Robot Framework 使用总结
最近项目上使用了RF快速实现了一些验收测试的自动化case,感觉不错,很好用,下面就记录一下使用RF实现自动化的过程。
什么是RF?
RF是一种测试框架,帮助测试人员在其框架下快速实现验收测试的自动化。提供很多的扩展库供你使用,在没有任何一种语言编程基础的情况下也能实现一些自动化测试用例。
说白了,任何一种框架的作用就是帮你完成一些基础的工作,使你更加关注于要测试的业务逻辑,而不是关心技术细节,这些技术细节包括用例如何运行、如何组织、日志怎么记录,怎么展现,如何与CI集成等等。
使用RF框架与Jenkins CI工具结合,可以很容易的实现测试的远程部署、运行与结果展现。比起重写造轮子,自己写一套系统,这种方式还是快得多,最适合刚刚起步的项目。
RF能做什么?
RF能做什么取决于使用什么样的扩展框架,RF提供的默认内置库与外部扩展库,当然也可以自己写扩展库来定制功能。基本提供的库已经可以满足一般的测试需求了,包括对手机端、网页端的自动化测试,还有API接口的测试。
编写RF文件
RF文件通常以robot为后缀名,并且提供了很多的编辑工具,方便的进行robot文件的编辑。我使用的是pycharm的RF插件进行编辑,因为需要使用python写大量的扩展库,所以在pycharm里面统一进行robot与py文件的编辑,还是很方便的。或者使用官方的RIDE也是很好的选择,纯图形化界面,方便团队没有开发经验的人参与其中。
RF文件的结构
先看一个RF文件示例: 
如上所示,一个RF文件通常包括三个节点:
-
Settings节点:
1. 设置此test suite的setup与tearndown操作
2. 此test suite 中每个test case的setup与tearndown操作
3. 指定测试模板test template
4. 指定此test suite引用的资源文件的位置
5. 使用Library关键字引用RF标准库,或者自定义库: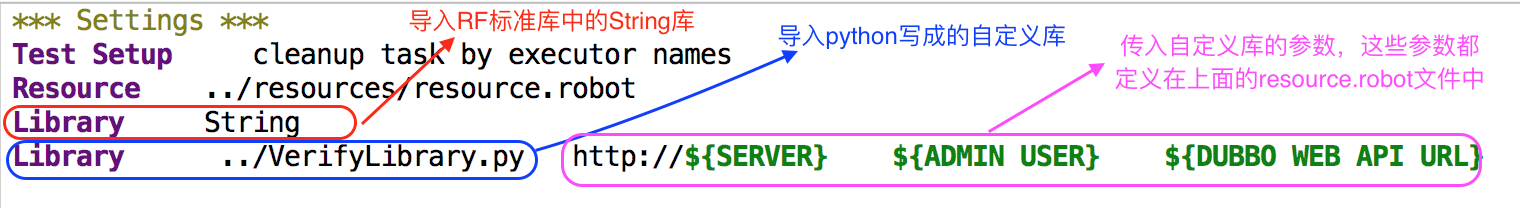
-
Test Cases节点:
1. 可以定义一个普通的测试用例
2. 也可以调用模板,并给模板传入它所需要的参数
3. 测试用例里面所调用的关键词可能来自下面三个地方:
* 当前test suite文件的keywords节点中定义的keyword
* Setttings节点指定的资源文件中所定义的keyword
* 内建的BuiltIn库中定义的keyword -
Keywords节点:
1. keyword可以理解为一个公用的方法,供test case使用
2. keyword可以传入参数,返回结果
3. RF也提供很多逻辑判断IF,循环FOR等关键词
Resource资源文件的结构
其实resource文件与普通robot文件没多大区别,只不过它是被导入的库文件,通常用来定义一些公用的变量和keywords:
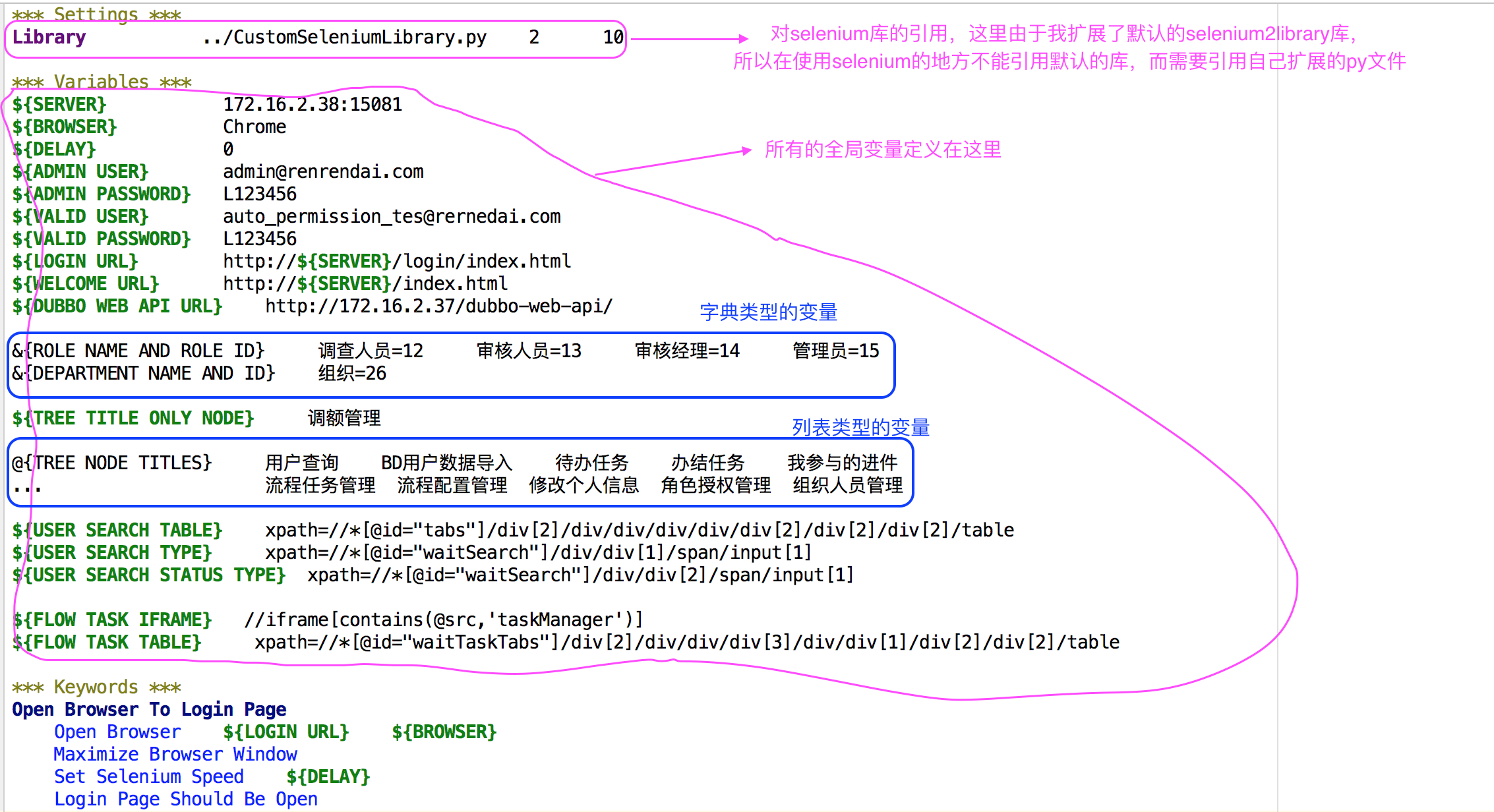
编写自己的Library文件
RF运行使用很多语言编写自己的Library文件,这里选择python编写,首先看一下对已存在的库文件的扩展
对selenium2library库文件的扩展:
1 # 导入Selenium2Library模块 2 from Selenium2Library import Selenium2Library模块 3 from selenium.common.exceptions import StaleElementReferenceException 4 import time 5 6 7 def _get_table_field_value(element, field): 8 return element.find_element_by_xpath("./td[@field='" + field + "']").text.strip() 9 10 # 继承Selenium2Library 11 class CustomSeleniumLibrary(Selenium2Library): 12 def get_table_row_count(self, table_locator): 13 attempts = 0 14 while True: 15 try: 16 table = self._table_element_finder.find(self._current_browser(), table_locator) 17 return len(table.find_elements_by_xpath("./tbody/tr")) 18 except StaleElementReferenceException: 19 time.sleep(1) 20 if attempts >= 1: 21 raise AssertionError("Cell in table %s could not be found." % table_locator) 22 else: 23 pass 24 attempts += 1 25 26 def get_user_search_results(self, table_locator, row_index): 27 table = self._table_element_finder.find(self._current_browser(), table_locator) 28 ret = [] 29 if table is not None: 30 rows = table.find_elements_by_xpath("./tbody/tr") 31 if len(rows) <= 0: 32 return None 33 row_index = int(row_index) 34 if len(rows)-1 < row_index: 35 raise AssertionError("The row index '%s' is large than row length '%s'." % (row_index, len(rows))) 36 for row in rows: 37 dic = { 38 'userId': _get_table_field_value(row, 'userId'), 39 'nickName': _get_table_field_value(row, 'nickName'), 40 'realName': _get_table_field_value(row, 'realName'), 41 'mobile': _get_table_field_value(row, 'mobile'), 42 'idNo': _get_table_field_value(row, 'idNo'), 43 'userType': _get_table_field_value(row, 'userType'), 44 'verifyUserStatus': _get_table_field_value(row, 'verifyUserStatus'), 45 'operator': _get_table_field_value(row, 'operater'), 46 'operateTime': _get_table_field_value(row, 'operateTime'), 47 } 48 ret.append(dic) 49 return ret[row_index] 50 else: 51 return None 52 53 ...
创建全新的库文件:
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 3 from libs.DB_utils.utils import * 4 from libs.request_utils import utils 5 from libs.request_utils import flow_task_manage 6 from libs.global_enum import * 7 from libs.model import user_search_result 8 from robot.libraries.BuiltIn import BuiltIn 9 import time 10 11 12 class VerifyLibrary(object): 13 14 def __init__(self, base_URL, username, dubbo_web_base_URL=None): 15 self.base_URL = base_URL 16 self.username = username 17 self.request_utils = utils.RequestUtil(base_URL, username) 18 self.flow_task_request_utils = flow_task_manage.FlowTaskManage(base_URL, username) 19 self.built_in = BuiltIn() 20 if dubbo_web_base_URL is not None: 21 self.dubbo_web_request_utils = utils.RequestUtil(dubbo_web_base_URL) 22 23 def update_verify_user_role(self, email, dept_id, role_id, amount_limit=5000): 24 real_name = get_verify_user_name_by_email(email) 25 verify_user_id = get_verify_user_id_by_email(email) 26 self.request_utils.login() 27 response = self.request_utils.update_verify_user(real_name, verify_user_id, amount_limit, dept_id, role_id) 28 return response.json()
注意VerifyLibrary的构造函数,需要最少传入两个参数,这是在robot文件引用此库文件的时候传入的: 
RF框架与Jenkins CI集成
使用Jenkins来运行RF写的test case很简单,首先需要在Jenkins上安装RF扩展插件:

然后,使用pybot命令行去运行写好的RF测试用例:

最后执行完测试后,可以在jenkins上很好的解析出测试结果的走势与具体的每个build的测试结果:





