ,volatile----"); } }, "t1"); t1.start(); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { isStop = true; }, "t2"); t2.start(); } private static void m2_atomicBoolean() { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { if (atomicBoolean.get()) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " isStop被修改为true,线程中止"); break; } System.out.println("hello ,atomicBoolean----"); } }, "t1"); t1.start(); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { atomicBoolean.set(true); }, "t2"); t2.start(); } }
2.踩坑
/** * 1.中断标志位,默认为false * 2.t2 --->t1发出了中断协商,她调用t1.interrupt(),中断标志位true * 3.中断标志位true,正常情况,程序停止 * 4.中断标志位true,异常情况InterruptedException,中断标志位false,无限循环 * 5.在catch块中,需要再次给中断标志位设置为true,2次调用停止程序才OK */ public class InterruptDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " isStop被修改为true,线程中止"); break; } try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("hello ,interrupt api----"); } }, "t1"); t1.start(); try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } new Thread(() -> { t1.interrupt(); }, "t2").start(); } }
3.
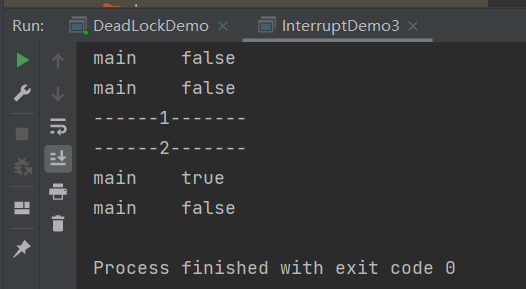
public class InterruptDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+Thread.interrupted()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+Thread.interrupted()); System.out.println("------1-------"); Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); System.out.println("------2-------"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+Thread.interrupted()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+Thread.interrupted()); } }


源码如下:


