二叉搜索树
由于普通链表的查找,删除的时间复杂度为o(n),插入的时间复杂度为o(1),现介绍一种查找,删除,插入的时间复杂度均在o(logn)~o(n)之间的数据结构,这就是二叉搜索树。
二叉搜索树的规则:
1.每一个父节点都有0~2个子结点,分别为左孩子节点,右孩子节点。
2.左孩子节点的值小于父节点的值,父节点的值小于右孩子节点的值。
根据第一条规则,我们可以将一个二叉搜索树分解为两个子二叉搜索树加一个根节点。从第二条规则我们可以知道,左子树上的任意节点值都小于根节点值,而右子树上的任意节点值都大于根节点值。如图所示,(a)为二叉搜索树,而(b)不是。因为(b)中左子二叉树上的值为7的节点大于根节点6。
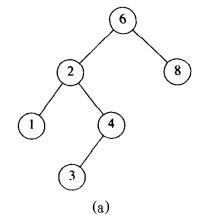
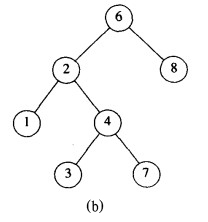
具体的实现代码为:
1 template<typename T> 2 struct bs_tree_node 3 { 4 bs_tree_node(const T& _element, bs_tree_node *_left, bs_tree_node *_right) 5 : element(_element) 6 , left(_left) 7 , right(_right) 8 { 9 } 10 T element; 11 bs_tree_node *left; 12 bs_tree_node *right; 13 }; 14 15 template<typename T> 16 class bs_tree 17 { 18 typedef bs_tree_node<T> bs_tree_node; 19 public: 20 bs_tree() { m_root = NULL; } 21 bs_tree(const bs_tree& rhs) 22 : m_root(rhs.m_root) 23 {} 24 const bs_tree& operator=(const bs_tree& rhs) 25 { 26 if(this!=&rhs) 27 { 28 clear(); 29 m_root = clone(rhs.m_root); 30 } 31 } 32 33 ~bs_tree() 34 { 35 clear(m_root); 36 } 37 38 public: 39 const T& find_min() const 40 { 41 bs_tree_node* node = find_min(m_root); 42 if(node) 43 { 44 return node->element; 45 } 46 throw std::runtime_error("查找二叉树无任何节点"); 47 } 48 49 const T& find_max() const 50 { 51 bs_tree_node* node = find_max(m_root); 52 if(node) 53 { 54 return node->element; 55 } 56 throw std::runtime_error("查找二叉树无任何节点"); 57 } 58 59 bool contains(const T& x) const 60 { 61 return contains(x,m_root); 62 } 63 64 bool is_empty() const 65 { 66 return m_root==NULL; 67 } 68 69 void clear() 70 { 71 clear(m_root); 72 } 73 74 void insert(const T& x) 75 { 76 insert(x,m_root); 77 } 78 79 void remove(const T& x) 80 { 81 remove(x,m_root); 82 } 83 84 bs_tree_node* clone(bs_tree_node* t) const 85 { 86 if( t==NULL ) 87 { 88 return NULL; 89 } 90 return new bs_tree_node(t->element, clone(t->left), clone(t->right)); 91 } 92 93 template<typename Functor> 94 void foreach(Functor& functor) 95 { 96 foreach(m_root,functor); 97 } 98 99 private: 100 bs_tree_node* find_min(bs_tree_node* t) const 101 { 102 if( t==NULL ) 103 { 104 return NULL; 105 } 106 while(t->left!=NULL) 107 { 108 t = t->left; 109 } 110 return t; 111 } 112 113 bs_tree_node* find_max(bs_tree_node* t) const 114 { 115 if( t==NULL ) 116 { 117 return NULL; 118 } 119 while(t->right!=NULL) 120 { 121 t = t->right; 122 } 123 return t; 124 } 125 126 bool contains(const T& x, bs_tree_node* t) const 127 { 128 if( t == NULL ) 129 { 130 return false; 131 } 132 else if( x<t->element ) 133 { 134 return contains( x, t->left ); 135 } 136 else if( x>t->element ) 137 { 138 return contains(x, t->right); 139 } 140 else 141 { 142 return true; 143 } 144 } 145 146 void insert(const T& x, bs_tree_node*& t) 147 { 148 if( t == NULL ) 149 { 150 t = new bs_tree_node(x,NULL,NULL); 151 } 152 else if( x<t->element) 153 { 154 insert(x,t->left); 155 } 156 else if( x>t->element ) 157 { 158 insert(x,t->right); 159 } 160 else 161 {} 162 } 163 164 void remove(const T& x, bs_tree_node*& t) 165 { 166 if( t== NULL ) 167 { 168 return; 169 } 170 else if( x < t->element) 171 { 172 remove(x,t->left); 173 } 174 else if( x > t->element ) 175 { 176 remove(x,t->right); 177 } 178 else if( t->left != NULL && t->right != NULL) 179 { 180 t->element = find_min( t->right )->element; 181 remove( t->element, t->right); 182 } 183 else 184 { 185 bs_tree_node *old_node = t; 186 t = (t->left != NULL)?t->left:t->right; 187 delete old_node; 188 } 189 } 190 191 void clear(bs_tree_node*& t) 192 { 193 if(t != NULL) 194 { 195 clear(t->left); 196 clear(t->right); 197 delete t; 198 t = NULL; 199 } 200 } 201 202 template<typename Functor> 203 void foreach(bs_tree_node* t, Functor& functor) 204 { 205 if(t!=NULL) 206 { 207 functor(t); 208 foreach(t->left, functor); 209 foreach(t->right, functor); 210 } 211 } 212 213 private: 214 bs_tree_node *m_root; 215 };
由于二叉搜索树的查找,删除,添加在理想的情况下都与二分搜索算法类似,可以知道它的最优时间复杂度为o(logn),然而像极端情况下,如所有节点都是左孩子或者所有节点都是右孩子,则二叉搜索树退化为普通有序链表,各项操作的时间复杂度为o(n)。二叉搜索树的具体形状则与插入顺序有关。比如:
1 bs_tree<int> tree; 2 for(int i = 0; i<1000*1000*1000; ++i) 3 { 4 tree.insert(i); 5 }
像上述代码则产生了一个所有节点都为左孩子的二叉搜索树,性能与普通有序链表一致。由此可知经过频繁的插入删除操作,二叉搜索树的性能可能下降或者上升。
除了上述缺点之外,实际上上述代码无法运行,因为插入操作的具体实现是一个递归调用过程,极端情况下它需要遍历每一个元素才能确定插入位置,而上述插入操作会导致函数栈溢出。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号