fastp安装及使用
fastp是一款快速处理NGS下机序列的工具,官网地址fastp
一、安装
conda install -c bioconda fastp二、使用
#过滤接头以及低质量碱基相关参数默认开启
#输入双端序列文件支持SE/PE,可以是.fq/.fq.gz格式,fastp最多可用16个线程
#输出会同时产生HTML以及JSON格式文件
fastp -i <in.R1.fq.gz> -I <in.R2.fq.gz> -o <out.R1.fq.gz> -O <out.R2.fq.gz> --thread 16三、结果输出
除了生成HTML以及JSON格式的统计信息,还包括一个标准输出信息如下:
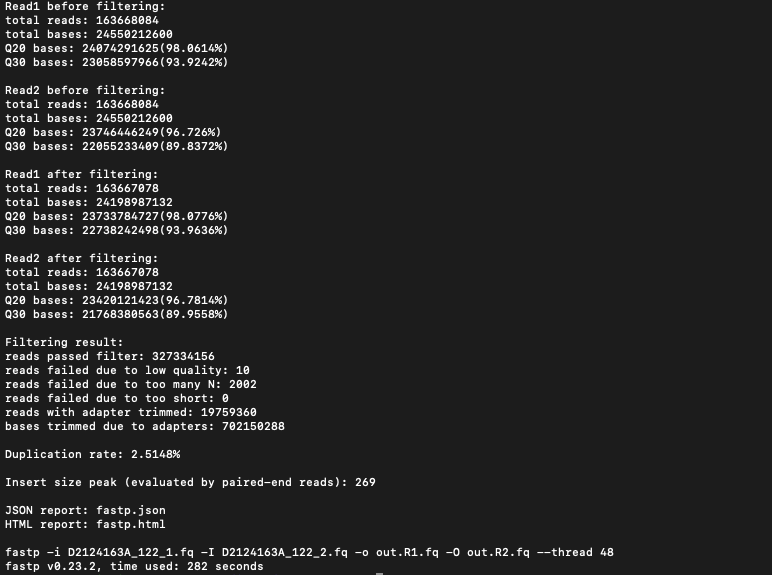
四、参数详情
usage: fastp -i <in1> -o <out1> [-I <in1> -O <out2>] [options...]
options:
# I/O options
-i, --in1 read1 input file name (string)
-o, --out1 read1 output file name (string [=])
-I, --in2 read2 input file name (string [=])
-O, --out2 read2 output file name (string [=])
--unpaired1 for PE input, if read1 passed QC but read2 not, it will be written to unpaired1. Default is to discard it. (string [=])
--unpaired2 for PE input, if read2 passed QC but read1 not, it will be written to unpaired2. If --unpaired2 is same as --unpaired1 (default mode), both unpaired reads will be written to this same file. (string [=])
--failed_out specify the file to store reads that cannot pass the filters. (string [=])
--overlapped_out for each read pair, output the overlapped region if it has no any mismatched base. (string [=])
-m, --merge for paired-end input, merge each pair of reads into a single read if they are overlapped. The merged reads will be written to the file given by --merged_out, the unmerged reads will be written to the files specified by --out1 and --out2. The merging mode is disabled by default.
--merged_out in the merging mode, specify the file name to store merged output, or specify --stdout to stream the merged output (string [=])
--include_unmerged in the merging mode, write the unmerged or unpaired reads to the file specified by --merge. Disabled by default.
-6, --phred64 indicate the input is using phred64 scoring (it'll be converted to phred33, so the output will still be phred33)
-z, --compression compression level for gzip output (1 ~ 9). 1 is fastest, 9 is smallest, default is 4. (int [=4])
--stdin input from STDIN. If the STDIN is interleaved paired-end FASTQ, please also add --interleaved_in.
--stdout output passing-filters reads to STDOUT. This option will result in interleaved FASTQ output for paired-end input. Disabled by default.
--interleaved_in indicate that <in1> is an interleaved FASTQ which contains both read1 and read2. Disabled by default.
--reads_to_process specify how many reads/pairs to be processed. Default 0 means process all reads. (int [=0])
--dont_overwrite don't overwrite existing files. Overwritting is allowed by default.
--fix_mgi_id the MGI FASTQ ID format is not compatible with many BAM operation tools, enable this option to fix it.
# adapter trimming options
-A, --disable_adapter_trimming adapter trimming is enabled by default. If this option is specified, adapter trimming is disabled
-a, --adapter_sequence the adapter for read1. For SE data, if not specified, the adapter will be auto-detected. For PE data, this is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. (string [=auto])
--adapter_sequence_r2 the adapter for read2 (PE data only). This is used if R1/R2 are found not overlapped. If not specified, it will be the same as <adapter_sequence> (string [=])
--adapter_fasta specify a FASTA file to trim both read1 and read2 (if PE) by all the sequences in this FASTA file (string [=])
--detect_adapter_for_pe by default, the adapter sequence auto-detection is enabled for SE data only, turn on this option to enable it for PE data.
# global trimming options
-f, --trim_front1 trimming how many bases in front for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-t, --trim_tail1 trimming how many bases in tail for read1, default is 0 (int [=0])
-b, --max_len1 if read1 is longer than max_len1, then trim read1 at its tail to make it as long as max_len1. Default 0 means no limitation (int [=0])
-F, --trim_front2 trimming how many bases in front for read2. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-T, --trim_tail2 trimming how many bases in tail for read2. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
-B, --max_len2 if read2 is longer than max_len2, then trim read2 at its tail to make it as long as max_len2. Default 0 means no limitation. If it's not specified, it will follow read1's settings (int [=0])
# duplication evaluation and deduplication
-D, --dedup enable deduplication to drop the duplicated reads/pairs
--dup_calc_accuracy accuracy level to calculate duplication (1~6), higher level uses more memory (1G, 2G, 4G, 8G, 16G, 24G). Default 1 for no-dedup mode, and 3 for dedup mode. (int [=0])
--dont_eval_duplication don't evaluate duplication rate to save time and use less memory.
# polyG tail trimming, useful for NextSeq/NovaSeq data
-g, --trim_poly_g force polyG tail trimming, by default trimming is automatically enabled for Illumina NextSeq/NovaSeq data
--poly_g_min_len the minimum length to detect polyG in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
-G, --disable_trim_poly_g disable polyG tail trimming, by default trimming is automatically enabled for Illumina NextSeq/NovaSeq data
# polyX tail trimming
-x, --trim_poly_x enable polyX trimming in 3' ends.
--poly_x_min_len the minimum length to detect polyX in the read tail. 10 by default. (int [=10])
# per read cutting by quality options
-5, --cut_front move a sliding window from front (5') to tail, drop the bases in the window if its mean quality < threshold, stop otherwise.
-3, --cut_tail move a sliding window from tail (3') to front, drop the bases in the window if its mean quality < threshold, stop otherwise.
-r, --cut_right move a sliding window from front to tail, if meet one window with mean quality < threshold, drop the bases in the window and the right part, and then stop.
-W, --cut_window_size the window size option shared by cut_front, cut_tail or cut_sliding. Range: 1~1000, default: 4 (int [=4])
-M, --cut_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option shared by cut_front, cut_tail or cut_sliding. Range: 1~36 default: 20 (Q20) (int [=20])
--cut_front_window_size the window size option of cut_front, default to cut_window_size if not specified (int [=4])
--cut_front_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option for cut_front, default to cut_mean_quality if not specified (int [=20])
--cut_tail_window_size the window size option of cut_tail, default to cut_window_size if not specified (int [=4])
--cut_tail_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option for cut_tail, default to cut_mean_quality if not specified (int [=20])
--cut_right_window_size the window size option of cut_right, default to cut_window_size if not specified (int [=4])
--cut_right_mean_quality the mean quality requirement option for cut_right, default to cut_mean_quality if not specified (int [=20])
# quality filtering options
-Q, --disable_quality_filtering quality filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, quality filtering is disabled
-q, --qualified_quality_phred the quality value that a base is qualified. Default 15 means phred quality >=Q15 is qualified. (int [=15])
-u, --unqualified_percent_limit how many percents of bases are allowed to be unqualified (0~100). Default 40 means 40% (int [=40])
-n, --n_base_limit if one read's number of N base is >n_base_limit, then this read/pair is discarded. Default is 5 (int [=5])
-e, --average_qual if one read's average quality score <avg_qual, then this read/pair is discarded. Default 0 means no requirement (int [=0])
# length filtering options
-L, --disable_length_filtering length filtering is enabled by default. If this option is specified, length filtering is disabled
-l, --length_required reads shorter than length_required will be discarded, default is 15. (int [=15])
--length_limit reads longer than length_limit will be discarded, default 0 means no limitation. (int [=0])
# low complexity filtering
-y, --low_complexity_filter enable low complexity filter. The complexity is defined as the percentage of base that is different from its next base (base[i] != base[i+1]).
-Y, --complexity_threshold the threshold for low complexity filter (0~100). Default is 30, which means 30% complexity is required. (int [=30])
# filter reads with unwanted indexes (to remove possible contamination)
--filter_by_index1 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index1 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index2 specify a file contains a list of barcodes of index2 to be filtered out, one barcode per line (string [=])
--filter_by_index_threshold the allowed difference of index barcode for index filtering, default 0 means completely identical. (int [=0])
# base correction by overlap analysis options
-c, --correction enable base correction in overlapped regions (only for PE data), default is disabled
--overlap_len_require the minimum length to detect overlapped region of PE reads. This will affect overlap analysis based PE merge, adapter trimming and correction. 30 by default. (int [=30])
--overlap_diff_limit the maximum number of mismatched bases to detect overlapped region of PE reads. This will affect overlap analysis based PE merge, adapter trimming and correction. 5 by default. (int [=5])
--overlap_diff_percent_limit the maximum percentage of mismatched bases to detect overlapped region of PE reads. This will affect overlap analysis based PE merge, adapter trimming and correction. Default 20 means 20%. (int [=20])
# UMI processing
-U, --umi enable unique molecular identifier (UMI) preprocessing
--umi_loc specify the location of UMI, can be (index1/index2/read1/read2/per_index/per_read, default is none (string [=])
--umi_len if the UMI is in read1/read2, its length should be provided (int [=0])
--umi_prefix if specified, an underline will be used to connect prefix and UMI (i.e. prefix=UMI, UMI=AATTCG, final=UMI_AATTCG). No prefix by default (string [=])
--umi_skip if the UMI is in read1/read2, fastp can skip several bases following UMI, default is 0 (int [=0])
# overrepresented sequence analysis
-p, --overrepresentation_analysis enable overrepresented sequence analysis.
-P, --overrepresentation_sampling One in (--overrepresentation_sampling) reads will be computed for overrepresentation analysis (1~10000), smaller is slower, default is 20. (int [=20])
# reporting options
-j, --json the json format report file name (string [=fastp.json])
-h, --html the html format report file name (string [=fastp.html])
-R, --report_title should be quoted with ' or ", default is "fastp report" (string [=fastp report])
# threading options
-w, --thread worker thread number, default is 3 (int [=3])
# output splitting options
-s, --split split output by limiting total split file number with this option (2~999), a sequential number prefix will be added to output name ( 0001.out.fq, 0002.out.fq...), disabled by default (int [=0])
-S, --split_by_lines split output by limiting lines of each file with this option(>=1000), a sequential number prefix will be added to output name ( 0001.out.fq, 0002.out.fq...), disabled by default (long [=0])
-d, --split_prefix_digits the digits for the sequential number padding (1~10), default is 4, so the filename will be padded as 0001.xxx, 0 to disable padding (int [=4])
# help
-?, --help print this message

