|这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE/ |
| ---- | ---- | ---- |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE/homework/11406 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 学习算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度和对数器 |
| 学号 | 20189600 |
- 寻找数组中第K大数 算法:选择排序
解题思路:定义一个数组,根据输入的数字在数组中取出区间内元素到另外一个数组,然后对另外一个数组进行选择排序(从小到大),根据顺序定位第K大的元素,放入新数组依次输出。
对数器:简单实现了对数器,math函数的随机数生成随机的数组长度和元素,然后通过比较调用系统Arrays.sort函数排序的数组和自定义排序函数排序的数组长度和元素上是否相等来判断算法是否正确。(不知道是否符合对数器要求)
代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class sort {
//定义排序方法,选择排序,从小到大排列
public static void resort(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
index = arr[j] < arr[index] ? j : index;
}
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[index];
arr[index] = temp;
}
}
//随机数组发生器 长度 和 大小
public static int[] generateRandomArray(int maxSize, int maxValue) {
int[] arr = new int[(int) ((maxSize + 1) * Math.random())];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = (int) ((maxValue + 1) * Math.random()) - (int) (maxValue * Math.random());
}
return arr;
}
//复制数组数据
public static int[] copyArray(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null) {
return null;
}
int[] res = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
res[i] = arr[i];
}
return res;
}
// 判断两个数组是否相等
public static boolean isEqual(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
if ((arr1 == null && arr2 != null) || (arr1 != null && arr2 == null)) { // 一个空 一个不空 返回flase
return false;
}
if (arr1 == null && arr2 == null) { //都为空返回ture 两个数组一样
return true;
}
if (arr1.length != arr2.length) { //长度不相等 返回flase
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) { //数组中的每一个元素 有不相等的 返回flase
if (arr1[i] != arr2[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true; //返回true 两个数组相等
}
//创建数组函数,输入数组长度,创建数组,并输入数据然后返回数组
public static int[] arry()
{
System.out.println("请输入数组长度");
Scanner a =new Scanner(System.in);
int n=a.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
System.out.println("请输入数组数字");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
arr[i]=a.nextInt();
return arr;
}
//输出第K大的数方法
private static int k_sort(int[] num , int start ,int end ,int k){
int len = end-start+1;//区间数组长度
int[] temp = new int[len];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = start - 1; i < end; i++) {
temp[cnt++] = num[i];
}
//选择方法排序
resort(temp);
//返回区间内第K大的值
return temp[temp.length-k];
}
public static void project()
{
int[] f =arry();
System.out.println("请输入要查找的个数");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入查找区间和位数");
while(m > 0){
int l = sc.nextInt();
int r = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(k_sort(f,l,r,k));
m--;
}
}
public static void test(int testTime,int maxSize,int maxValue )
{
boolean succeed = true;
for (int i = 1; i <=testTime; i++) {
int[] arr1 = generateRandomArray(maxSize, maxValue); //生成一个随机数组发生器给 arr1
int[] arr2 = copyArray(arr1);// 把 arr1 的元素拷贝给arr2
resort(arr1); //要测试的方法
Arrays.sort(arr2); //绝对正确的方法
if (isEqual(arr1, arr2)) //判断是否相等
if (i%10000==0)
System.out.println("第"+i/10000+"万次测试成功");
else;
else {
succeed = false;
break;
}
}
System.out.println(succeed ? "全部结果测试正确!" : "算法有误!");
}
//主程序
public static void main(String[] args) {
project();
test(50000,100,100);
}
}

- 二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
解题思路:
前序遍历:根结点 ---> 左子树 ---> 右子树
中序遍历:左子树---> 根结点 ---> 右子树
后序遍历:左子树 ---> 右子树 ---> 根结点
深度遍历:前序、中序以及后序可用采用递归的方法去实现
广度遍历 层次遍历:先在队列中增加根结点。之后对于随意一个结点来说。在其出队列的时候,进行访问。同一时候假设左孩子和右孩子有不为空的,入队列。
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 二叉树的结构
A
/ \
T 6
/
D
/ \
N 5
/ \ /
B 4 1
\
9
*/
Node root = into();
// 先序遍历
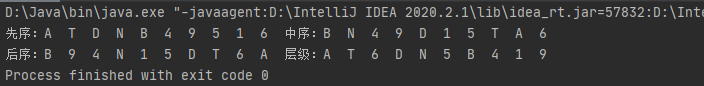
System.out.print("先序:");
A(root);
// 中序遍历
System.out.print("中序:");
B(root);
System.out.println();
// 后续遍历
System.out.print("后序:");
C(root);
// 层级遍历
System.out.print("层级:");
D(root);
}
private static void A(Node root) {
// TODO 先序遍历
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
//递归调用
A(root.l);
A(root.r);
}
}
private static void B(Node root) {
// TODO 中序遍历
if (root != null) {
B(root.l);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
B(root.r);
}
}
private static void C(Node root) {
// TODO 后续遍历
if (root != null) {
C(root.l);
C(root.r);
System.out.print(root.data+" ");
}
}
private static void D(Node root) {
// TODO 层级遍历
if (root == null) {
return;
}
//创建队列
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//增加根节点
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
System.out.print(node.data+" ");
//如果左孩子不为空则入队列
if (node.l != null) {
queue.offer(node.l);
}
//如果右孩子不为空则入队列
if (node.r != null) {
queue.offer(node.r);
}
}
}
// 构建一颗树,返回根节点
private static Node into(){
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
root.l = node1;
node1.l = node2;
node2.l = node3;
node2.r = node6;
node3.r = node7;
node7.r = node8;
node6.l = node9;
node3.l = node4;
root.r = node5;
return root;
}
// 节点
static class Node{
// 数据
Object data;
// 左孩子
Node l;
// 右孩子
Node r;
public Node(){}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.l = null;
this.r = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) {
this.data = data;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号