Spring实例化Bean三种方法:构造器、静态工厂、实例工厂
Spring中Bean相当于java中的类,可以通过xml文件对bean进行配置和管理。
一、Bean的实例化:
构造器实例化、静态工厂实例化、实例工厂方式实例化。
目录:
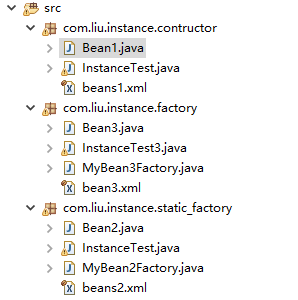
构造器实例化:
xml配置文件:

id唯一,calss指定Bean具体实现类,必须是完整的类名,可以在Bean1.java文件中右击“public class Bean1”中的Bean1,选中Copy Qualifiel Name得到。注意这里用"."分隔。
测试函数:
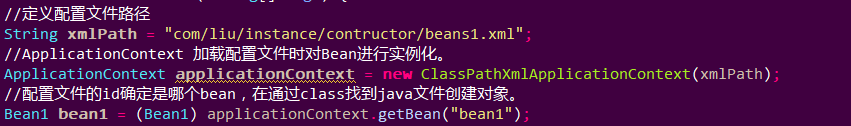
测试函数中首先定义xml配置文件的路径,可以在目录视图中右键选中Copy Qualifiel Name得到,注意这里从com开始,因为是路径所以用/隔开。
然后加载配置文件对Bean进行实例化,在通过getBean函数获得指定id的实例对象,注意类型转换。
完整代码:

package com.liu.instance.contructor; public class Bean1 { }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="bean1" class="com.liu.instance.contructor.Bean1"></bean> </beans>

package com.liu.instance.contructor; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class InstanceTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //定义配置文件路径 String xmlPath = "com/liu/instance/contructor/beans1.xml"; //ApplicationContext 加载配置文件时对Bean进行实例化。 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); //配置文件的id确定是哪个bean,在通过class找到java文件创建对象。 Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) applicationContext.getBean("bean1"); System.out.println(bean1); } }
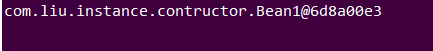
运行截图:
静态工厂实例化:
xml配置文件:
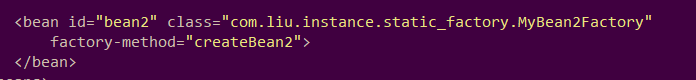
id唯一,class为工厂方法类,factory-method值为方法名,确定使用了工厂中的哪个方法。
静态工厂类:
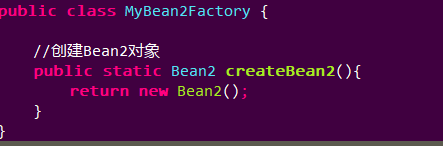
静态方法返回一个Bean2对象。

package com.liu.instance.static_factory; /* * lsq * 2019-9-10 * Spring静态工厂实例化被实例化的类Bean2 */ public class Bean2 { }

package com.liu.instance.static_factory; /* * lsq * 2019-9-10 * Spring静态工厂实例化 */ public class MyBean2Factory { //创建Bean2对象 public static Bean2 createBean2(){ return new Bean2(); } }

package com.liu.instance.static_factory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /* * lsq * 2019-9-10 * Spring静态工厂实例化对象测试类 */ public class InstanceTest { public static void main(String[] agrs){ //定义配置文件路径 String xmlPath = "com/liu/instance/static_factory/beans2.xml"; //实例化对象 ApplicationContext ApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); //调用函数 //getBean函数传入id属性值获取对象 System.out.println(ApplicationContext.getBean("bean2")); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="bean2" class="com.liu.instance.static_factory.MyBean2Factory" factory-method="createBean2"> </bean> </beans>
运行截图:

实例工厂实例化:
xml配置文件:
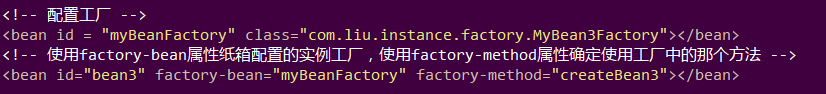
两个bean第一个为静态工厂,class为静态工厂类。第二个为bean3,factory-method属性配置实例工厂,factory-method确定使用工厂中哪个方法。
工厂类:
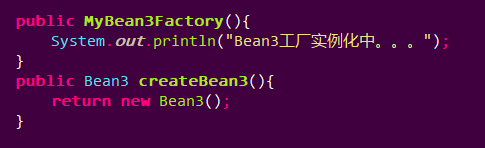
返回一个Bean3对象。
完整代码:

package com.liu.instance.factory; /* * lsq * 2019-9-10 * Spring工厂实例化对象 */ public class Bean3 { }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> <bean id="bean2" class="com.liu.instance.static_factory.MyBean2Factory" factory-method="createBean2"> </bean> </beans>

package com.liu.instance.factory; /* * lsq * 2019-9-10 * Spring工厂实例化对象 */ public class MyBean3Factory { public MyBean3Factory(){ System.out.println("Bean3工厂实例化中。。。"); } public Bean3 createBean3(){ return new Bean3(); } }

package com.liu.instance.factory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /* * lsq * 2019-9-10 * Spring工厂实例化测试类 */ public class InstanceTest3 { public static void main(String[]args){ //指定配置文件路径 String xmlPath= "com/liu/instance/factory/bean3.xml"; //ApplicationContext加载配置文件时,对Bean进行实例化 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("bean3")); } }
运行截图:
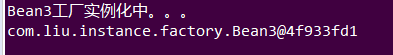
三种方法区别:





