Oracle ——数据库 SQL 分页性能分析
本文内容
- 创建测试表 test 及其数据
- 创建 test 表索引
- 创建 test 表的统计数据
- 测试数据分布情况
- 演示三种数据库分页的性能
- 总结
- 参考资料
本文内容并不新鲜,很早就有人写过,但那毕竟是别人的。还是自己动手看看较好。本文使用 Oracle 11g Release 1 (11.1)。
另外,执行计划和统计信息的具体含义,参看本文最后的参考资料链接。
创建测试表 test 及其数据
利用 Oracle 自己的视图,伪造一个测试表,并插入测试数据。即便是新装的 Oracle,也会有将近 56000 行数据。测试表有四个字段,分别表示类别 ID,产品名称,价格和供应商。
SQL> drop table test
2 /
Table dropped
SQL> create table test
2 as select mod(object_id,4)*10 category_id,
3 object_name product_name,
4 object_id price,
5 rpad('a',5,'b') supplier
6 from all_objects order by 2,1
7 /
Table created
SQL>
创建 test 表索引
演示数据库分页时,我们使用了 category_id 为过滤条件,并用 product_name 字段排序,所以为它们建立组合索引。
SQL> create index test_cid_pname on test(category_id,product_name)
2 /
Index created
SQL>
创建 test 表的统计数据
利用 ANALYZE 语句统计 test 表,和其所有索引以及索引列。
SQL> analyze table test compute statistics
2 for table
3 for all indexes
4 for all indexed columns
5 /
Table analyzed
SQL> select t.table_name,
2 t.num_rows,
3 t.blocks,
4 t.empty_blocks,
5 t.avg_space,
6 t.avg_row_len,
7 t.sample_size,
8 t.last_analyzed
9 from user_tables t
10 where T.table_name = 'TEST'
11 /
TABLE_NAME NUM_ROWS BLOCKS EMPTY_BLOCKS AVG_SPACE AVG_ROW_LEN SAMPLE_SIZE LAST_ANALYZED
---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ----------- ----------- --------------------
TEST 65058 821 75 863 86 65058 2012-9-10 11:02:45
SQL>
测试数据分布情况
在演示数据库分页前,先大概了解数据情况。已上面方式创建的测试表和其数据,即便是新安装的 Oracle 数据库,也又差不多 6 万条数据。
分析后,可以看出 test 表,有 65058 行,使用了 821 个数据块,平均行长度为 86。
执行下面 SQL 语句,查看一下各个类别的数据都有多少条。类别是之后分页的其中一个条件。
SQL> select t.category_id, count(t.category_id) as categorycount
2 from test t
3 group by t.category_id
4 order by t.category_id asc
5 /
CATEGORY_ID CATEGORYCOUNT
----------- -------------
0 16266
10 16290
20 16283
30 16219
SQL>
测试表的数据,有四个类别,每个类别都有 1.6 万条数据。
演示三种数据库分页的性能
下面所有 SQL 语句中的 category_id 为类别 ID;beginrno 为开始行号;endrno 为结束行号。它们都是需要输入的回话变量。
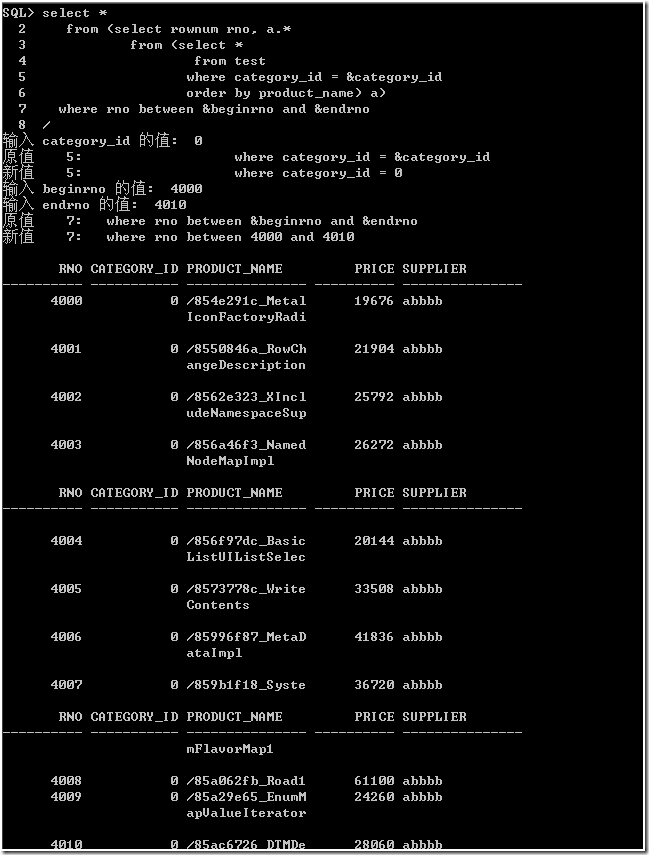
作法 1
1, 先选择指定类别的所有行,并排序。
2, 再在此内部视图选择开始行号 beginrno 和结束行号 endrno 之间的所有数据。
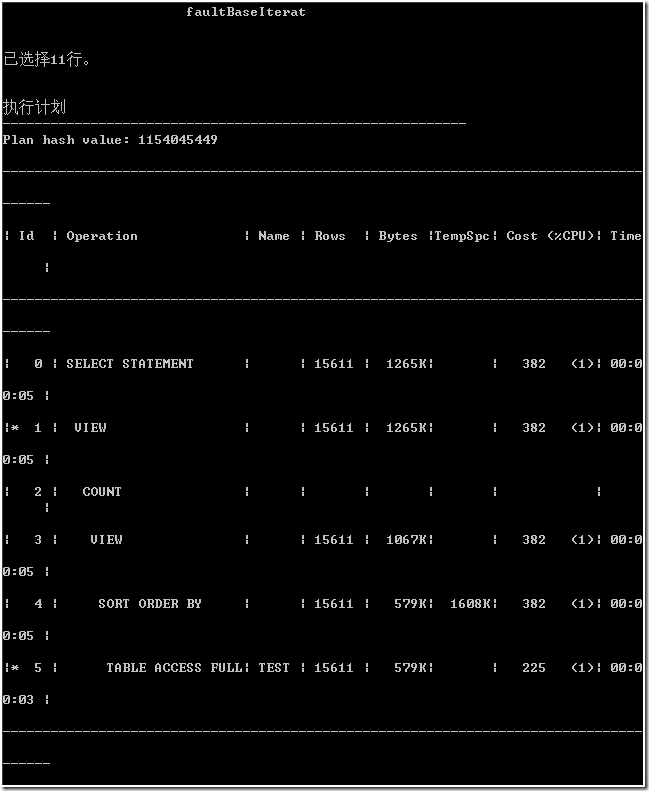
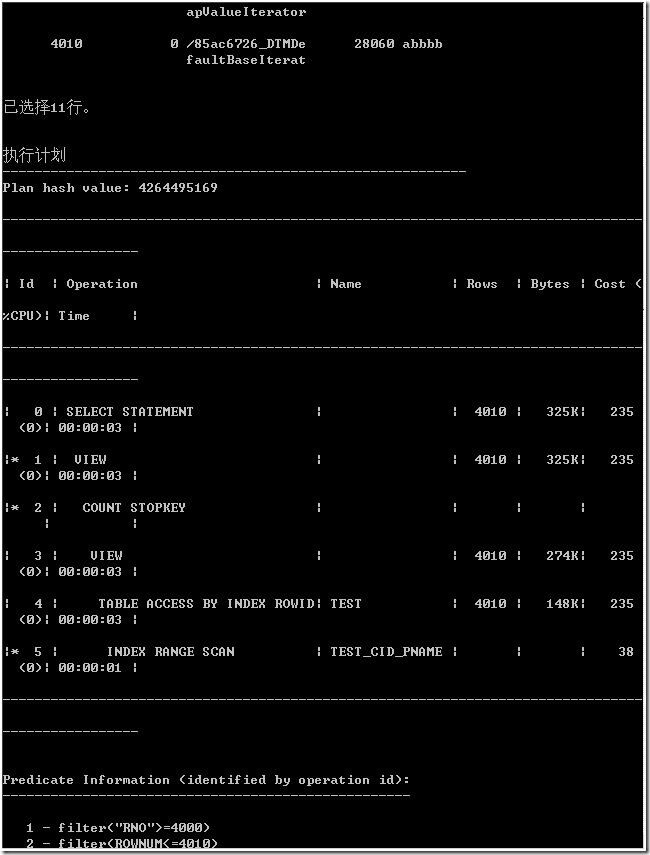
执行计划是“倒”着看的。
从执行计划上看,从始至终数据库都处理类别为 0 所有的数据行(16266 行)。在过滤类别时,进行了全表扫描,文中开始创建索引没有使用。最后为了获得指定开始和结束行号的数据。
这显然很多余。因为,既然是分页,我们只关心开始行号和结束行号之间的数据,至少,刚开始,只关心结束行号之前的数据。另外,cost 列值也不小,为了排序还使用了 1608K 的临时表空间。这要是在互联网上还了得。
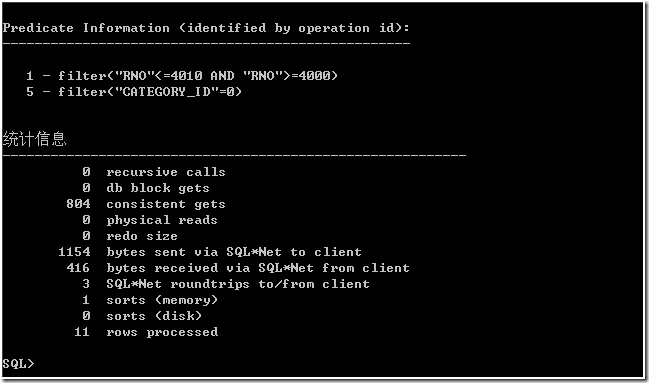
统计信息也反映出,consistent gets 值很大,接下来的 sorts(memory) 值还为 1。该 SQL 语句造成 Oracle 在内存中排序 16266 行数据。
其中,category_id 为 类别ID;beginrno 为开始行号;endrno 为结束行号。
作法 2
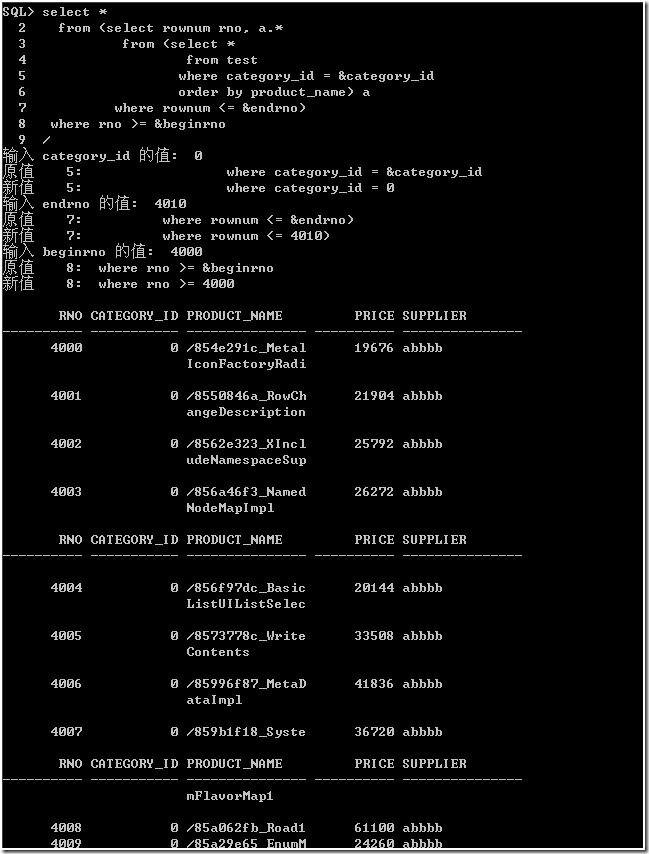
既然没必要全部获,就可以先获得 endrno 之前的数据,再利用 beginrno 截取。
1, 先选择指定类别的行,并排序。
2, 再次内部视图选择 endrno 之前的所有行。
3, 最后利用 beginrno 选择,从而得到 beginrno 和 endrno 之间的行。
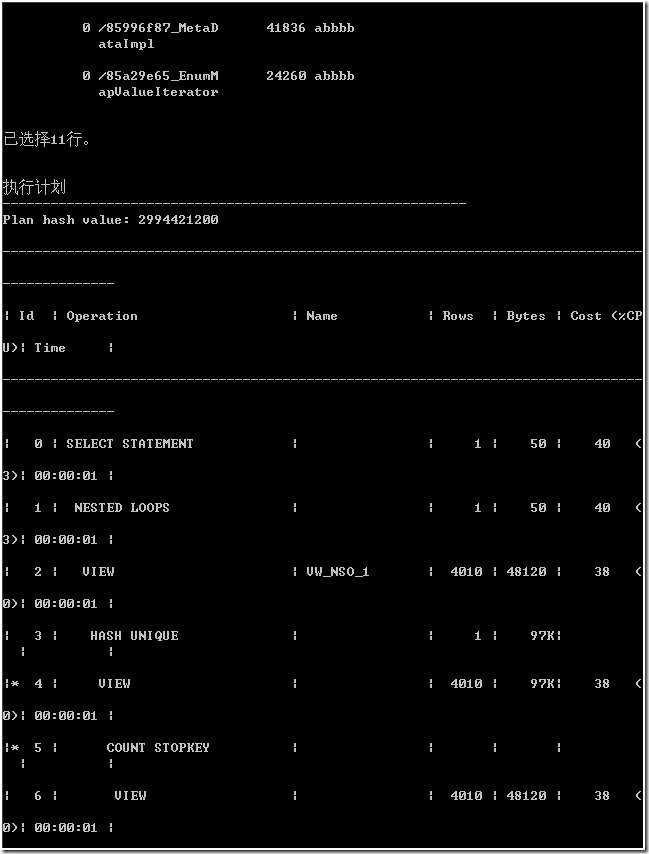
在执行计划中,从 ROWS、COST、TIME 看上去比作法 1 好多了,数值明显减少。其中,STOPKEY 起了重要作用。它为了 TOP n 操作做了优化,即本例 SQL 的内部语句:
select rownum rno, a.*
from (select *
from test
where category_id = &category_id
order by product_name) a
where rownum <= &endrno
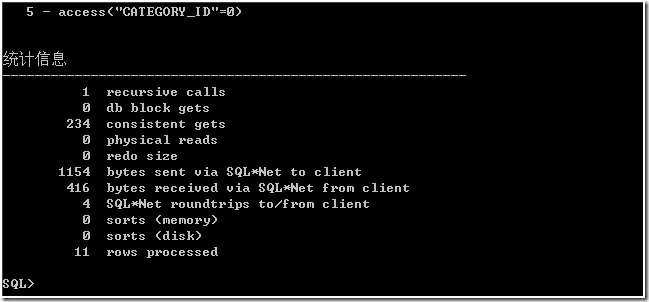
从统计信息看,consistent gets 值也减少了。sorts(memory) 值是 0。
作法 3
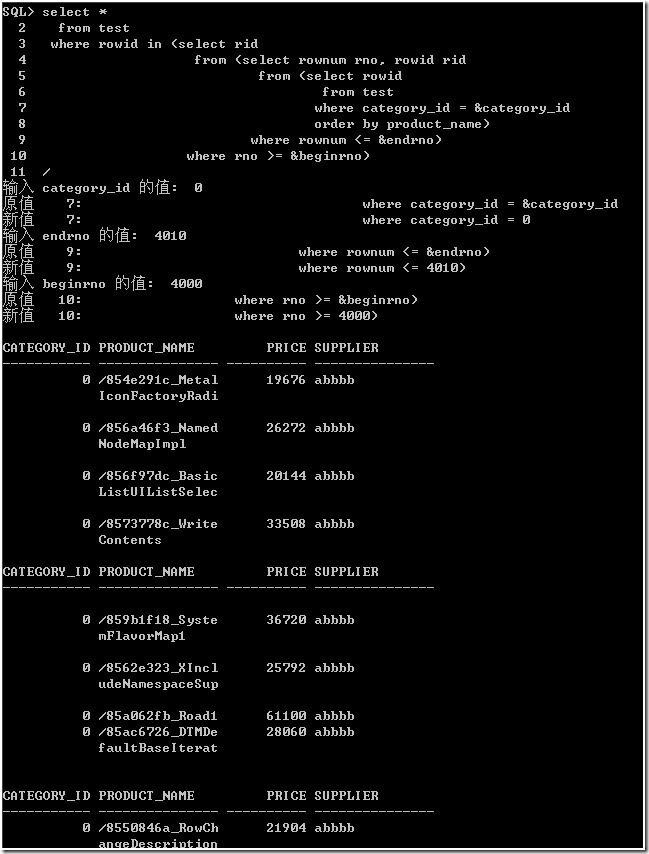
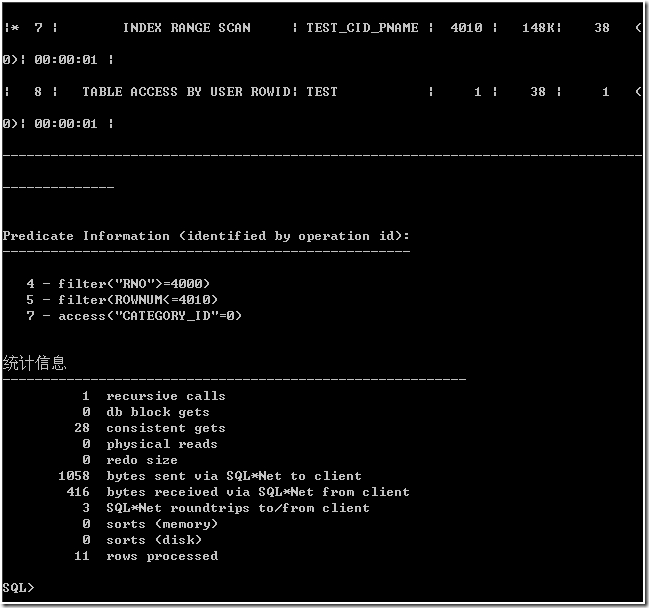
根据作法 2,选择过滤条件以及开始行号和结束行号,获得行 ROWID,再根据获得制定行 ROWID 的记录。这种看起来有点多余,但的确有效。
总结
如下表所示,是本文使用数据库分页的三种形式。
表 1 三种数据库分页
|
作法 |
SQL 语句 |
描述 |
|
作法 1 |
select *
from (select rownum rno, a.* from (select * from test
where category_id = &category_id
order by product_name) a) where rno between &beginrno and &endrno |
|
|
作法 2 |
select *
from (select rownum rno, a.* from (select * from test
where category_id = &category_id
order by product_name) a where rownum <= &endrno)
where rno >= &beginrno
|
|
|
作法 3 |
select *
from test
where rowid in (select rid from (select rownum rno, rowid rid from (select rowid from test
where category_id = &category_id
order by product_name) where rownum <= &endrno)
where rno >= &beginrno)
|
如下表所示,是本文三种数据库分页方式的统计信息。
表 2 三种数据库分页的统计信息
|
统计信息 |
作法1 |
作法2 |
作法3 |
|
recursive calls |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
db block gets |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
consistent gets |
804 |
234 |
28 |
|
physical gets |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
redo size |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
bytes sent via SQL*Net to client |
1154 |
1154 |
1058 |
|
bytes received via SQL*Net from client |
416 |
416 |
416 |
|
SQL*Net roundtrips to/from client |
3 |
4 |
3 |
|
sorts(memory) |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
sorts(disk) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
rows processed |
11 |
11 |
11 |
参考资料
- Using EXPLAIN PLAN http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28274/ex_plan.htm#PFGRF009
- Statistics Descriptions http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28320/stats002.htm#i375475