人工智能必备数学知识学习笔记8:线性系统

线性系统与消元
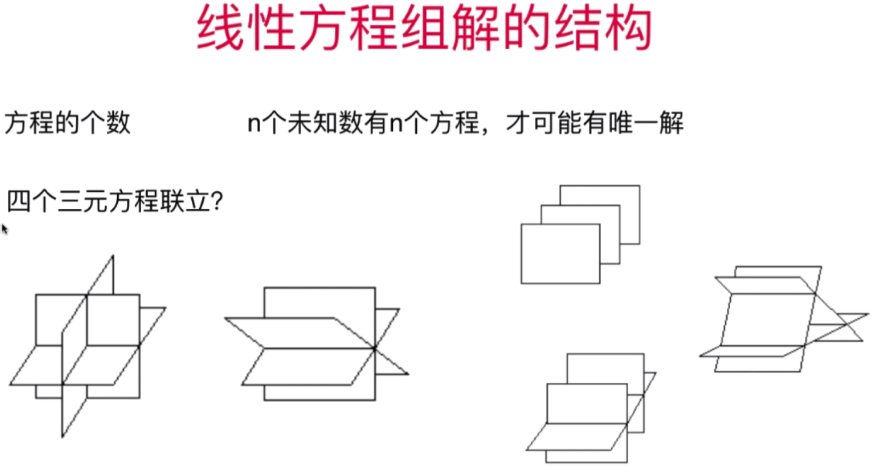
非线性: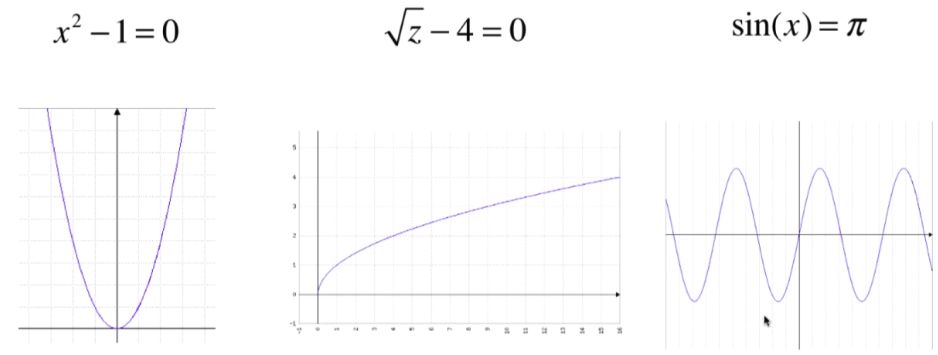
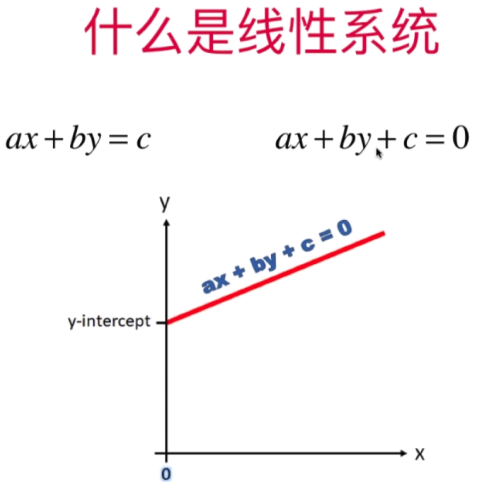


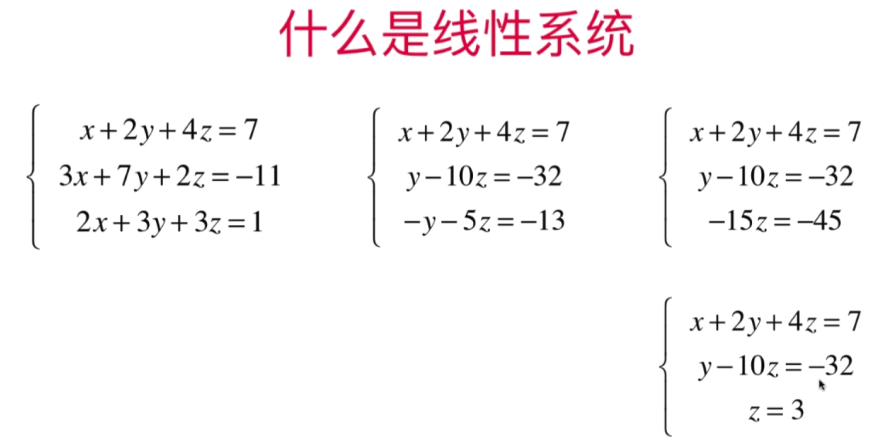
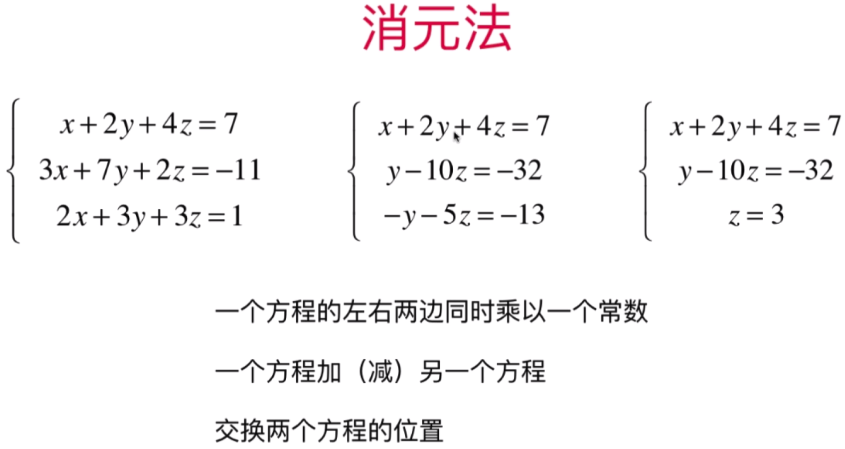
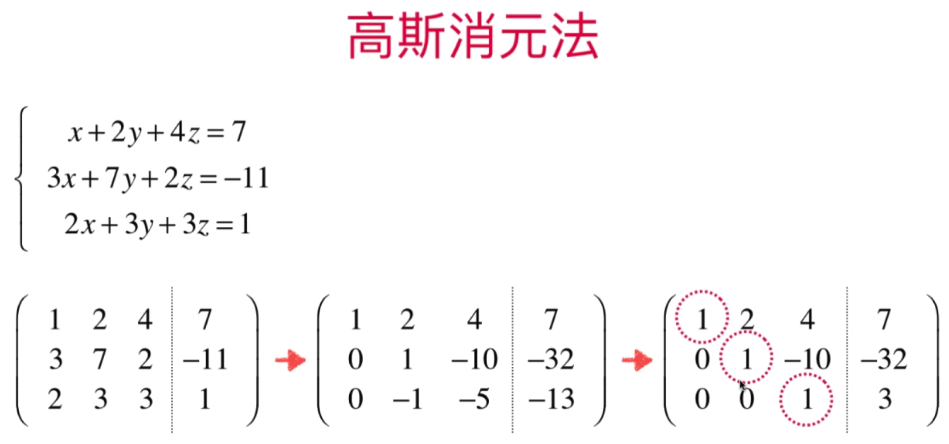
方程式1,2,3 将
第一组:方程式2 - 方程式1 *3 =得出第二组 y-10z = -32;
第二组:方程式3-方程式1=得出第三组-y-5z=-13;
第三组:方程式2+方程式3=得出-15z =-45

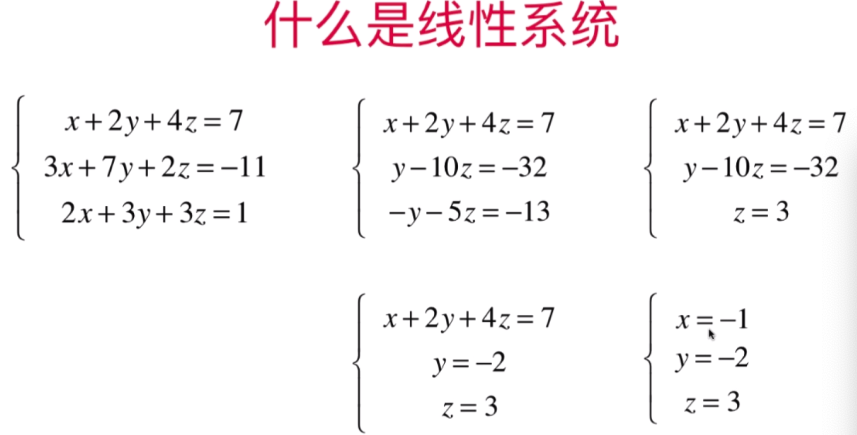
此时:下图第三组方程式3:-15z = -45 得出第四组:方程式3:z=3
根据第三组方程式3:z=3,将z=3带入方程式2:y-10z =-32 得出第四组方程式2:y= -2;
根据第四组 y=-2、z=3带入方程式1:x+2y+4z=7 得出第五组方程式1:x=-1
- 高斯消元法
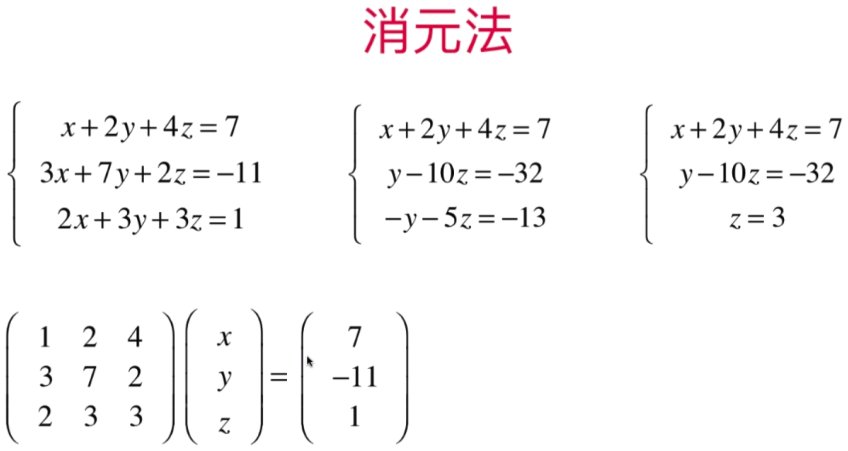
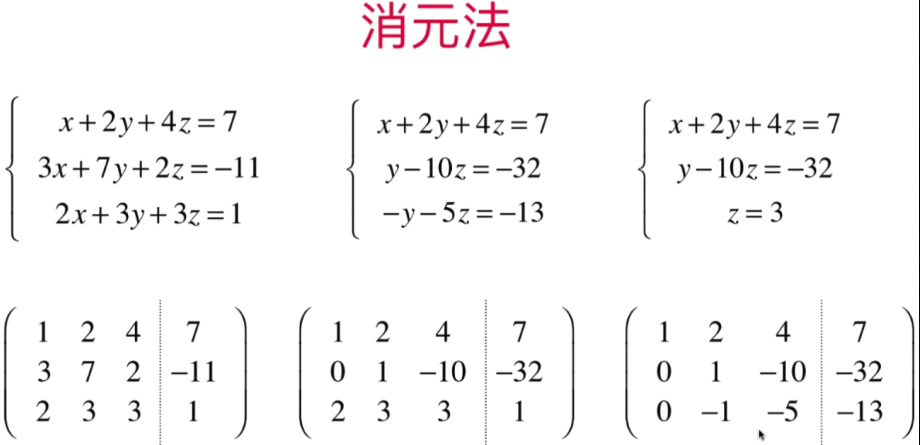
增广矩阵:将第一组的系数与等号右侧的值直接组成一个新的矩阵:从而进行消元
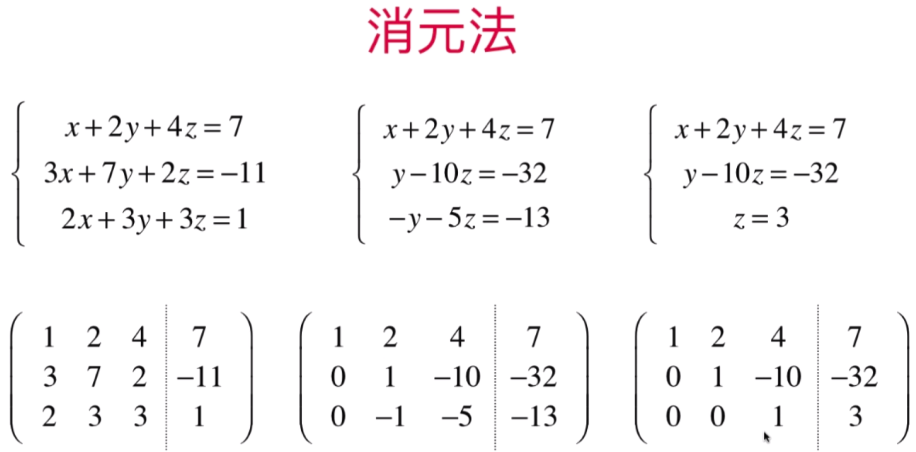
高斯消元法是根据增光矩阵的角度:等价于线性方程组的消元法
且有N个未知数就会有N行矩阵(n个方程)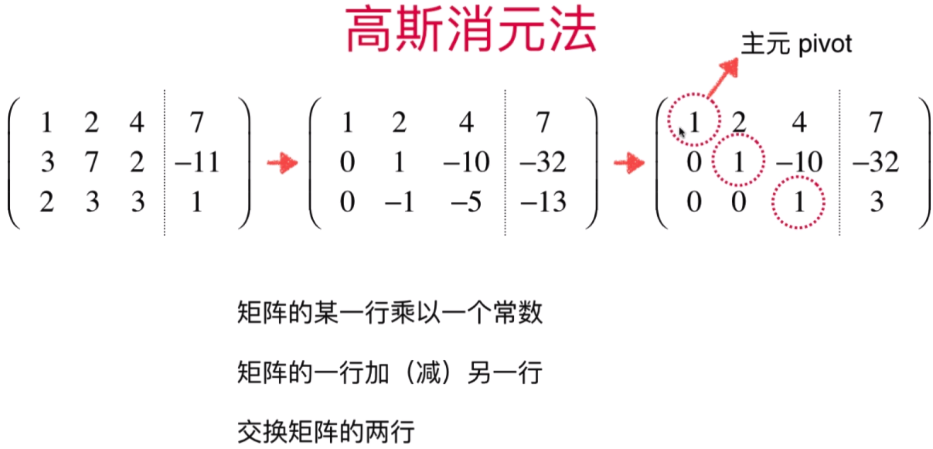
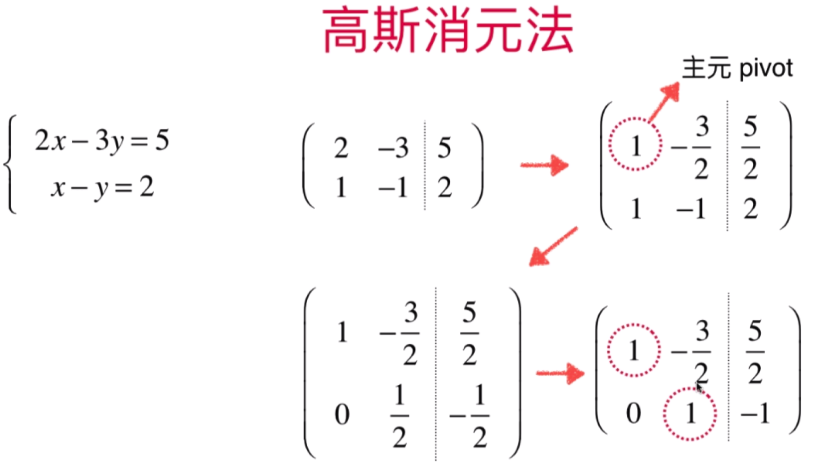
此时:主源不能为0,需要将矩阵进行位置调换(调换原则为与主源值最大的进行矩阵行的进行交换位置<可以尽量小的避免误差-涉及数值分析方面的内容>)
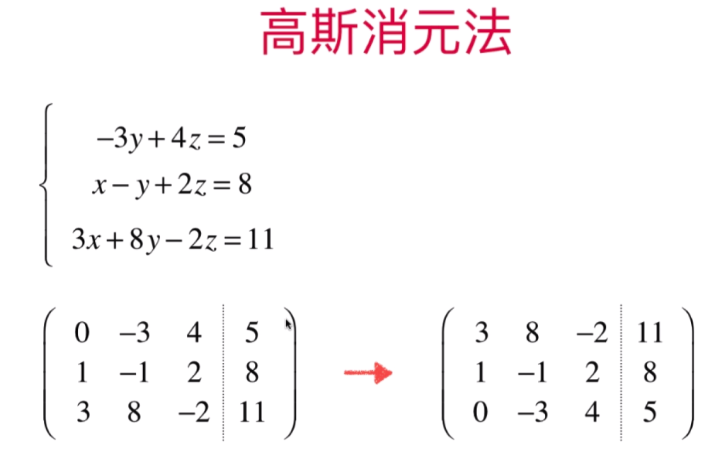
- 高斯-约旦消元
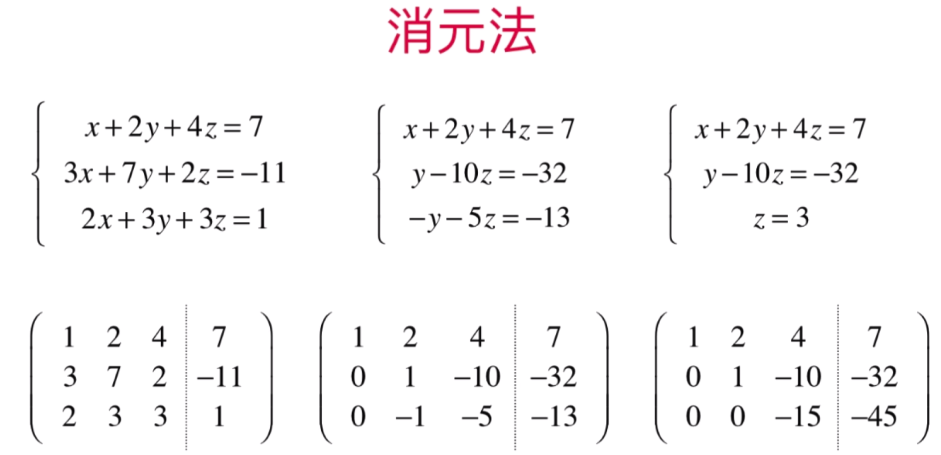
将增广矩阵的第二组中的 方程3*10 + 方程2 得出将方程2的第三个元素消成0,从而得出方程2的第二个元素的值
高斯-约旦消元法:
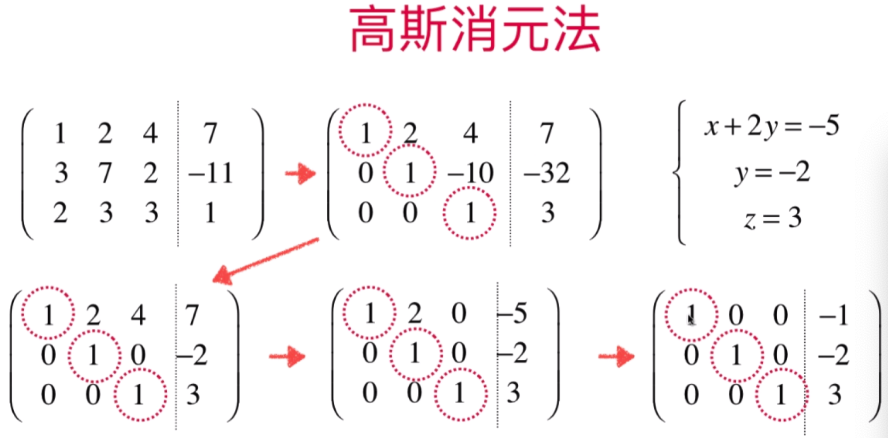
1.前向过程指的是从上到下找到主源将其划为1,直至将最后一个方程的未知数数量变为一个
2.后项过程指的是从下到上找到主源将非组源位置划归为0,直至第一个方程

高斯-约旦消元法说明:
前向过程:将主源对应列自上而下全部归为0(每行主源元素会归为1)
后向过程:反过来将主源对应列自下而上全部归为0
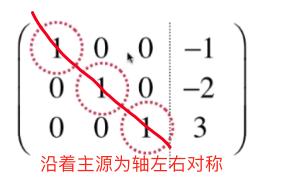
前向后向过程会根据主源形成对称轴(此时主源均为1),前向操作将对称轴的左侧全部划归为0,后向操作将对称轴右侧全部划归为0
下面代码实现会根据上图以及此注释进行代码编写
代码实现:
1. 在Vector.py编写代码:返回当前向量的底层列表 underlying_list
1 #向量类 2 #__values() 与 _values()区别更多体现在继承上,如果是在类的内部使用时官方建议使用_values()发方法 3 from ._global import EPSILON 4 import math 5 6 7 class Vector: 8 9 def __init__(self,lst): 10 self._values = list(lst)#将数组赋值给向量类中(注:使用list方法将列表lst复制一份保证他的不被外界调用时修改) 11 12 #零向量类方法:参数1:为当前的类(cls) 参数2:维度(dim) 返回dim维的零向量 13 @classmethod 14 def zero(cls,dim): 15 return cls([0] * dim) 16 17 #返回向量的模(向量长度): 18 def norm(self): 19 return math.sqrt(sum(e**2 for e in self))#sqrt()方法为开平方根,sum()求和方法,e**2 e的平方 20 21 #返回向量的单位向量 22 def normalize(self): 23 if self.norm() < EPSILON: #此处判断一个精度范围(该精度范围调用内部自定义全局变量文件 _global.py)(由于浮点数计算机含有误差所以无法使用 == 0 的操作) 24 raise ZeroDivisionError("Normalize error! norm is zero.") #考虑零向量时报此处异常即可 25 #方案一:return Vector(1/self.norm() * [e for e in self])#循环遍历向量中的每个元素分别除以该向量的模即为单位向量 26 #方案二:return 1/self.norm() * Vector(self._values)#当前向量除以模即为单位向量 27 return Vector(self._values) / self.norm() 28 29 #返回当前向量的底层列表 TODO:2020-08-12 17:04:00 30 def underlying_list(self): 31 return self._values[:]#此时为返回该列表的一个副本 32 33 #向量加法,返回结果向量 34 def __add__(self, another): 35 # assert判断传入的向量维度是否相等 36 assert len(self) == len(another),\ 37 "Error in adding. Length of vectors must be same." 38 return Vector([a+b for a,b in zip(self,another)])#使用zip()方法将两个向量取出来 39 40 # 向量减法 41 def __sub__(self, another): 42 #判断维度相等 43 assert len(self) == len(another), \ 44 "Error in adding. Length of vectors must be same." 45 return Vector([a - b for a, b in zip(self, another)]) 46 47 #向量点乘(向量之间相乘):返回结果标量 48 def dot(self,another): 49 #判断维度相等 50 assert len(self) == len(another), \ 51 "Error in dot product. Length of vectors must be same." 52 return sum(a * b for a,b in zip(self,another))# 方法zip()将两组向量配成对应位置的数据对 53 54 # 向量数量乘法(数乘数组),返回数量乘法的结果向量:self * k 55 def __mul__(self, k): 56 return Vector([k * e for e in self]) 57 58 # 向量数量乘法(数组乘数),返回数量乘法的结果向量:k * self 59 def __rmul__(k, self): 60 return k * self #此处直接调用的是上方的乘法函数 61 62 # 向量除法:返回数量除法的结果向量 self / k 63 def __truediv__(self, k): 64 return (1 / k) * self 65 66 #返回向量取正的结果向量 67 def __pos__(self): 68 return 1 * self 69 70 # 返回向量取负的结果向量 71 def __neg__(self): 72 return -1 * self 73 74 #返回向量迭代器(当有迭代器时,zip()方法中就不用再次传入两个向量数组,直接传入向量对象即可<zip(self._values,another._values)>) 75 def __iter__(self): 76 return self._values.__iter__() 77 78 #取向量的index个元素 79 def __getitem__(self, index): 80 return self._values[index] 81 82 #返回向量的长度(有多少个元素) 83 def __len__(self): 84 return len(self._values) 85 86 # 向量展示(系统调用) 87 def __repr__(self): 88 return "Vector({})".format(self._values) 89 90 # 向量展示(用户调用) 91 def __str__(self): 92 return "({})".format(", ".join(str(e) for e in self._values))#通过遍历 self.__values 将e转成字符串通过逗号加空格来链接放入大括号中 93 94 # u = Vector([5,2]) 95 # print(u)
2. 在LinearSystem.py编写代码:
1 from.Matrix import Matrix 2 from.Vector import Vector 3 4 5 #线性系统 6 class LinearSystem: 7 8 #初始化函数:参数A:增广矩阵的等号左边的系数 参数b:增广矩阵的等号右边的值(方程右边的结果) 9 def __init__(self,A,b): 10 #判断矩阵A的行数是否等于b的列数 11 assert A.row_num() == len(b),\ 12 "row number of A must be equal to the length of b" 13 self._m = A.row_num()#行数 14 self._n = A.col_num()#列数 15 16 #判断矩阵A的行数是否等于列数 17 assert self._m == self._n #TODO: no this restriction 将来要解除该限制 18 19 #增广矩阵 20 self.Ab = [Vector(A.row_vector(i).underlying_list() + [b[i]]) 21 for i in range(self._m)] 22 23 #寻找最大主源系数 24 def _max_row(self,index,n): 25 best, ret = self.Ab[index][index], index #存储第index行index列的元素值与当前index的值 26 for i in range(index + 1, n): #从index+1开始一直遍历到n 27 if self.Ab[i][index] < best: 28 best, ret = self.Ab[i][index], i 29 return ret 30 31 #高斯—约旦消元法-前向过程 32 def _forward(self): 33 n = self._m #行数 34 for i in range(n): 35 #Ab[i][i]为主源 36 max_row = self._max_row(i,n)#寻找最大主源系数的行数 37 self.Ab[i], self.Ab[max_row] = self.Ab[max_row],self.Ab[i] 38 39 #将主源归为一 40 self.Ab[i] = self.Ab[i] / self.Ab[i][i] #TODO: self.Ab[i][i] == 0 时会报错 41 #将当前主源下的所有行对应主源列的元素全部归为0 :也就是第一次循环会将该主源下的所有对应列变为0,第二次循环会将第二次主源列下的所有对应列变为0 42 for j in range(i + 1, n): 43 self.Ab[j] =self.Ab[j] -self.Ab[j][i] * self.Ab[i]#该主源行下的所有行减去主源行 44 45 #高斯-约旦消元法-后向过程 46 def _backward(self): 47 n = self._m #行数 48 for i in range(n-1, -1, -1): #反向遍历且 从参数1的位置遍历到参数2的位置,也就是从倒数第一个位置遍历到第一个位置,参数3为步长(遍历的方向及单位) 49 #Ab[i][i]为主源 50 for j in range(i-1, -1, -1): 51 self.Ab[j] = self.Ab[j] - self.Ab[j][i] * self.Ab[i]#该主源行上的所有行减去主源行 52 53 #高斯-约旦消元法 54 def gauss_jordan_elimination(self): 55 # 高斯—约旦消元法-前向过程 56 self._forward() 57 # 高斯-约旦消元法-后向过程 58 self._backward() 59 60 # 打印结果(求每个未知数的值) 61 def fancy_print(self): 62 for i in range(self._m): 63 print(" ".join(str(self.Ab[i][j]) for j in range(self._n)),end=" ") 64 print("|",self.Ab[i][-1])
3.在main_linear_system.py编写代码:
1 from playLA.Matrix import Matrix 2 from playLA.Vector import Vector 3 from playLA.LinearSystem import LinearSystem 4 5 if __name__ == "__main__": 6 7 # 高斯—约旦消元法 8 A = Matrix([[1,2,4],[3,7,2],[2,3,3]]) 9 b = Vector([7,-11,1]) 10 ls = LinearSystem(A,b) #线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 11 ls.gauss_jordan_elimination() #高斯—约旦消元 12 ls.fancy_print() #打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 13 print("*" * 50)#分隔线 14 15 # 高斯—约旦消元法 16 A2 = Matrix([[1, -3, 5], [2, -1, -3], [3, 1, 4]]) 17 b2 = Vector([-9, 19, 13]) 18 ls2 = LinearSystem(A2, b2) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 19 ls2.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 20 ls2.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 21 print("*" * 50) # 分隔线 22 23 # 高斯—约旦消元法 24 A3 = Matrix([[1, 2, -2], [2, -3, 1], [3, -1, 3]]) 25 b3 = Vector([6, -10, -16]) 26 ls3 = LinearSystem(A3, b3) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 27 ls3.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 28 ls3.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 29 print("*" * 50) # 分隔线 30 31 # 高斯—约旦消元法 32 A4 = Matrix([[3, 1, -2], [5, -3, 10], [7, 4, 16]]) 33 b4 = Vector([4, 32, 13]) 34 ls4 = LinearSystem(A4, b4) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 35 ls4.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 36 ls4.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 37 print("*" * 50) # 分隔线 38 39 # 高斯—约旦消元法 40 A5 = Matrix([[6, -3, 2], [5, 1, 12], [8, 5, 1]]) 41 b5 = Vector([31, 36, 11]) 42 ls5 = LinearSystem(A5, b5) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 43 ls5.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 44 ls5.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 45 print("*" * 50) # 分隔线 46 47 # 高斯—约旦消元法 48 A6 = Matrix([[1, 1, 1], [1, -1, -1], [2, 1, 5]]) 49 b6 = Vector([3, -1, 8]) 50 ls6 = LinearSystem(A6, b6) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 51 ls6.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 52 ls6.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 53 print("*" * 50) # 分隔线
4.运行main_linear_system.py 结果为:
1 /Users/liuxiaoming/PycharmProjects/LinearAlgebra/venv/bin/python /Users/liuxiaoming/PycharmProjects/LinearAlgebra/main_linear_system.py 2 1.0 0.0 0.0 | -1.0 3 0.0 1.0 0.0 | -2.0 4 -0.0 -0.0 1.0 | 3.0 5 ************************************************** 6 1.0 0.0 0.0 | 6.853333333333333 7 0.0 1.0 0.0 | 1.5066666666666668 8 0.0 0.0 1.0 | -2.2666666666666666 9 ************************************************** 10 1.0 0.0 0.0 | -2.0 11 0.0 1.0 0.0 | 1.0000000000000009 12 0.0 0.0 1.0 | -2.999999999999999 13 ************************************************** 14 1.0 0.0 3.7007434154171876e-17 | 3.0 15 0.0 1.0 -4.440892098500626e-16 | -4.000000000000001 16 0.0 0.0 0.9999999999999999 | 0.5000000000000001 17 ************************************************** 18 1.0 0.0 0.0 | 2.9999999999999996 19 0.0 1.0 0.0 | -3.0 20 -0.0 -0.0 1.0 | 2.0 21 ************************************************** 22 1.0 0.0 0.0 | 1.0 23 -0.0 1.0 0.0 | 1.0 24 0.0 0.0 1.0 | 1.0 25 ************************************************** 26 27 Process finished with exit code 0
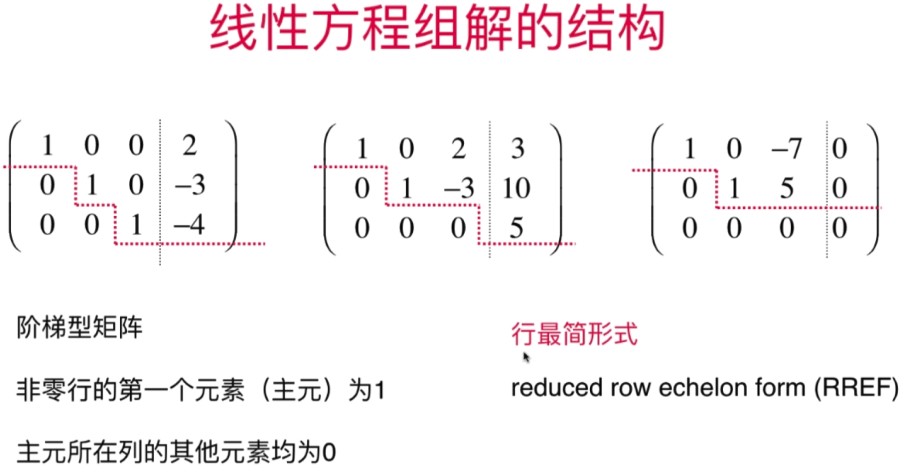
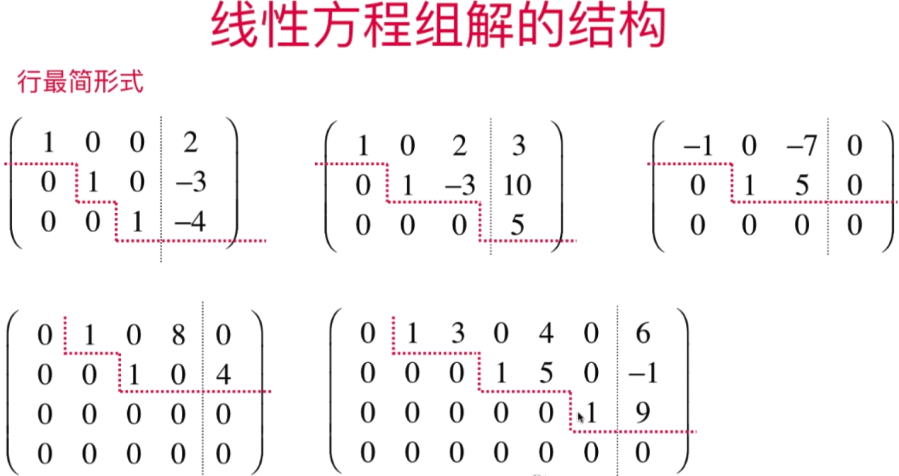
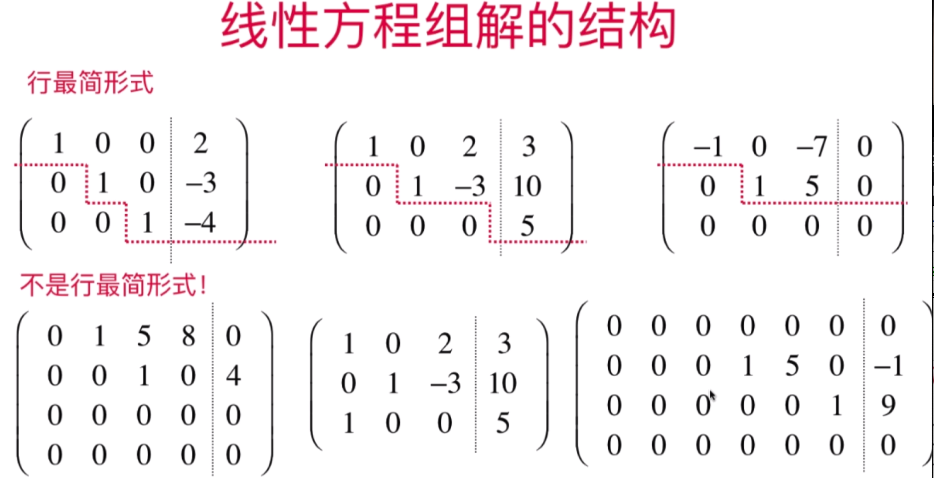
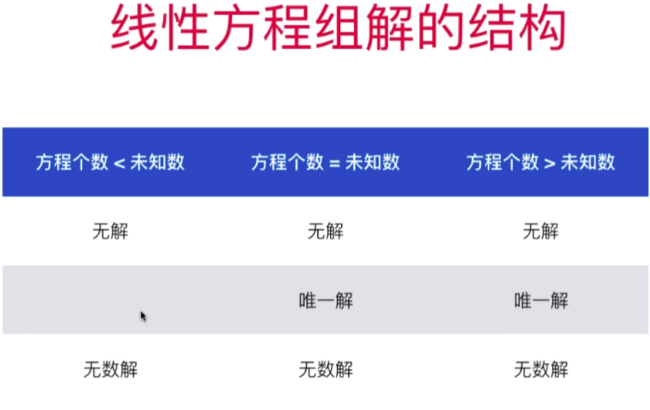
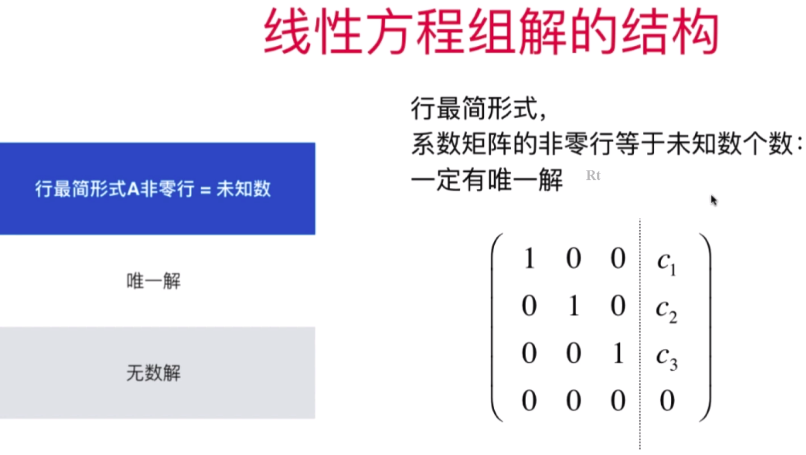
- 行最简形式和线性方程组解的结构
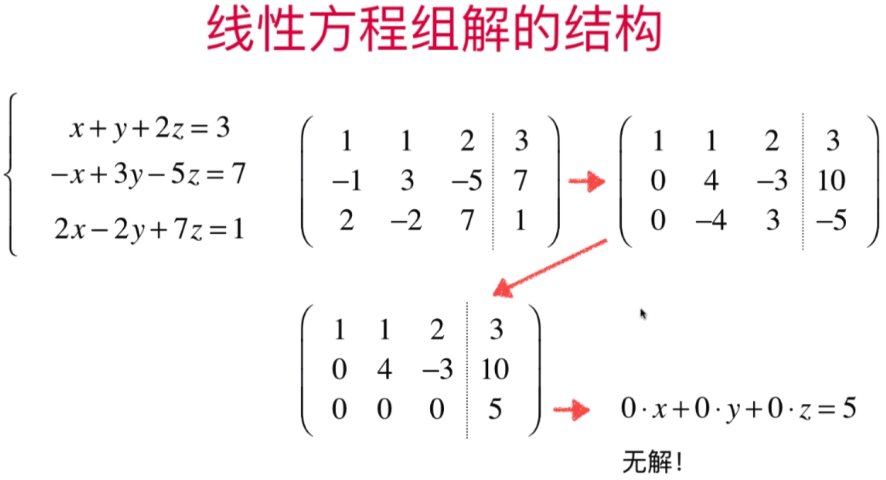
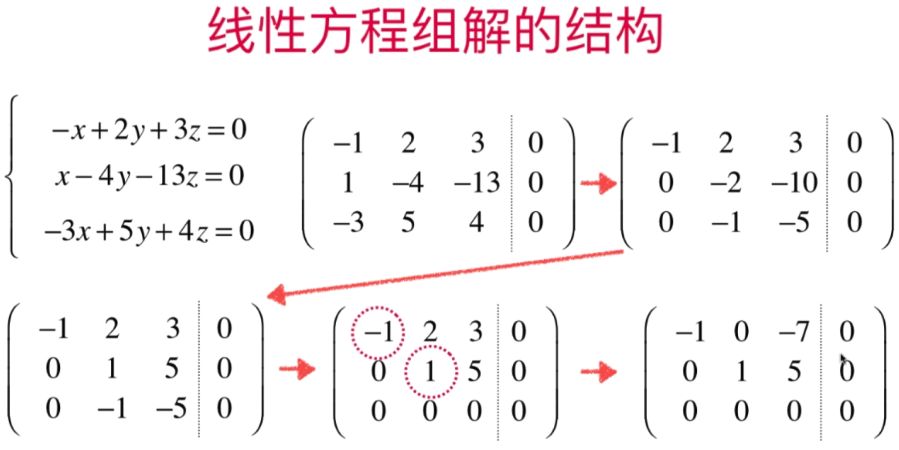
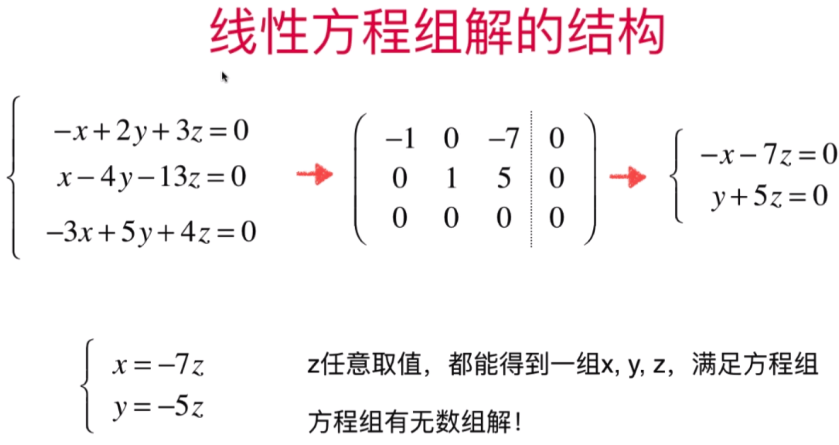
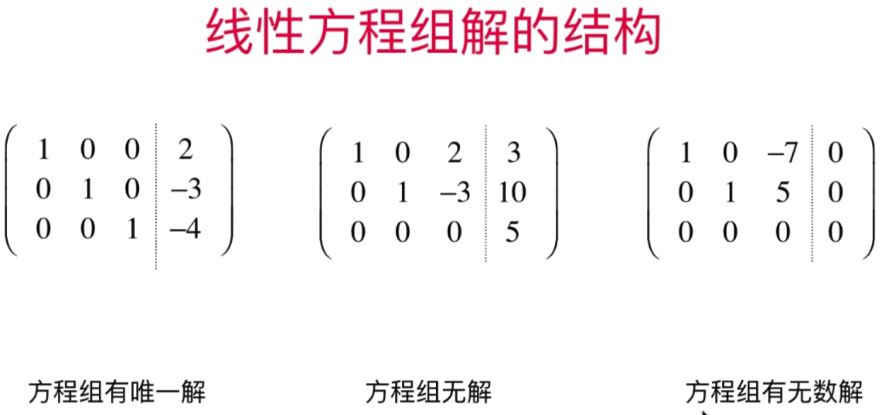
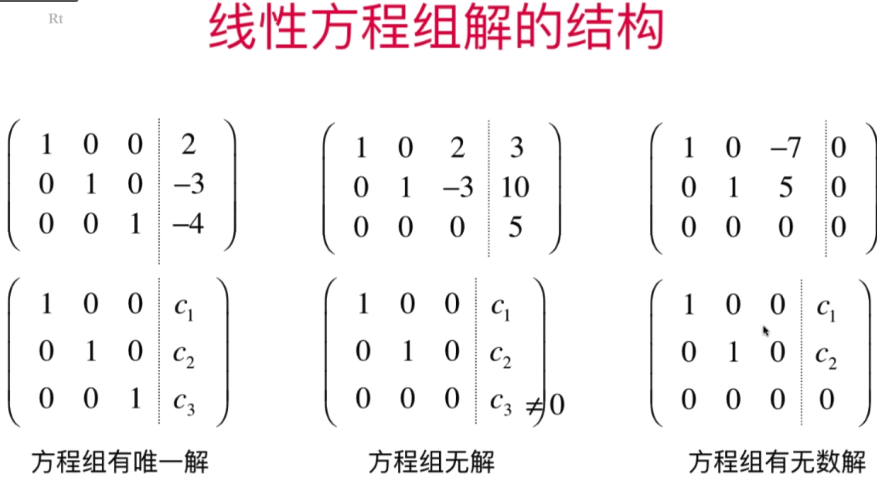
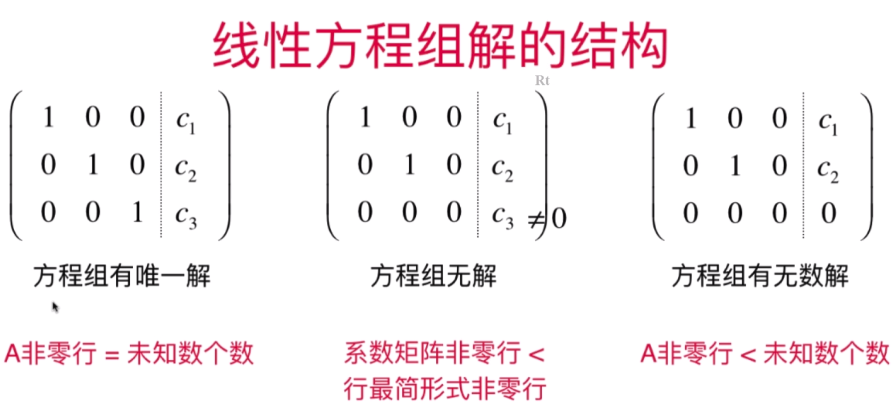

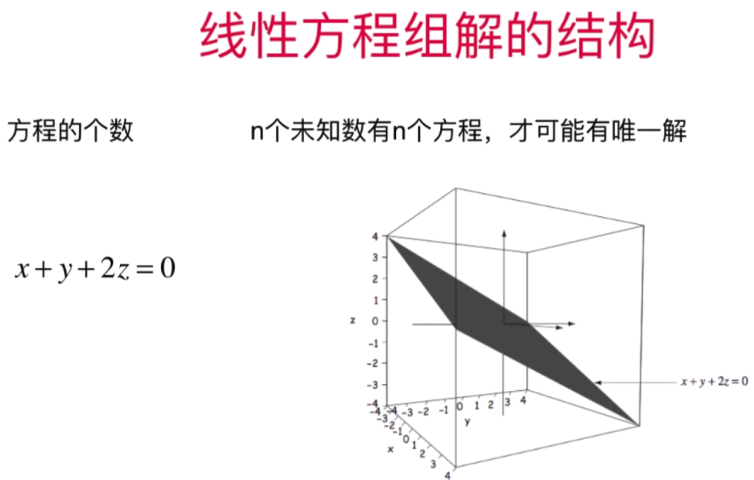
- 直观理解线性方程组解的结构



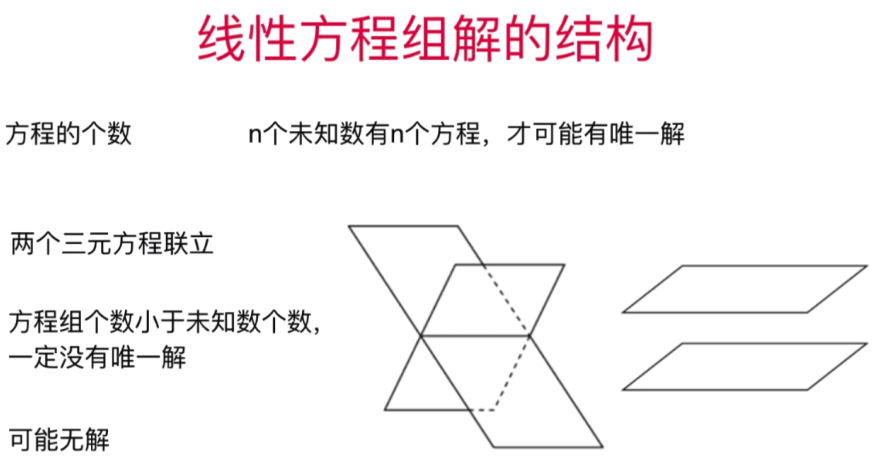
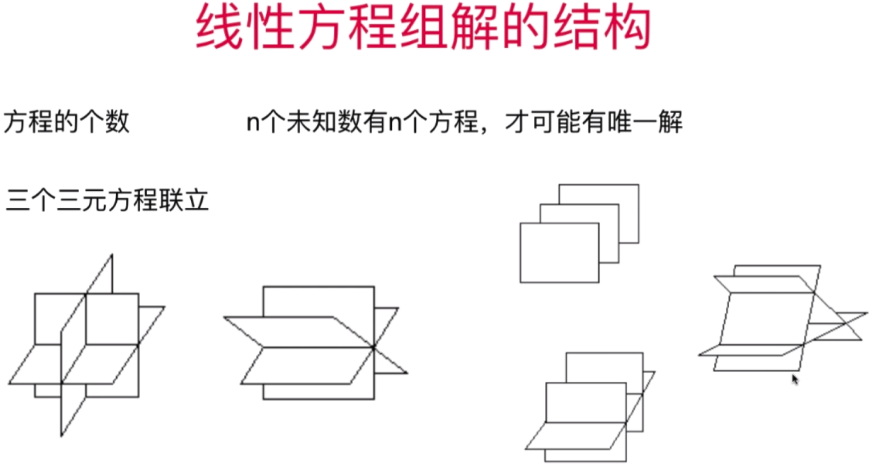

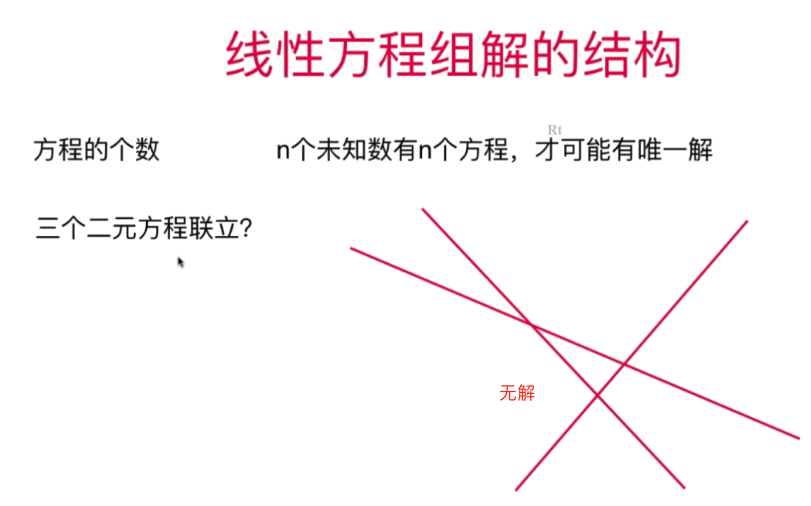

三根直线重合,此时该方程组有无数解
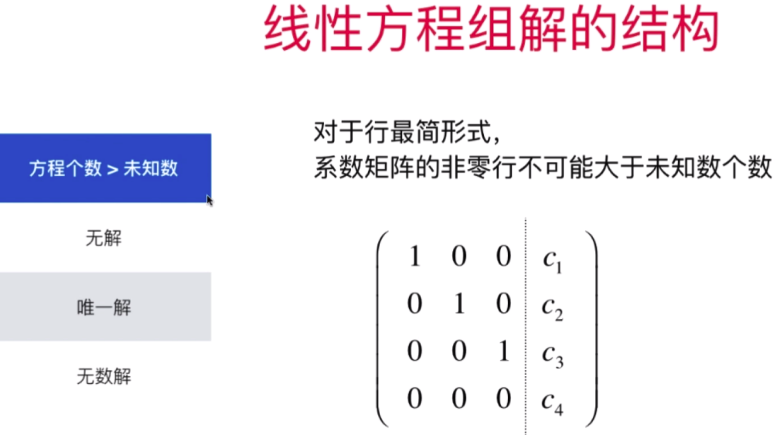



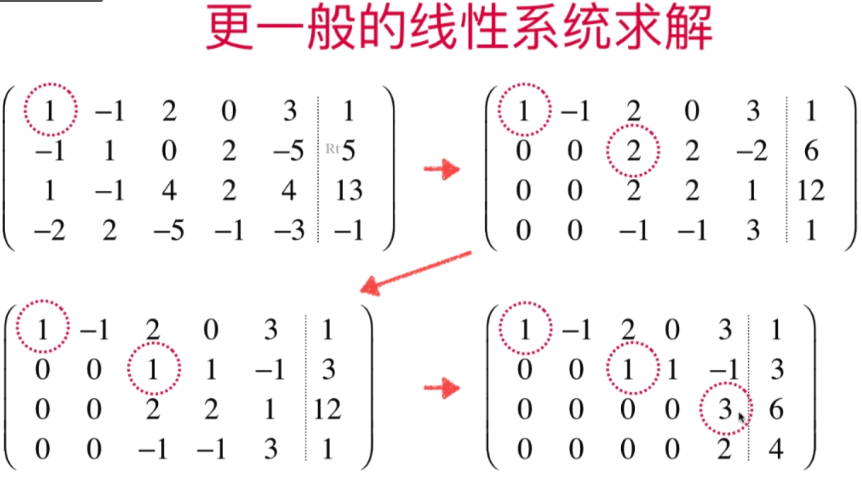
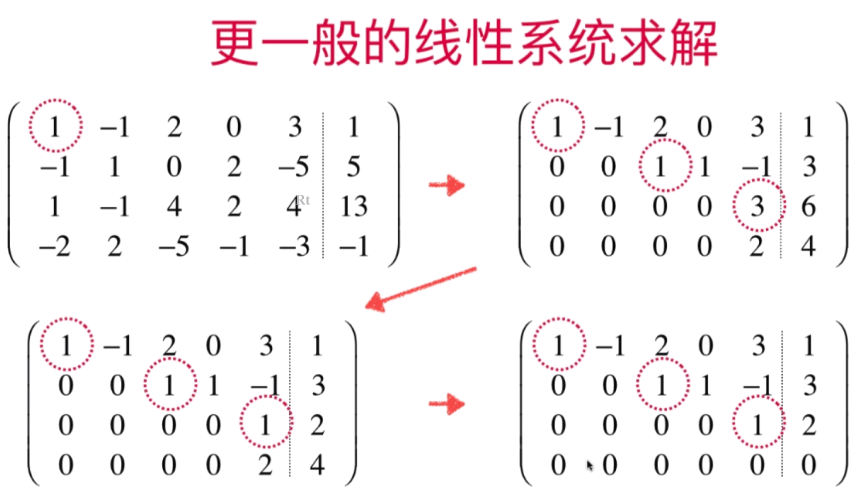
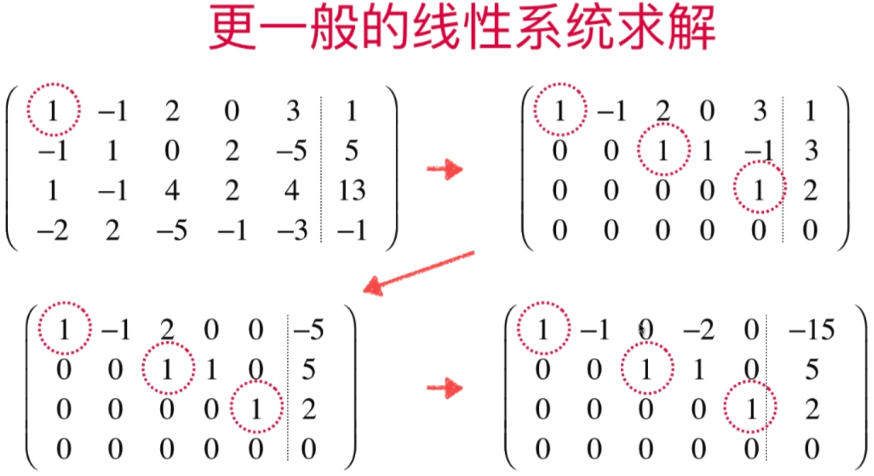
- 更一般化的高斯-约旦消元法



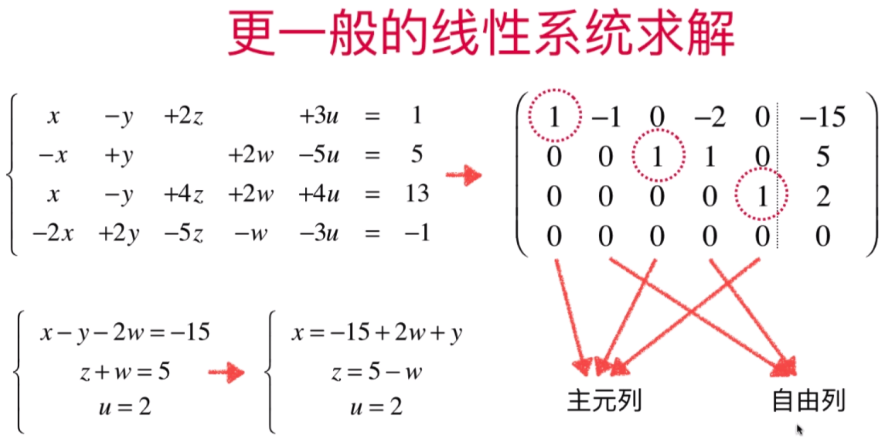
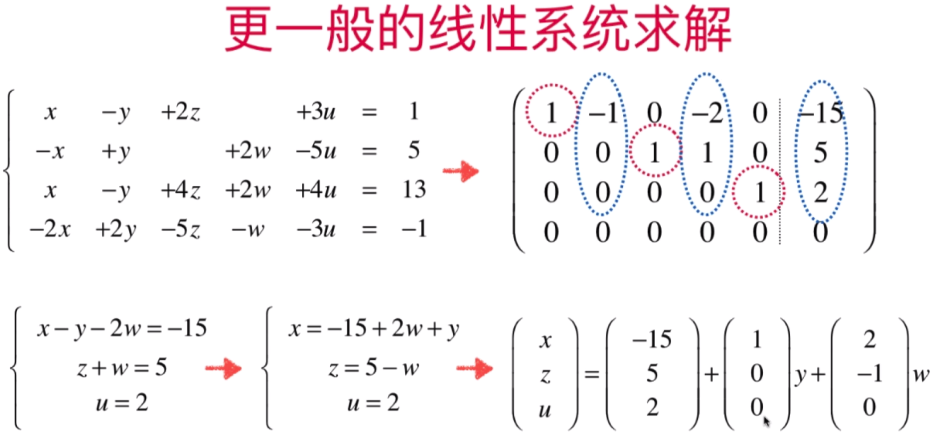

代码实现:
1. 在 文件 _global.py 中编写代码: is_zero(x)、is_equal(a,b)
1 #包内部使用的全局变量 2 3 EPSILON = 1e-8 #精度范围为 1除以10的八次方 4 5 6 #判断x的绝对值是否小于精度范围(EPSILON) 7 def is_zero(x): 8 return abs(x) < EPSILON 9 10 11 #判断a和b两个浮点值是否相等 12 def is_equal(a,b): 13 return abs(a - b) < EPSILON #判断差值的绝对值是否在精度范围内
2.在 文件 Vector.py 中编写代码:修改第24行判断形式 is_zero()
1 #向量类 2 #__values() 与 _values()区别更多体现在继承上,如果是在类的内部使用时官方建议使用_values()发方法 3 from ._global import is_zero 4 import math 5 6 7 8 class Vector: 9 10 def __init__(self,lst): 11 self._values = list(lst)#将数组赋值给向量类中(注:使用list方法将列表lst复制一份保证他的不被外界调用时修改) 12 13 #零向量类方法:参数1:为当前的类(cls) 参数2:维度(dim) 返回dim维的零向量 14 @classmethod 15 def zero(cls,dim): 16 return cls([0] * dim) 17 18 #返回向量的模(向量长度): 19 def norm(self): 20 return math.sqrt(sum(e**2 for e in self))#sqrt()方法为开平方根,sum()求和方法,e**2 e的平方 21 22 #返回向量的单位向量 23 def normalize(self): 24 if is_zero(self.norm()): #此处判断一个精度范围(该精度范围调用内部自定义全局变量文件 _global.py)(由于浮点数计算机含有误差所以无法使用 == 0 的操作) 25 raise ZeroDivisionError("Normalize error! norm is zero.") #考虑零向量时报此处异常即可 26 #方案一:return Vector(1/self.norm() * [e for e in self])#循环遍历向量中的每个元素分别除以该向量的模即为单位向量 27 #方案二:return 1/self.norm() * Vector(self._values)#当前向量除以模即为单位向量 28 return Vector(self._values) / self.norm() 29 30 #返回当前向量的底层列表 TODO:2020-08-12 17:04:00 31 def underlying_list(self): 32 return self._values[:]#此时为返回该列表的一个副本 33 34 #向量加法,返回结果向量 35 def __add__(self, another): 36 # assert判断传入的向量维度是否相等 37 assert len(self) == len(another),\ 38 "Error in adding. Length of vectors must be same." 39 return Vector([a+b for a,b in zip(self,another)])#使用zip()方法将两个向量取出来 40 41 # 向量减法 42 def __sub__(self, another): 43 #判断维度相等 44 assert len(self) == len(another), \ 45 "Error in adding. Length of vectors must be same." 46 return Vector([a - b for a, b in zip(self, another)]) 47 48 #向量点乘(向量之间相乘):返回结果标量 49 def dot(self,another): 50 #判断维度相等 51 assert len(self) == len(another), \ 52 "Error in dot product. Length of vectors must be same." 53 return sum(a * b for a,b in zip(self,another))# 方法zip()将两组向量配成对应位置的数据对 54 55 # 向量数量乘法(数乘数组),返回数量乘法的结果向量:self * k 56 def __mul__(self, k): 57 return Vector([k * e for e in self]) 58 59 # 向量数量乘法(数组乘数),返回数量乘法的结果向量:k * self 60 def __rmul__(k, self): 61 return k * self #此处直接调用的是上方的乘法函数 62 63 # 向量除法:返回数量除法的结果向量 self / k 64 def __truediv__(self, k): 65 return (1 / k) * self 66 67 #返回向量取正的结果向量 68 def __pos__(self): 69 return 1 * self 70 71 # 返回向量取负的结果向量 72 def __neg__(self): 73 return -1 * self 74 75 #返回向量迭代器(当有迭代器时,zip()方法中就不用再次传入两个向量数组,直接传入向量对象即可<zip(self._values,another._values)>) 76 def __iter__(self): 77 return self._values.__iter__() 78 79 #取向量的index个元素 80 def __getitem__(self, index): 81 return self._values[index] 82 83 #返回向量的长度(有多少个元素) 84 def __len__(self): 85 return len(self._values) 86 87 # 向量展示(系统调用) 88 def __repr__(self): 89 return "Vector({})".format(self._values) 90 91 # 向量展示(用户调用) 92 def __str__(self): 93 return "({})".format(", ".join(str(e) for e in self._values))#通过遍历 self.__values 将e转成字符串通过逗号加空格来链接放入大括号中 94 95 # u = Vector([5,2]) 96 # print(u)
3.在文件 LinearSystem.py 中编写代码:修改__init__、_max_row、_forward、_backward、gauss_jordan_elimination使之可以适应解决更多非唯一解的矩阵
1 from.Matrix import Matrix 2 from.Vector import Vector 3 from playLA._global import is_zero 4 5 #线性系统 6 class LinearSystem: 7 8 #初始化函数:参数A:增广矩阵的等号左边的系数 参数b:增广矩阵的等号右边的值(方程右边的结果) 9 def __init__(self, A, b): 10 #判断矩阵A的行数是否等于b的列数 11 assert A.row_num() == len(b),\ 12 "row number of A must be equal to the length of b" 13 self._m = A.row_num()#行数 14 self._n = A.col_num()#列数 15 16 #增广矩阵 17 self.Ab = [Vector(A.row_vector(i).underlying_list() + [b[i]]) 18 for i in range(self._m)] 19 #主元 20 self.pivots = [] 21 22 #寻找最大主源系数 23 def _max_row(self, index_i, index_j, n): 24 best, ret = self.Ab[index_i][index_j], index_i #存储第index行index列的元素值与当前index的值 25 for i in range(index_i + 1, n): #从index+1开始一直遍历到n 26 if self.Ab[i][index_j] > best: 27 best, ret = self.Ab[i][index_j], i 28 return ret 29 30 #高斯—约旦消元法-前向过程 31 def _forward(self): 32 33 i,k = 0,0 34 while i < self._m and k < self._n: 35 #看Ab[i][k]位置是否为主元 36 max_row = self._max_row(i, k, self._m)#寻找最大主源系数的行数 37 self.Ab[i], self.Ab[max_row] = self.Ab[max_row],self.Ab[i] #行交换操作 38 39 if is_zero(self.Ab[i][k]):#判断此时该值是否为0 40 k += 1 41 else: 42 #将主元归为一 43 self.Ab[i] = self.Ab[i] / self.Ab[i][k] 44 #将当前主源下的所有行对应主源列的元素全部归为0 :也就是第一次循环会将该主源下的所有对应列变为0,第二次循环会将第二次主源列下的所有对应列变为0 45 for j in range(i + 1, self._m): 46 self.Ab[j] =self.Ab[j] -self.Ab[j][k] * self.Ab[i]#该主源行下的所有行减去主源行 47 self.pivots.append(k) 48 i += 1 49 50 #高斯-约旦消元法-后向过程 51 def _backward(self): 52 n = len(self.pivots) 53 #n = self._m #行数 54 for i in range(n-1, -1, -1): #反向遍历且 从参数1的位置遍历到参数2的位置,也就是从倒数第一个位置遍历到第一个位置,参数3为步长(遍历的方向及单位) 55 k = self.pivots[i] 56 #Ab[i][k]为主源 57 for j in range(i-1, -1, -1): 58 self.Ab[j] = self.Ab[j] - self.Ab[j][k] * self.Ab[i]#该主源行上的所有行减去主源行 59 60 #高斯-约旦消元法:如果有解,返回True;如果没有解,返回False 61 def gauss_jordan_elimination(self): 62 # 高斯—约旦消元法-前向过程 63 self._forward() 64 # 高斯-约旦消元法-后向过程 65 self._backward() 66 for i in range(len(self.pivots), self._m):#此处为最后一行的非零行下一行的全零行的结果值不为零的判断 0.0 0.0 | 5.0 67 if not is_zero(self.Ab[i][-1]): 68 return False 69 return True 70 71 72 73 # 打印结果(求每个未知数的值) 74 def fancy_print(self): 75 for i in range(self._m): 76 print(" ".join(str(self.Ab[i][j]) for j in range(self._n)),end=" ") 77 print("|",self.Ab[i][-1])
4.在文件 main_linear_system.py 编写代码:
1 from playLA.Matrix import Matrix 2 from playLA.Vector import Vector 3 from playLA.LinearSystem import LinearSystem 4 5 if __name__ == "__main__": 6 7 # 高斯—约旦消元法 8 A = Matrix([[1,2,4],[3,7,2],[2,3,3]]) 9 b = Vector([7,-11,1]) 10 ls = LinearSystem(A,b) #线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 11 ls.gauss_jordan_elimination() #高斯—约旦消元 12 ls.fancy_print() #打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 13 print("-" * 50)#分隔线 14 15 # 高斯—约旦消元法 16 A2 = Matrix([[1, -3, 5], [2, -1, -3], [3, 1, 4]]) 17 b2 = Vector([-9, 19, 13]) 18 ls2 = LinearSystem(A2, b2) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 19 ls2.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 20 ls2.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 21 print("-" * 50) # 分隔线 22 23 # 高斯—约旦消元法 24 A3 = Matrix([[1, 2, -2], [2, -3, 1], [3, -1, 3]]) 25 b3 = Vector([6, -10, -16]) 26 ls3 = LinearSystem(A3, b3) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 27 ls3.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 28 ls3.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 29 print("-" * 50) # 分隔线 30 31 # 高斯—约旦消元法 32 A4 = Matrix([[3, 1, -2], [5, -3, 10], [7, 4, 16]]) 33 b4 = Vector([4, 32, 13]) 34 ls4 = LinearSystem(A4, b4) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 35 ls4.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 36 ls4.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 37 print("-" * 50) # 分隔线 38 39 # 高斯—约旦消元法 40 A5 = Matrix([[6, -3, 2], [5, 1, 12], [8, 5, 1]]) 41 b5 = Vector([31, 36, 11]) 42 ls5 = LinearSystem(A5, b5) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 43 ls5.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 44 ls5.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 45 print("-" * 50) # 分隔线 46 47 # 高斯—约旦消元法 48 A6 = Matrix([[1, 1, 1], [1, -1, -1], [2, 1, 5]]) 49 b6 = Vector([3, -1, 8]) 50 ls6 = LinearSystem(A6, b6) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 51 ls6.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 52 ls6.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 53 print("-" * 50) # 分隔线 54 55 # 高斯—约旦消元法 56 A7 = Matrix([[1, -1, 2, 0, 3], 57 [-1, 1, 0, 2, -5], 58 [1, -1, 4, 2, 4], 59 [-2, 2, -5, -1, -3]]) 60 b7 = Vector([1, 5, 13, -1]) 61 ls7 = LinearSystem(A7, b7) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 62 ls7.gauss_jordan_elimination() # 高斯—约旦消元 63 ls7.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 64 print("-" * 50) # 分隔线 65 print(ls7.pivots) #查看主源列数值 (从零开始算) 66 67 # 高斯—约旦消元法 68 A8 = Matrix([[2, 2], 69 [2, 1], 70 [1, 2]]) 71 b8 = Vector([3, 2.5, 7]) 72 ls8 = LinearSystem(A8, b8) # 线性系统赋值成一个增广矩阵 73 if not ls8.gauss_jordan_elimination(): 74 print("主元:",ls8.pivots 75 ,len(ls8.pivots)) # 查看主源列数值 (从零开始算) 76 print("No Solution!") 77 78 ls8.fancy_print() # 打印出结果(求每个未知数的值) 79 print("-" * 50) # 分隔线
5.运行文件 main_linear_system.py 结果为:
1 /Users/liuxiaoming/PycharmProjects/LinearAlgebra/venv/bin/python /Users/liuxiaoming/PycharmProjects/LinearAlgebra/main_linear_system.py 2 1.0 0.0 0.0 | -1.0 3 -0.0 1.0 0.0 | -2.0 4 -0.0 -0.0 1.0 | 3.0 5 -------------------------------------------------- 6 1.0 0.0 0.0 | 6.853333333333333 7 -0.0 1.0 0.0 | 1.506666666666665 8 0.0 0.0 1.0 | -2.266666666666666 9 -------------------------------------------------- 10 1.0 0.0 0.0 | -1.9999999999999998 11 0.0 1.0 0.0 | 1.0 12 -0.0 -0.0 1.0 | -3.0 13 -------------------------------------------------- 14 1.0 0.0 0.0 | 2.9999999999999996 15 -0.0 1.0 0.0 | -3.9999999999999996 16 0.0 0.0 1.0 | 0.4999999999999999 17 -------------------------------------------------- 18 1.0 0.0 0.0 | 3.0 19 -0.0 1.0 0.0 | -3.0 20 -0.0 -0.0 1.0 | 2.0 21 -------------------------------------------------- 22 1.0 0.0 0.0 | 1.0 23 0.0 1.0 0.0 | 1.0 24 -0.0 -0.0 1.0 | 1.0 25 -------------------------------------------------- 26 1.0 -1.0 0.0 -2.0 0.0 | -15.0 27 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 | 5.0 28 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 | 2.0 29 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 | 0.0 30 -------------------------------------------------- 31 [0, 2, 4] 32 2 5.0 33 主元: [0, 1] 2 34 No Solution! 35 1.0 0.0 | -4.0 36 0.0 1.0 | 5.5 37 0.0 0.0 | 5.0 38 -------------------------------------------------- 39 40 Process finished with exit code 0
- 齐次线性方程组

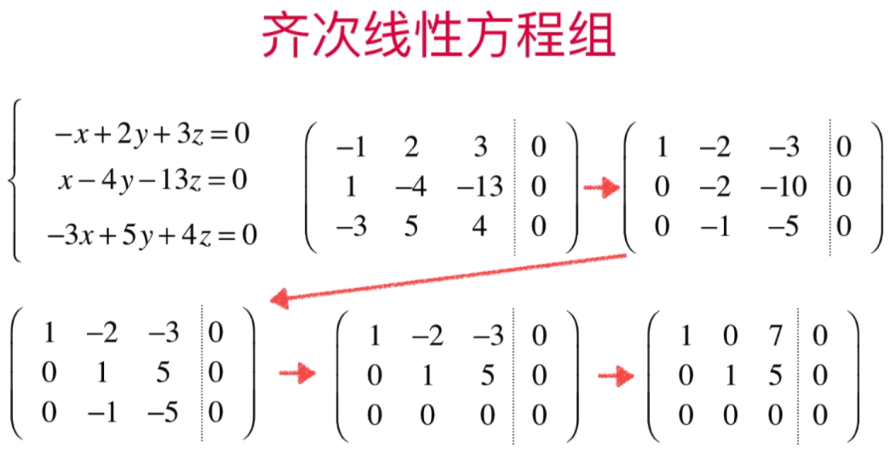

由于其次线性方程组等号右边全部为0所以不需要使用增广矩阵




