thread join
Thread join方法
表示等待线程的结束。但是到底是谁等待谁呢?
是main主线程等待线程t执行完毕再执行。
下面看个例子。
1 package com.citi.test.mutiplethread.demo0503; 2 3 import java.util.Date; 4 5 public class TestJoin implements Runnable{ 6 private String name; 7 public TestJoin(String name) { 8 this.name=name; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void run() { 13 System.out.println("start:"+name+new Date()); 14 try { 15 Thread.sleep(3000); 16 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 17 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } 20 System.out.println("end:"+name+new Date()); 21 } 22 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 23 Thread thread1=new Thread(new TestJoin("张三")); 24 Thread thread2=new Thread(new TestJoin("李四")); 25 thread1.start(); 26 thread2.start(); 27 thread1.join(); 28 thread2.join(); 29 System.out.println("main thread is finished"); 30 31 } 32 }
可以看到main线程会等待thread1和thread2线程执行完毕再执行。
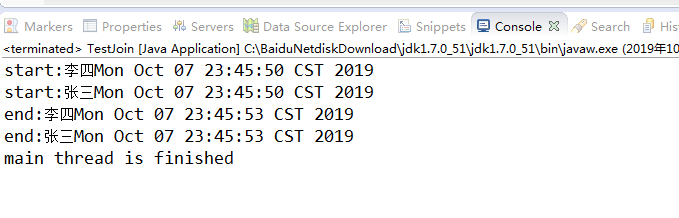
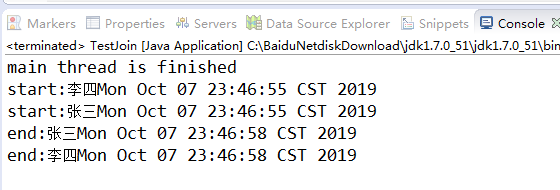
如果没有thread1.join(), thread2.join(),那么结果会是这样。
join方法
1 /** 2 * Waits for this thread to die. 3 *等待直到线程死亡。 4 * <p> An invocation of this method behaves in exactly the same 5 * way as the invocation 6 * 7 * <blockquote> 8 * {@linkplain #join(long) join}{@code (0)} 9 * </blockquote> 10 * 11 * @throws InterruptedException 12 * if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The 13 * <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is 14 * cleared when this exception is thrown. 15 */ 16 public final void join() throws InterruptedException { 17 join(0); 18 }
join(long millis)方法
/** * Waits at most {@code millis} milliseconds for this thread to * die. A timeout of {@code 0} means to wait forever. * 当millis是0时,表示永远等待 * <p> This implementation uses a loop of {@code this.wait} calls * conditioned on {@code this.isAlive}. As a thread terminates the * {@code this.notifyAll} method is invoked. It is recommended that * applications not use {@code wait}, {@code notify}, or * {@code notifyAll} on {@code Thread} instances. * 这里实现用了一个isAlive作为循环条件。因为一个线程停止,notifyAll方法被调用。 它要求应用不用wait,notify,或者notifyAll在线程实例上。 * @param millis * the time to wait in milliseconds * * @throws IllegalArgumentException * if the value of {@code millis} is negative * * @throws InterruptedException * if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The * <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is * cleared when this exception is thrown. */ public final synchronized void join(long millis) throws InterruptedException { long base = System.currentTimeMillis(); long now = 0; if (millis < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative"); } //当调用t.join()方法时,join会调用join(0),所以这里的millis是0、 if (millis == 0) { //这里的isAlive是表示线程t,而不是main线程是否为alive状态。 //所以这里如果线程t执行完毕了,那么t就不是alive状态了,所以就不等待了。 while (isAlive()) { //而这里的wait方法,到底是t线程等待还是main线程等待呢?//答案是main线程。就是调用t.join()的线程是处于等待状态。 //这样就说通了,当在main方法中调用t.join()方法时,是main线程等待t线程执行完毕再执行。 wait(0); } } else { while (isAlive()) { long delay = millis - now; if (delay <= 0) { break; } wait(delay); now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base; } } }
isAlive方法
1 /** 2 * Tests if this thread is alive. A thread is alive if it has 3 * been started and has not yet died. 4 测试线程是否是alive的状态。 5 一个线程如果已经开始了,并且没有死掉,那么这个线程就是alive状态。 6 * 7 * @return <code>true</code> if this thread is alive; 8 * <code>false</code> otherwise. 9 */ 10 public final native boolean isAlive();
参考资料:




