Docker入门
Docker基础
1. Hello World
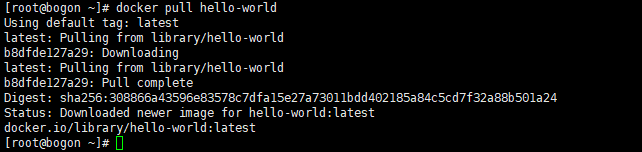
首先使用docker pull从镜像仓库Docker Hub下载hello-world镜像,
[root@bogon ~]# docker pull hello-world
Using default tag: latest
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
b8dfde127a29: Downloading
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
b8dfde127a29: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:308866a43596e83578c7dfa15e27a73011bdd402185a84c5cd7f32a88b501a24
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
docker.io/library/hello-world:latest
[root@bogon ~]#
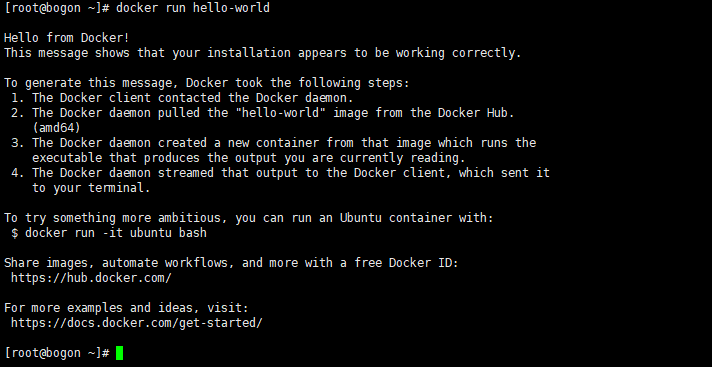
使用 docker run在容器内运行应用程序,输出Hello world
[root@bogon ~]# docker run hello-world
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
[root@bogon ~]#
各个参数解析如下:
- docker,docker的二进制执行文件。
- run,与前面的docker组合以运行一个容器。
- hello-world:latest,指定要运行的镜像。
- /bin/echo "Hello world",在启动的容器里执行的命令
以上命令的含义为:docker以hello-world:latest镜像创建一个新容器,并运行了该容器输出了相关信息。
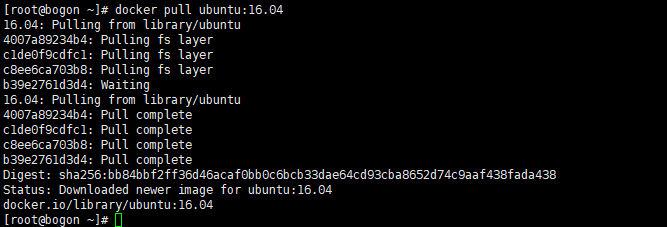
接下来,使用Ubuntu:16.04镜像生成容器,并输出hello world,首先下载ubuntu:16.04镜像,
[root@bogon ~]# docker pull ubuntu:16.04
16.04: Pulling from library/ubuntu
4007a89234b4: Pulling fs layer
c1de0f9cdfc1: Pulling fs layer
c8ee6ca703b8: Pulling fs layer
b39e2761d3d4: Waiting
16.04: Pulling from library/ubuntu
4007a89234b4: Pull complete
c1de0f9cdfc1: Pull complete
c8ee6ca703b8: Pull complete
b39e2761d3d4: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:bb84bbf2ff36d46acaf0bb0c6bcb33dae64cd93cba8652d74c9aaf438fada438
Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:16.04
docker.io/library/ubuntu:16.04
[root@bogon ~]#
接着,运行docker run命令使用Ubuntu容器输出hello world,命令如下:
[root@bogon ~]# docker run ubuntu:16.04 /bin/echo "hello world"
hello world
[root@bogon ~]#

该命令的含义为:docker以ubuntu 16.04 镜像创建一个新容器,然后在容器里执行bin/echo "Hello world",最后输出结果。
2. 运行交互式容器
通过docker的两个参数-i -t,让docker运行的容器实现"对话"的能力:
[root@bogon ~]# docker run -i -t ubuntu:16.04 /bin/bash
root@fc7558995c87:/#
各个参数解析:
- -t: 在新容器内指定一个伪终端或终端。
- -i: 允许你对容器内的标准输入 (STDIN) 进行交互。

注意上图中的第二行root@fc7558995c87:/# ,此时我们已进入一个 ubuntu 16.04 系统的容器
在容器中使用命令 cat /proc/version查看当前系统的版本信息
[root@bogon ~]# docker run -i -t ubuntu:16.04 /bin/bash
root@fc7558995c87:/# cat /proc/version
Linux version 3.10.0-1160.el7.x86_64 (mockbuild@kbuilder.bsys.centos.org) (gcc version 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Mon Oct 19 16:18:59 UTC 2020
root@fc7558995c87:/#

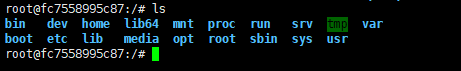
在容器中使用命令ls查看当前目录下的文件列表
root@fc7558995c87:/# ls
bin dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var
boot etc lib media opt root sbin sys usr
root@fc7558995c87:/#
通过exit命令或者使用CTRL+D退出容器。
root@fc7558995c87:/# exit
exit
[root@bogon ~]#

注意第三行中 [root@bogon ~]# 表明已退出当前的容器,返回到当前的主机中。
3. 启动容器(后台模式)
使用以下命令创建一个以进程方式运行的容器
[root@bogon ~]# docker run -d ubuntu:16.04 /bin/bash -c "while true;do echo hello world; sleep 1; done"
078ebb0bd591faa830eb68ed2e39347f315057703ae6624c8305e7ff97632b53
[root@bogon ~]#
在输出中,没有看到期望的 "hello world",而是一串长字符:
078ebb0bd591faa830eb68ed2e39347f315057703ae6624c8305e7ff97632b53
这个长字符串叫做容器ID,对每个容器来说都是唯一的。可以通过容器ID操作、查看对应的容器。
首先,我们需要确认容器有在运行,可以通过docker ps来查看:
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
078ebb0bd591 ubuntu:16.04 "/bin/bash -c 'while…" 38 seconds ago Up 37 seconds clever_goldwasser
[root@bogon ~]#
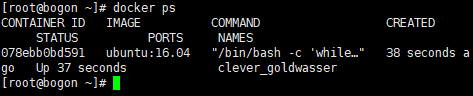
输出详情介绍:
- CONTAINER ID:容器 ID。
- IMAGE:使用的镜像。
- COMMAND:启动容器时运行的命令。
- CREATED:容器的创建时间。
- STATUS:容器状态,共包含7种状态。
- created:已创建
- restarting:重启中
- running:运行中
- removing:迁移中
- paused:暂停
- exited:停止
- dead:死亡
- PORTS:容器的端口信息和使用的连接类型(tcp\udp)。
- NAMES:自动分配的容器名称。
在宿主主机内使用docker logs命令,查看容器内的标准输出:
[root@bogon ~]# docker logs 078
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
...
使用容器名称查看日志:
[root@bogon ~]# docker logs naughty_hellman
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
hello world
...
4. 停止容器
使用docker stop命令来停止容器:
[root@bogon ~]# docker stop 078
078
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
[root@bogon ~]#
通过docker ps查看,容器已经停止工作。
注意,在上述命令中,容器ID只使用了078,而没有写上完整的078ebb0bd591,这是由于docker会自动按照前缀搜索,如果某个容器ID可以和这个前缀匹配,则会定位到该容器。因此可以使用078这种简写的方式,当然,如果确定只有一个容器以0开头,也可以直接用命令docker stop 0。
[root@bogon ~]# docker start 0
0
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
078ebb0bd591 ubuntu:16.04 "/bin/bash -c 'while…" 17 hours ago Up 2 seconds clever_goldwasser
[root@bogon ~]# docker stop 0
0
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
[root@bogon ~]#
同样地,在停止容器时,也可以使用容器名称来操作:
[root@bogon ~]# docker start 0
0
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
078ebb0bd591 ubuntu:16.04 "/bin/bash -c 'while…" 17 hours ago Up 5 seconds clever_goldwasser
[root@bogon ~]# docker stop clever_goldwasser
clever_goldwasser
[root@bogon ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
[root@bogon ~]#





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了