数据结构-简单选择排序和归并排序
本文内容
- 通用数据结构
- 简单选择排序
- 归并排序
- Main 函数
- 运行结果
本文用 CodeBlocks 编写。同时也提供 VS C 和 VS C# 代码。
通用数据结构
- MyElement.h
#ifndef MYELEMENT_H_INCLUDED
#define MYELEMENT_H_INCLUDED
#define N 11
#define LQ(a,b) ((a)<=(b))
typedef int ElementType;
void Print(ElementType e[], int n);
#endif // MYELEMENT_H_INCLUDED
- MyElement.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "MyElement.h"
void Print(ElementType e[], int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
printf("%d ",e[i]);
printf("\n");
}
简单选择排序
- SelectSort.h
#ifndef SELECTSORT_H_INCLUDED
#define SELECTSORT_H_INCLUDED
#include "MyElement.h"
void SelectSort(ElementType e[], int n);
void Main_SelectSort();
#endif // SELECTSORT_H_INCLUDED
- SelectSort.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "SelectSort.h"
#include "MyElement.h"
int SelectMin(ElementType e[], int i, int n)
{
/* 返回在L.r[i..L.length]中key最小的记录的序号 */
ElementType min;
int j,k;
k=i; /* 设第i个为最小 */
min=e[i];
for(j=i+1; j<n; j++)
if(e[j]<min) /* 找到更小的 */
{
k=j;
min=e[j];
}
return k;
}
/* 简单选择排序 */
void SelectSort(ElementType e[], int n)
{
int i,j;
ElementType t;
for(i=1; i<n; ++i)
{
/* 选择第i小的记录,并交换到位 */
j=SelectMin(e,i,n); /* 在L.r[i..L.length]中选择key最小的记录 */
if(i!=j)
{
/* 与第i个记录交换 */
t=e[i];
e[i]=e[j];
e[j]=t;
}
}
}
/* 测试 */
void Main_SelectSort()
{
ElementType d[N]= {0,49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,55,10};
printf("排序前:\n");
Print(d,N);
SelectSort(d, N);
printf("排序后:\n");
Print(d,N);
printf("\n");
}
归并排序
- MergeSort.h
#ifndef MERGESORT_H_INCLUDED
#define MERGESORT_H_INCLUDED
#include "MyElement.h"
void MergeSort(ElementType e[], int n);
void Main_MergeSort();
#endif // MERGESORT_H_INCLUDED
- MergeSort.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "MergeSort.h"
#include "MyElement.h"
void Merge(ElementType SR[],ElementType TR[],int i,int m,int n)
{
/* 将有序的SR[i..m]和SR[m+1..n]归并为有序的TR[i..n] */
int j,k,l;
for(j=m+1,k=i; i<=m&&j<=n; ++k) /* 将SR中记录由小到大地并入TR */
if LQ(SR[i],SR[j])
TR[k]=SR[i++];
else
TR[k]=SR[j++];
if(i<=m)
for(l=0; l<=m-i; l++)
TR[k+l]=SR[i+l]; /* 将剩余的SR[i..m]复制到TR */
if(j<=n)
for(l=0; l<=n-j; l++)
TR[k+l]=SR[j+l]; /* 将剩余的SR[j..n]复制到TR */
}
void MSort(ElementType SR[],ElementType TR1[],int s, int t)
{
/* 将SR[s..t]归并排序为TR1[s..t]。*/
int m;
ElementType TR2[N+1];
if(s==t)
TR1[s]=SR[s];
else
{
m=(s+t)/2; /* 将SR[s..t]平分为SR[s..m]和SR[m+1..t] */
MSort(SR,TR2,s,m); /* 递归地将SR[s..m]归并为有序的TR2[s..m] */
MSort(SR,TR2,m+1,t); /* 递归地将SR[m+1..t]归并为有序的TR2[m+1..t] */
Merge(TR2,TR1,s,m,t); /* 将TR2[s..m]和TR2[m+1..t]归并到TR1[s..t] */
}
}
/* 归并排序 */
void MergeSort(ElementType e[], int n)
{
MSort(e,e,1,n-1);
}
void Main_MergeSort()
{
ElementType d[N]= {0,49,38,65,97,76,13,27,49,55,10};
printf("排序前:\n");
Print(d,N);
MergeSort(d,N);
printf("排序后:\n");
Print(d,N);
printf("\n");
}
Main 函数
#include "SelectSort.h"
#include "MergeSort.h"
main()
{
Main_SelectSort();
Main_MergeSort();
}
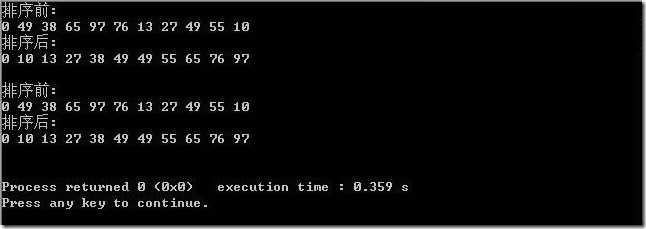
运行结果