MapReduce(二)常用三大组件
mapreduce三大组件:Combiner\Sort\Partitioner
默认组件:排序,分区(不设置,系统有默认值)
一、mapreduce中的Combiner
1、什么是combiner
Combiner 是 MapReduce 程序中 Mapper 和 Reducer 之外的一种组件,它的作用是在 maptask 之后给 maptask 的结果进行局部汇总,以减轻 reducetask 的计算负载,减少网络传输
2、如何使用combiner
Combiner 和 Reducer 一样,编写一个类,然后继承 Reducer, reduce 方法中写具体的 Combiner 逻辑,然后在 job 中设置 Combiner 类: job.setCombinerClass(FlowSumCombine.class)
(如果combiner和reduce逻辑一样,就不用写combiner类了,直接在job设置信息)

3、使用combiner注意事项
(1) Combiner 和 Reducer 的区别在于运行的位置:
Combiner 是在每一个 maptask 所在的节点运行
Reducer 是接收全局所有 Mapper 的输出结果
(2) Combiner 的输出 kv 应该跟 reducer 的输入 kv 类型要对应起来
(3) Combiner 的使用要非常谨慎,因为 Combiner 在 MapReduce 过程中可能调用也可能不调 用,可能调一次也可能调多次,所以: Combiner 使用的原则是:有或没有都不能影响业务 逻辑,都不能影响最终结果(求平均值时,combiner和reduce逻辑不一样)
二、mapreduce中的序列化
1、概述
Java 的序列化是一个重量级序列化框架( Serializable),一个对象被序列化后,会附带很多额 外的信息(各种校验信息, header,继承体系等),不便于在网络中高效传输;所以, hadoop 自己开发了一套序列化机制( Writable),精简,高效
Hadoop 中的序列化框架已经对基本类型和 null 提供了序列化的实现了。分别是:
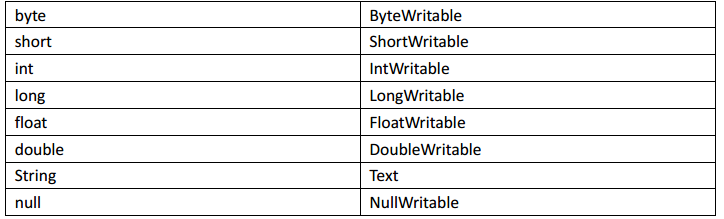
2、Java序列化
以案例说明为例:
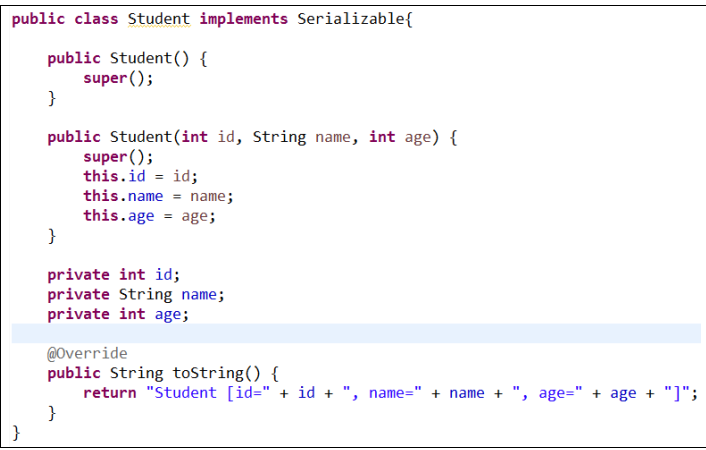
3、自定义对象实现mapreduce框架的序列化
如果需要将自定义的 bean 放在 key 中传输,则还需要实现 Comparable 接口,因为 mapreduce框中的 shuffle 过程一定会对 key 进行排序,此时,自定义的 bean 实现的接口应该是:
public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean>
以案例为例说明
下面是进行了序列化的 FlowBean 类:




案例:
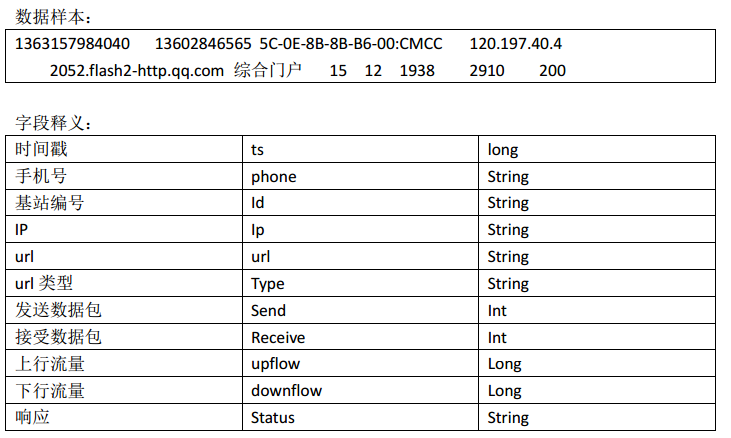

1、
package com.ghgj.mr.exerciseflow;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class Flow implements WritableComparable<Flow>{
private String phone;
private long upflow; // 上行流量
private long downflow; // 下行流量
private long sumflow; // 上行和下行流量之和
public long getUpflow() {
return upflow;
}
public void setUpflow(long upflow) {
this.upflow = upflow;
}
public long getDownflow() {
return downflow;
}
public void setDownflow(long downflow) {
this.downflow = downflow;
}
public long getSumflow() {
return sumflow;
}
public void setSumflow(long sumflow) {
this.sumflow = sumflow;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public Flow() {
}
public Flow(long upflow, long downflow, String phone) {
super();
this.upflow = upflow;
this.downflow = downflow;
this.sumflow = upflow + downflow;
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return phone +"\t" + upflow +"\t" + downflow +"\t" + sumflow;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
out.writeLong(upflow);
out.writeLong(downflow);
out.writeLong(sumflow);
out.writeUTF(phone);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.upflow = in.readLong();
this.downflow = in.readLong();
this.sumflow = in.readLong();
this.phone = in.readUTF();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Flow flow) {
if((flow.getSumflow() - this.sumflow) == 0){
return this.phone.compareTo(flow.getPhone());
}else{
return (int)(flow.getSumflow() - this.sumflow);
}
}
}
package com.ghgj.mr.exerciseflow;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
/**
* 手机号 上行流量 下行流量 总流量
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class FlowExercise1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(FlowExercise1.class);
job.setMapperClass(FlowExercise1Mapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowExercise1Reducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Flow.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, "d:/flow/input");
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:/flow/output13"));
boolean status = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(status? 0 : 1);
}
static class FlowExercise1Mapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Flow>{
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] splits = value.toString().split("\t");
String phone = splits[1];
long upflow = Long.parseLong(splits[8]);
long downflow = Long.parseLong(splits[9]);
Flow flow = new Flow(upflow, downflow);
context.write(new Text(phone), flow);
}
}
static class FlowExercise1Reducer extends Reducer<Text, Flow, Text, Flow>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Text phone, Iterable<Flow> flows, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long sumUpflow = 0; // 该phone用户的总上行流量
long sumDownflow = 0;
for(Flow f : flows){
sumUpflow += f.getUpflow();
sumDownflow += f.getDownflow();
}
Flow sumFlow = new Flow(sumUpflow, sumDownflow);
context.write(phone, sumFlow);
// String v = sumUpflow +"\t" + sumDownflow +"\t" + (sumUpflow + sumDownflow);
// context.write(phone, new Text(v));
}
}
}
2、
package com.ghgj.mr.exerciseflow;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class FlowExercise2Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(FlowExercise2Sort.class);
job.setMapperClass(FlowExercise2SortMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(FlowExercise2SortReducer.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Flow.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
// job.setCombinerClass(FlowExercise1Combiner.class);
// job.setCombinerClass(FlowExercise1Reducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Flow.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, "d:/flow/output1");
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("d:/flow/sortoutput6"));
boolean status = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.exit(status? 0 : 1);
}
static class FlowExercise2SortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Flow, Text>{
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Flow, Text>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] splits = value.toString().split("\t");
String phone = splits[0];
long upflow = Long.parseLong(splits[1]);
long downflow = Long.parseLong(splits[2]);
// long sumflow = Long.parseLong(splits[3]);
Flow flow = new Flow(upflow, downflow, phone);
context.write(flow, new Text(phone));
}
}
static class FlowExercise2SortReducer extends Reducer<Flow, Text, NullWritable, Flow>{
@Override
protected void reduce(Flow flow, Iterable<Text> phones, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for(Text t : phones){
context.write(NullWritable.get(), flow);
}
}
}
}
三、mapreduce中的sort
需求: 把上例求得的流量综合从大到小倒序排
基本思路:实现自定义的 bean 来封装流量信息,并将 bean 作为 map 输出的 key 来传输 MR 程序在处理数据的过程中会对数据排序(map 输出的 kv 对传输到 reduce 之前,会排序), 排序的依据是 map 输出的 key, 所以,我们如果要实现自己需要的排序规则,则可以考虑将
排序因素放到 key 中,让 key 实现接口: WritableComparable, 然后重写 key 的 compareTo 方法
(上面第二题)
四、mapreduce中的partitioner
需求: 根据归属地输出流量统计数据结果到不同文件,以便于在查询统计结果时可以定位到 省级范围进行
思路:MapReduce 中会将 map 输出的 kv 对,按照相同 key 分组,然后分发给不同的 reducetask
默认的分发规则为:根据 key 的 hashcode%reducetask 数来分发, 所以:如果要按照我们自 己的需求进行分组,则需要改写数据分发(分组)组件 Partitioner
自定义一个 CustomPartitioner 继承抽象类: Partitioner
然后在 job 对象中,设置自定义 partitioner: job.setPartitionerClass(ProvincePartitioner.class)
(上面第三题)








