【介绍】
# vue3 的变化
1.性能的提升
-打包大小减少41%
-初次渲染快55%, 更新渲染快133%
-内存减少54%
2.源码的升级
使用Proxy代替defineProperty实现响应式
重写虚拟DOM的实现和Tree-Shaking
3.拥抱TypeScript
Vue3可以更好的支持TypeScript
4.新的特性
Composition API(组合API)
setup配置
ref与reactive
watch与watchEffect
provide与inject
新的内置组件
Fragment
Teleport
Suspense
其他改变
新的生命周期钩子
data 选项应始终被声明为一个函数
移除keyCode支持作为 v-on 的修饰符
--------------------------------
# 组合式API和配置项API
vue2 :配置项API
new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{}
})
vue3: 组合式API
let name='lqz'
let add=()=>{
}
。
。
【vue3项目创建】
# 1 跟之前创建vue2一样
# 2 步骤: 1 vue create vue3_demo001 2 注意选择vue3,其他都一样
# 3 webstorm打开--》配置启动
# 4 配置npm 镜像站 npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com
检测:npm config get registry
【vite创建(推荐)】
#1 什么是vite?—— 新一代前端构建工具。
优势如下:
开发环境中,无需打包操作,可快速的冷启动。
轻量快速的热重载(HMR)。
真正的按需编译,不再等待整个应用编译完成。
传统构建 与 vite构建对比图
# 2 兼容性注意
Vite 需要 Node.js 版本 18+,20+。然而,有些模板需要依赖更高的 Node 版本才能正常运行,当你的包管理器发出警告时,请注意升级你的 Node 版本
官网:https://cn.vitejs.dev/
# 3 创建工程
# 不指定名字创建:npm create vite@latest
# 配置npm镜像站:npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com
# 查看镜像站:npm config get registry
# 指定名字创建
# 创建项目方式一
npm create vite@latest
# 创建项目方式二:指定名字
npm create vite@latest vue3_demo002
# 创建项目方式三
cnpm create vite@latest vue3_demo002
# 创建项目方式四
cnpm create vite vue3_demo002
# 3 使用编辑器打开vue3项目
# 4 安装依赖
npm install
# 5 运行项目
npm run dev
。
。
。
【常用API】
1.setup函数
# 1 如果使用配置项API---》写起来跟vue2一样
# 2 如果写组合式API---》所有代码都要写在setup函数中
-后期除了setup函数,其他都不带了
# 3 setup函数必须返回变量或函数--》在template中才能使用
# 4 默认不带响应式,需要使用ref或reactive包裹
1 <template> 2 <div class="home"> 3 <h2>姓名:{{ name }}</h2> 4 <h2>年龄:{{ age }}</h2> 5 <button @click="handleAdd">点击加年龄</button> 6 <button @click="handleChange">点击改名字</button> 7 </div> 8 </template> 9 10 <script> 11 12 13 import {ref} from "vue"; 14 15 export default { 16 name: 'HomeView', 17 setup() { 18 //1.插值语法 19 // let name='张三' 20 let name = ref('张三') 21 // let age=18 默认没有响应式 22 let age = ref(18) //做成响应式,需要导入模块 23 //2.方法--点击年龄+1 24 function handleAdd() { 25 console.log(age) //age的类型是RefImpl, 26 age.value += 1 //age的值+1需要通过value来操作 27 28 } 29 30 //3.方法--改名字 31 function handleChange() { 32 name.value = '小龙女' 33 } 34 35 //.必须return,然后才能在template中使用 36 return {name, age, handleAdd, handleChange} 37 } 38 } 39 </script>
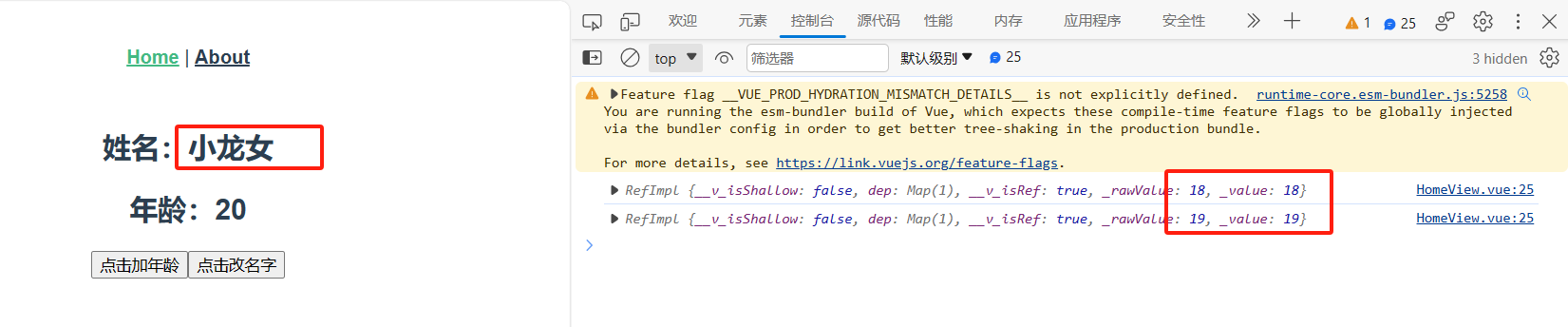
2.ref和reactive
# 1 ref 包裹值类型[数字,字符串,布尔],做成响应式
# 2 reactive包裹引用类型[对象,数组],做成响应式
# 3 使用reactive包裹的对象,直接通过 . [] 取值赋值就是响应式的
ref包裹的对象,需要使用 对象.value 修改值
# 4 使用ref包裹的,在template中,不用使用 变量.value
##### js### const hobby = ref('篮球') const wife = reactive({name: '刘亦菲', age: 38, height: 168}) const handleAddHeight = () => { wife.height += 1 } #### template#### <h1>ref和reacitve</h1> <p>爱好是:{{ hobby }}</p> <p>wife名字是:{{ wife.name }}-->wife年龄是:{{ wife.age }}---》wife身高是:{{ wife.height }}</p> <button @click="handleAddHeight">点击wife身高+1</button>
3.计算属性computed
##### js### // 3 计算属性 const person = reactive({ firstName: '', lastName: '' }) // 只有 计算属性,不修改值的情况 // person.fullName = computed(() => { // return person.firstName+person.lastName // }) // 支持修改 person.fullName = computed({ get() { return person.firstName + person.lastName }, set(value) { person.firstName = value.slice(0, 1) person.lastName = value.slice(1) }, }) #### template### <h1>计算属性</h1> <p>姓:<input type="text" v-model="person.firstName"></p> <p>名:<input type="text" v-model="person.lastName"></p> <p>全名:{{ person.fullName }}</p> <p>全名修改:<input type="text" v-model="person.fullName"></p>

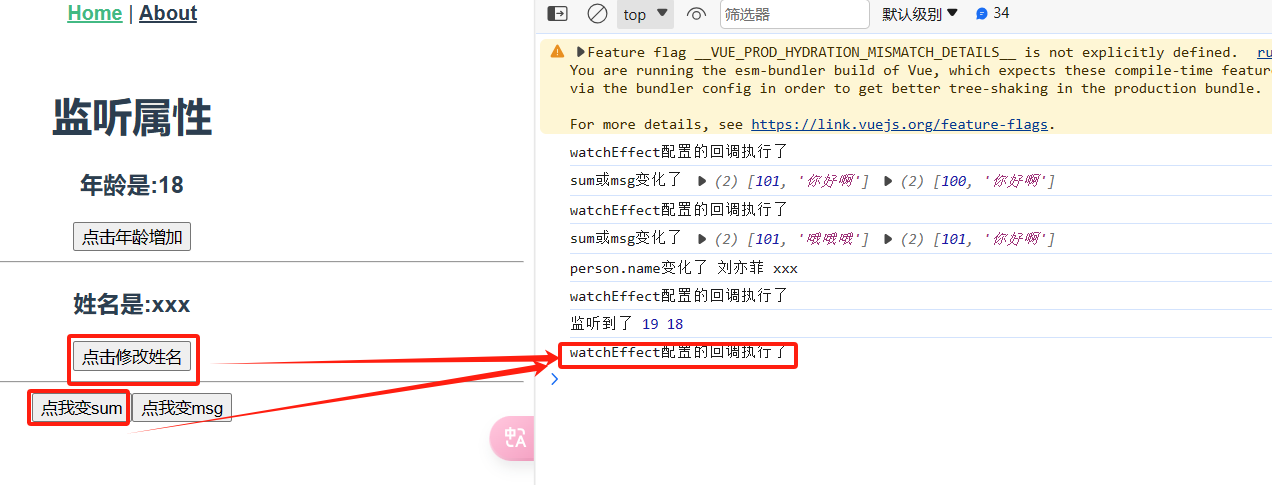
4.监听属性
4.1监听值类型,监听对象类型,监听多个变量,watchEffect函数
1 <template> 2 <div class="home"> 3 <h1>监听属性</h1> 4 <h3>年龄是:{{ age }}</h3> 5 <button @click="ageAdd">点击年龄增加</button> 6 <hr> 7 <h3>姓名是:{{ person.name }}</h3> 8 <button @click="changeName">点击修改姓名</button> 9 <hr> 10 <button @click="changeSum">点我变sum</button> 11 <button @click="changeMsg">点我变msg</button> 12 </div> 13 </template> 14 15 <script> 16 import {ref, watch, reactive, watchEffect} from "vue"; 17 18 export default { 19 name: 'HomeView', 20 setup() { 21 const age = ref(18) 22 23 const person = reactive({name: 'xxx'}) 24 25 const sum = ref(100) 26 const msg = ref('你好啊') 27 28 function ageAdd() { 29 age.value++ 30 } 31 32 function changeName() { 33 person.name = '刘亦菲' 34 } 35 36 function changeSum() { 37 sum.value++ 38 } 39 40 function changeMsg() { 41 msg.value = '哦哦哦' 42 } 43 44 //1.监听属性 普通监听 45 watch(age, (newValue, oldValue) => { 46 console.log('监听到了', newValue, oldValue) 47 }) 48 49 //2.监听对象 50 watch(() => person.name, (newValue, oldValue) => { 51 console.log('person.name变化了', newValue, oldValue) 52 }) 53 54 //3.监听多个 55 watch([sum, msg], (newValue, oldValue) => { 56 console.log('sum或msg变化了', newValue, oldValue) 57 }) 58 59 //watchEffect函数,使用:不用指定监听谁,只要watchEffect内部用了某个变量,某个变量发送变化,就会触发 60 watchEffect(() => { 61 const x1 = sum.value 62 const x2 = person.name 63 console.log('watchEffect配置的回调执行了') 64 }) 65 return {age, ageAdd, watch, changeName, person, sum, msg, changeSum, changeMsg} 66 } 67 } 68 </script>
5.生命周期
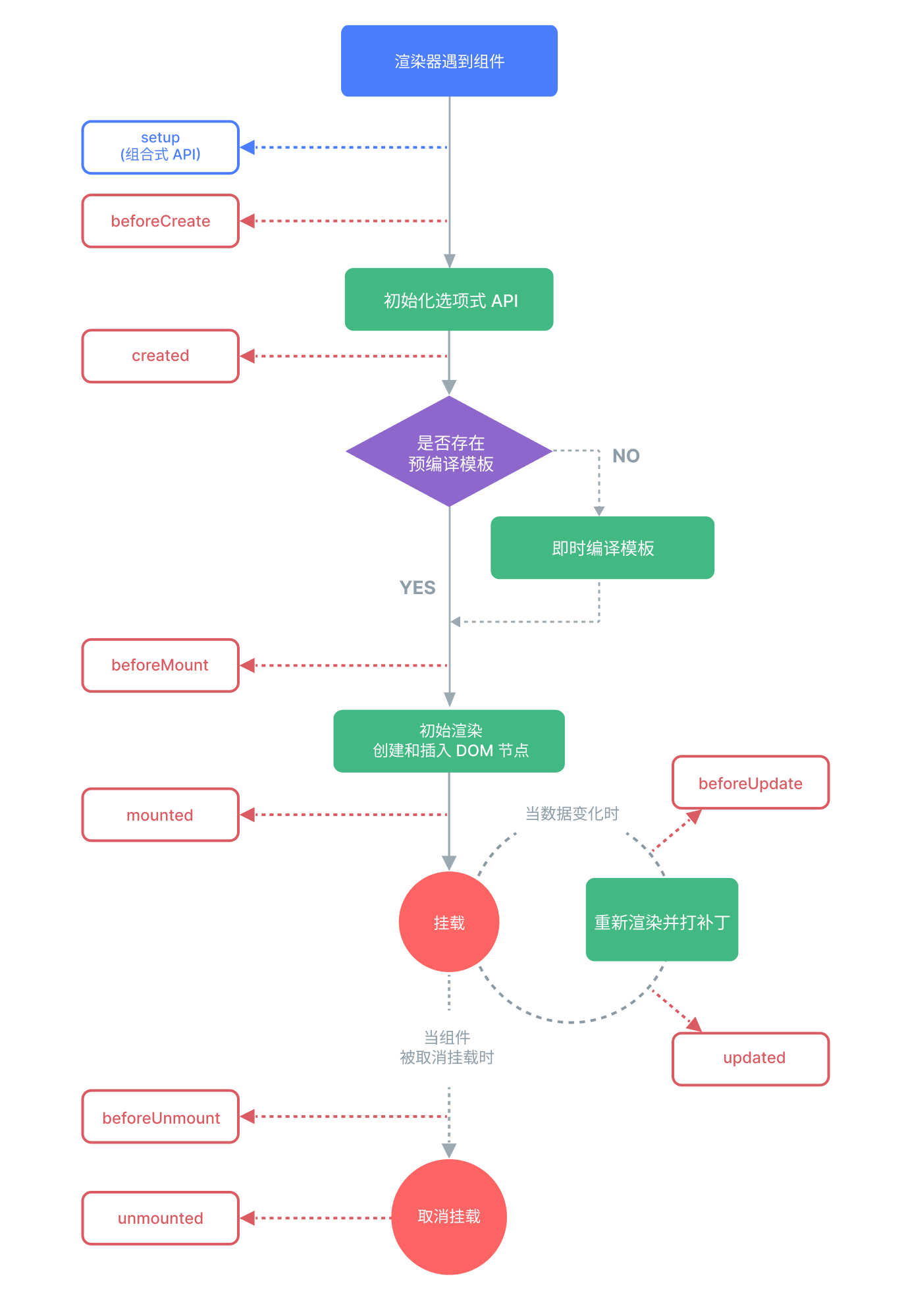
5.1配置项API生命周期
beforeCreate
created
beforeMount
mounted
beforeUpdate
updated
beforeUnmount
unmounted
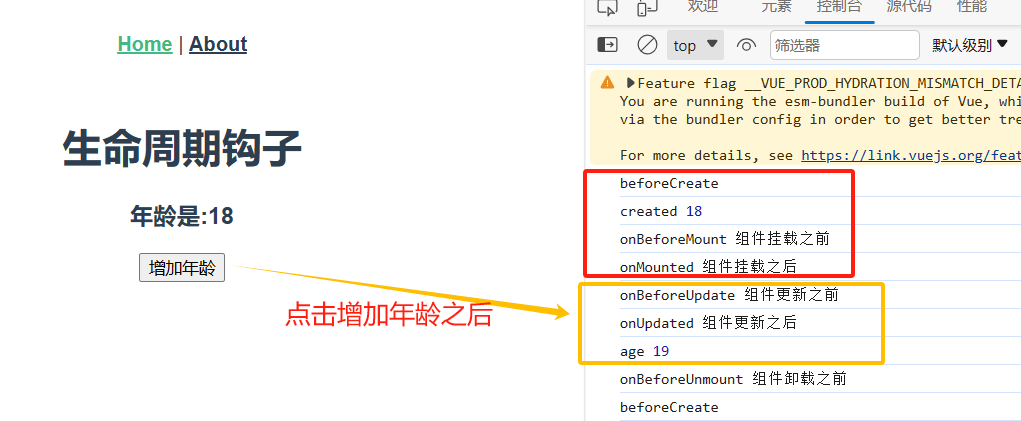
5.2组合式API生命周期
beforeCreate===>setup()
created=======>setup()
beforeMount ===>onBeforeMount
mounted=======>onMounted
beforeUpdate===>onBeforeUpdate
updated =======>onUpdated
beforeUnmount ==>onBeforeUnmount
unmounted =====>onUnmounted
<template> <div class="home"> <h1>生命周期钩子</h1> <h3>年龄是:{{ age }}</h3> <button @click="ageAdd">增加年龄</button> </div> </template> <script> import {ref, onBeforeMount, onMounted, onBeforeUpdate, onUpdated, onBeforeUnmount, onUnmounted} from "vue"; export default { name: 'HomeView', setup() { //1.写在这里就是beforeCreate console.log('beforeCreate') const age = ref(18) function ageAdd() { age.value++ } //2.created console.log('created', age.value) //3.onBeforeMount onBeforeMount(() => { console.log('onBeforeMount', '组件挂载之前') }) //4.,onMounted onMounted(() => { console.log('onMounted', '组件挂载之后') }) //5.onBeforeUpdate onBeforeUpdate(() => { console.log('onBeforeUpdate', '组件更新之前') }) //6.onUpdated onUpdated(() => { console.log('onUpdated', '组件更新之后') console.log('age', age.value) }) //7.onBeforeUnmount onBeforeUnmount(() => { console.log('onBeforeUnmount', '组件卸载之前') }) //8.onUnmounted onUnmounted(() => { console.log('onUnmounted', '组件卸载之后') }) return {age, ageAdd} }, } </script>
6.toRefs
将响应式对象转换为普通对象,但其属性被转换为 ref
1 <template> 2 <div class="home"> 3 <h1>toRefs</h1> 4 <h3>{{ name }}----------{{ age }}</h3> 5 <button @click="age++">年龄+1</button> 6 <hr> 7 <button @click="handleShow">看控制台</button> 8 <button @click="ageAdd">年龄增加</button> 9 10 </div> 11 </template> 12 13 <script> 14 import {ref, reactive, toRefs} from "vue"; 15 16 export default { 17 name: 'HomeView', 18 setup() { 19 let person = reactive({name: '张三', age: 48}) 20 21 function ageAdd() { 22 person.age++ 23 console.log(person) 24 } 25 26 function handleShow() { 27 console.log(person) 28 } 29 30 return {...toRefs(person), ageAdd, handleShow}// toRefs: 将响应式对象转换为普通对象,但其属性被转换为 ref。 31 //相当于return {name:ref(person.name),age:ref(person.age} 32 //这样做的好处是,你可以在模板中直接使用 name 和 age(而不是 person.name 和 person.age),而它们仍然是响应式的。 33 }, 34 35 36 } 37 </script>
【用vit+vue3创建项目】
App.vue
1 <script setup>
// 以后,只要再 这样写[ <script setup> ] ,script就是setup函数中的
// 定义的变量和函数,不需要return,以后,就不再写配置项了
// 1 组件,只需要导入,就会自动注册
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'2 import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue' 3 import Child from "./components/Child.vue"; 4 import Child2 from "./components/Child2.vue"; 5 import utils from "../public/utils/index.js"; 6 import Child3 from "./components/Child3.vue"; 7 8 //1.setup写法 9 import {ref, reactive, computed, toRefs, toRef} from 'vue' 10 11 const name = ref('张三') 12 13 function changeName() { 14 name.value = '李四' 15 } 16 17 //2.生命周期钩子---created 18 console.log('created') 19 20 //3.计算属性 21 const newName = computed(() => { 22 return name.value + '123' 23 }) 24 25 //4.自定义属性---父传子 26 const msg1 = ref('猪猪侠') 27 28 //5.自定义事件---子传父 29 const child_name = ref('') 30 31 function handleEvent(name) { 32 child_name.value = name 33 } 34 35 //6.插槽 36 //7.没有全局mixin,只有局部自己建的 37 let b = utils.name = '我是熊大' 38 let a = utils.add(1, 2) 39 console.log(a, b) 40 41 //8.toRefs 42 const person = reactive({ 43 name2: '光头强', 44 age2: 8 45 }) 46 let {name2, age2} = toRefs(person) 47 console.log(typeof (name2), age2) 48 name2.value = '吉吉国王' 49 50 //9.toRef---只把对象中某一个做成响应式 51 let name3 = toRef(person, 'name2') 52 console.log(name3.value) 53 54 //10.ref属性 55 const child3 = ref() // 代指 this.$refs.child3 ,这个地方必须叫child3,放在组件上的ref是child3 56 // created--->还没挂载---》组件还没有 57 function showLog() { 58 console.log(child3.value.age) 59 child3.value.changeAge() 60 console.log(child3.value.age) 61 } 62 63 </script> 64 65 <template> 66 <h1>setup写法</h1> 67 <h2>{{ name }}</h2> 68 <button @click="changeName">点我改名字</button> 69 <h2>计算属性:{{ newName }}</h2> 70 <hr> 71 <h1>自定义属性---父传子</h1> 72 <HelloWorld :msg="msg1"></HelloWorld> 73 <h2>自定义事件--子传父</h2> 74 <h3>子组件传过来的---{{ child_name }}</h3> 75 <Child @myevent="handleEvent"></Child> 76 <hr> 77 <h2>插槽</h2> 78 <Child2> 79 <template v-slot:a> 80 <div>我是a</div> 81 </template> 82 > 83 <template v-slot:b> 84 <div>我是b</div> 85 </template> 86 > 87 </Child2> 88 <hr> 89 <h1>ref属性-放在组件上</h1> 90 <Child3 ref="child3"></Child3> 91 <button @click="showLog">点我看控制台</button> 92 93 </template> 94 95 <style scoped> 96 .logo { 97 height: 6em; 98 padding: 1.5em; 99 will-change: filter; 100 transition: filter 300ms; 101 } 102 103 .logo:hover { 104 filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #646cffaa); 105 } 106 107 .logo.vue:hover { 108 filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #42b883aa); 109 } 110 </style>
HelloWorld.vue-->父传子
<script setup> import {ref} from 'vue' // 父传子,接收父传过来的变量:数组形式 // defineProps(['msg']) //2.对象形式 defineProps({ msg: String }) const count = ref(0) </script> <template> <h1>{{ msg }}</h1> </template>
Child.vue-->父子通信子传父
<script setup> import {ref} from "vue"; let $emit = defineEmits(['myevent']) const name = ref('') function handleSend() { $emit('myevent', (name.value)) } </script> <template> <input type="text" v-model="name">--->{{ name }}---> <button @click="handleSend">点我传到父</button> </template> <style scoped> </style>
Child2.vue--》插槽
<script setup> </script> <template> <h2>child2</h2> <slot name="a"></slot> <hr> <slot name="b"></slot> </template> <style scoped> </style>
Child3.vue-->ref属性
<script setup> import {ref} from 'vue' const age = ref(0) function changeAge() { age.value += 4 } defineExpose({age, changeAge}) </script> <template> <h1>ref属性</h1> </template> <style scoped> </style>
mixin.index.js
export default {
name:'熊大',
add:function (a,b){
return a+b
}
}
。
。
。
2.axios使用
2.1 基本使用
import axios from "axios";
// 相当于写在了created中--》页面加载完,就发送请求
axios.get('自己地址').then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
2.1.1 小电影案例

<script setup> import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue' import axios from "axios"; import {reactive} from "vue"; const filmsList = reactive({result: []}) axios.get('http://127.0.0.1:8000/app01/films/').then(res => { console.log(res.data) if (res.data.code == 100) { //加载成功.把数据放到变量中 filmsList.result = res.data.result console.log('----', filmsList) } else { alert(res.data.msg) } }) </script> <template> <h1>加载电影案例</h1> <div v-for="item in filmsList.result"> <h3>{{ item.name }}</h3> <img :src="item.poster" alt="" height="200px" width="150px"> </div> </template> <style scoped> .logo { height: 6em; padding: 1.5em; will-change: filter; transition: filter 300ms; } .logo:hover { filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #646cffaa); } .logo.vue:hover { filter: drop-shadow(0 0 2em #42b883aa); } </style>
1 <script setup> 2 import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue' 3 import axios from "axios"; 4 import {reactive} from "vue"; 5 6 const filmsList = reactive({result: []}) 7 //2.升级 8 // axios.get('http://127.0.0.1:8000/app01/films/').then(res => { 9 // console.log(res.data) 10 // if (res.data.code == 100) { 11 // 2.1 直接把res.data.result 复制到filmList.result 12 // Object.assign(filmsList.result, res.data.result) 13 14 // 2.2 解构赋值 15 // let {data} = res // res={data:{code:100,msg:成功}} 16 // Object.assign(filmsList.result, data.result) 17 18 // 2.3 解构赋值 19 // let {data: {result}} = res 20 // Object.assign(filmsList.result, result) 21 22 // 2.4 解构赋值 23 // let {data} = res // {code:100,msg:成功,result:[]} 24 // Object.assign(filmsList, data) 25 // 26 // } else { 27 // alert(res.data.msg) 28 // } 29 // }) 30 31 // 3 async await 32 async function load() { 33 let{data}=await axios.get('http://127.0.0.1:8000/app01/films/') 34 Object.assign(filmsList, data) 35 } 36 load() 37 38 </script>
后端
。
。
。
【promise】
1.0 普通函数和回调函数
//普通函数: 正常调用的函数,一般函数执行完毕后才会继续执行下一行代码 <script> let fun1 = () =>{ console.log("fun1 执行了") } // 调用函数 fun1() // 函数执行完毕,继续执行后续代码 console.log("其他代码继续执行") </script> //回调函数: 一些特殊的函数,表示未来才会执行的一些功能,后续代码不会等待该函数执行完毕就开始执行了 <script> // 设置一个2000毫秒后会执行一次的定时任务,基于事件自动调用,console.log先执行 setTimeout(function (){ console.log("延迟演示执行了") },2000) console.log("其他代码执行") </script>
2.0promise基本使用(用来处理回调函数)
# Promise对象代表一个异步操作,有三种状态:`Pending`(进行中)、`Resolved`(已完成,又称 Fulfilled)和`Rejected`(已失败)
# 现实生活中对应 你跟你女朋友说,5年后等我赚够500w就结婚--》定义函数
-1 进行中(努力赚钱,其他代码继续执行)
-2 成功(赚够500w---》结婚)
-3 失败(没赚够---》分手)
1 <script setup> 2 import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue' 3 import axios from "axios"; 4 import {reactive} from "vue"; 5 6 let promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 7 // resolve,reject 是两个函数 8 console.log("promise 开始执行") 9 // resolve("promise 执行成功") 10 reject("promise 执行失败") 11 // 主动抛异常,也是执行失败 12 // throw new Error("error message") 13 }) 14 console.log('11111') 15 // promise.then( 16 // function (value) {console.log(`promise中执行了resolve:${value}`)}, 17 // function (error) {console.log(`promise中执行了reject:${error}`)}) 18 19 //2. 20 promise.then(res => { 21 console.log(res) 22 }).catch(err => { 23 console.log(err) 24 }) 25 console.log('222222') 26 </script>
3.0async和await的使用
promise对象 支持async和await 写法
1 <script setup> 2 import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue' 3 4 // async 和await 写法 5 // 1 async标识函数后,async函数的返回值会变成一个promise对象 6 async function demo01() { 7 let promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) { 8 // resolve,reject 是两个函数 9 console.log("promise 开始执行") 10 // resolve("promise 执行成功") 11 // reject("promise 执行失败") 12 // 主动抛异常,也是执行失败 13 throw new Error("error message") 14 }) 15 return promise 16 } 17 18 console.log('11111') 19 20 // await 关键字,必须写在async修饰的函数中 21 async function demo02() { 22 try { 23 let res = await demo01() // 正常调用,返回promise 对象,加await 调用--》返回正常then的数据 24 console.log(res) 25 } catch (err) { 26 console.log('出错了') 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 demo02() // 它会等正常执行完成才会调用 32 console.log('222222') 33 </script>
axios其它配置项
//axios.get() //axios.post() axios({ url:'地址', method:'post', headers: {'token': 'adsfa.adsfa.adsf',contentType:'application/json'}, params: {name: lqz,age:19}, data: {firstName: 'Fred'}, timeout: 1000, }) // 更多参数 { //1 `url` 是用于请求的服务器 URL url: '/user', //2 `method` 是创建请求时使用的方法 method: 'get', // 默认值 //3 `baseURL` 将自动加在 `url` 前面,除非 `url` 是一个绝对 URL。 // 它可以通过设置一个 `baseURL` 便于为 axios 实例的方法传递相对 URL baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/', //4 `transformRequest` 允许在向服务器发送前,修改请求数据 // 它只能用于 'PUT', 'POST' 和 'PATCH' 这几个请求方法 // 数组中最后一个函数必须返回一个字符串, 一个Buffer实例,ArrayBuffer,FormData,或 Stream // 你可以修改请求头。 transformRequest: [function (data, headers) { // 对发送的 data 进行任意转换处理 return data; }], // `transformResponse` 在传递给 then/catch 前,允许修改响应数据 transformResponse: [function (data) { // 对接收的 data 进行任意转换处理 return data; }], //5 自定义请求头 headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'}, //6 params` 是与请求一起发送的 URL 参数 // 必须是一个简单对象或 URLSearchParams 对象 params: { ID: 12345 }, // 7 aramsSerializer`是可选方法,主要用于序列化`params` // (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.jquery.com/jquery.param/) paramsSerializer: function (params) { return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: 'brackets'}) }, //8 data` 是作为请求体被发送的数据 // 仅适用 'PUT', 'POST', 'DELETE 和 'PATCH' 请求方法 // 在没有设置 `transformRequest` 时,则必须是以下类型之一: // - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams // - 浏览器专属: FormData, File, Blob // - Node 专属: Stream, Buffer data: { firstName: 'Fred' }, // 发送请求体数据的可选语法 // 请求方式 post // 只有 value 会被发送,key 则不会 data: 'Country=Brasil&City=Belo Horizonte', // 0imeout` 指定请求超时的毫秒数。 // 如果请求时间超过 `timeout` 的值,则请求会被中断 timeout: 1000, // 默认值是 `0` (永不超时) // 11 thCredentials` 表示跨域请求时是否需要使用凭证 withCredentials: false, // default //12 dapter` 允许自定义处理请求,这使测试更加容易。 // 返回一个 promise 并提供一个有效的响应 (参见 lib/adapters/README.md)。 adapter: function (config) { /* ... */ }, //13 auth` HTTP Basic Auth auth: { username: 'lqz' password: '123‘ }, //14 `responseType` 表示浏览器将要响应的数据类型 // 选项包括: 'arraybuffer', 'document', 'json', 'text', 'stream' // 浏览器专属:'blob' responseType: 'json', // 默认值 //15 `responseEncoding` 表示用于解码响应的编码 (Node.js 专属) // 注意:忽略 `responseType` 的值为 'stream',或者是客户端请求 // Note: Ignored for `responseType` of 'stream' or client-side requests responseEncoding: 'utf8', // 默认值 //16 `xsrfCookieName` 是 xsrf token 的值,被用作 cookie 的名称 xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', // 默认值 //17 `xsrfHeaderName` 是带有 xsrf token 值的http 请求头名称 xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', // 默认值 //18 `onUploadProgress` 允许为上传处理进度事件 // 浏览器专属 onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) { // 处理原生进度事件 }, //19 `onDownloadProgress` 允许为下载处理进度事件 // 浏览器专属 onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) { // 处理原生进度事件 }, // 20 `maxContentLength` 定义了node.js中允许的HTTP响应内容的最大字节数 maxContentLength: 2000, //21 `maxBodyLength`(仅Node)定义允许的http请求内容的最大字节数 maxBodyLength: 2000, // 22 `validateStatus` 定义了对于给定的 HTTP状态码是 resolve 还是 reject promise。 // 如果 `validateStatus` 返回 `true` (或者设置为 `null` 或 `undefined`), // 则promise 将会 resolved,否则是 rejected。 validateStatus: function (status) { return status >= 200 && status < 300; // 默认值 }, // 23 `maxRedirects` 定义了在node.js中要遵循的最大重定向数。 // 如果设置为0,则不会进行重定向 maxRedirects: 5, // 默认值 //24 `socketPath` 定义了在node.js中使用的UNIX套接字。 // e.g. '/var/run/docker.sock' 发送请求到 docker 守护进程。 // 只能指定 `socketPath` 或 `proxy` 。 // 若都指定,这使用 `socketPath` 。 socketPath: null, // default //25 `httpAgent` and `httpsAgent` define a custom agent to be used when performing http // and https requests, respectively, in node.js. This allows options to be added like // `keepAlive` that are not enabled by default. httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }), httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }), //26 `proxy` 定义了代理服务器的主机名,端口和协议。 // 您可以使用常规的`http_proxy` 和 `https_proxy` 环境变量。 // 使用 `false` 可以禁用代理功能,同时环境变量也会被忽略。 // `auth`表示应使用HTTP Basic auth连接到代理,并且提供凭据。 // 这将设置一个 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求头,它会覆盖 `headers` 中已存在的自定义 `Proxy-Authorization` 请求头。 // 如果代理服务器使用 HTTPS,则必须设置 protocol 为`https` proxy: { protocol: 'https', host: '127.0.0.1', port: 9000, auth: { username: 'lqz', password: '123' } }, // 27 see https://axios-http.com/zh/docs/cancellation cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) { }), // 28 `decompress` indicates whether or not the response body should be decompressed // automatically. If set to `true` will also remove the 'content-encoding' header // from the responses objects of all decompressed responses // - Node only (XHR cannot turn off decompression) decompress: true // 默认值 }
。
。
。
【vue-router插件】
安装:npm install vue-router@4
main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import './style.css'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from "./router/index.js";
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app')
App.vue
<script setup> import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue' </script> <template> <router-view></router-view> </template>
HomeView.vue-AboutView.vue--LoginView.vue
1 <script setup> 2 import {useRouter} from 'vue-router' 3 let router = useRouter() 4 function handleTo(){ 5 // router.push('/about') 6 // router.push({'name':'about',query:{name:'吉吉',age:8}}) 7 router.push({name:'about',params:{id:1}}) 8 } 9 </script> 10 11 <template> 12 <h1>首页</h1> 13 <h2>页面跳转</h2> 14 <router-link to="/about"><button>跳转到about-html跳</button></router-link> 15 <button @click="handleTo">js跳到about</button> 16 </template> 17 18 <style scoped> 19 20 </style> 21 22 23 ======================================== 24 <script setup> 25 //取出home页面传入的数据 26 import {useRoute} from 'vue-router' 27 28 let route = useRoute() 29 // console.log(route.query.name) 30 // let name=route.query.name 31 32 //路径中带数据取值 33 let id = route.params.id 34 </script> 35 36 <template> 37 <h1>about页面</h1> 38 <!-- <h1>{{name}}</h1>--> 39 <h1>{{ id }}</h1> 40 </template> 41 42 <style scoped> 43 44 </style> 45 46 ========================================== 47 <script setup></script> 48 49 <template> 50 <h1>登录</h1> 51 </template>
router/index.js
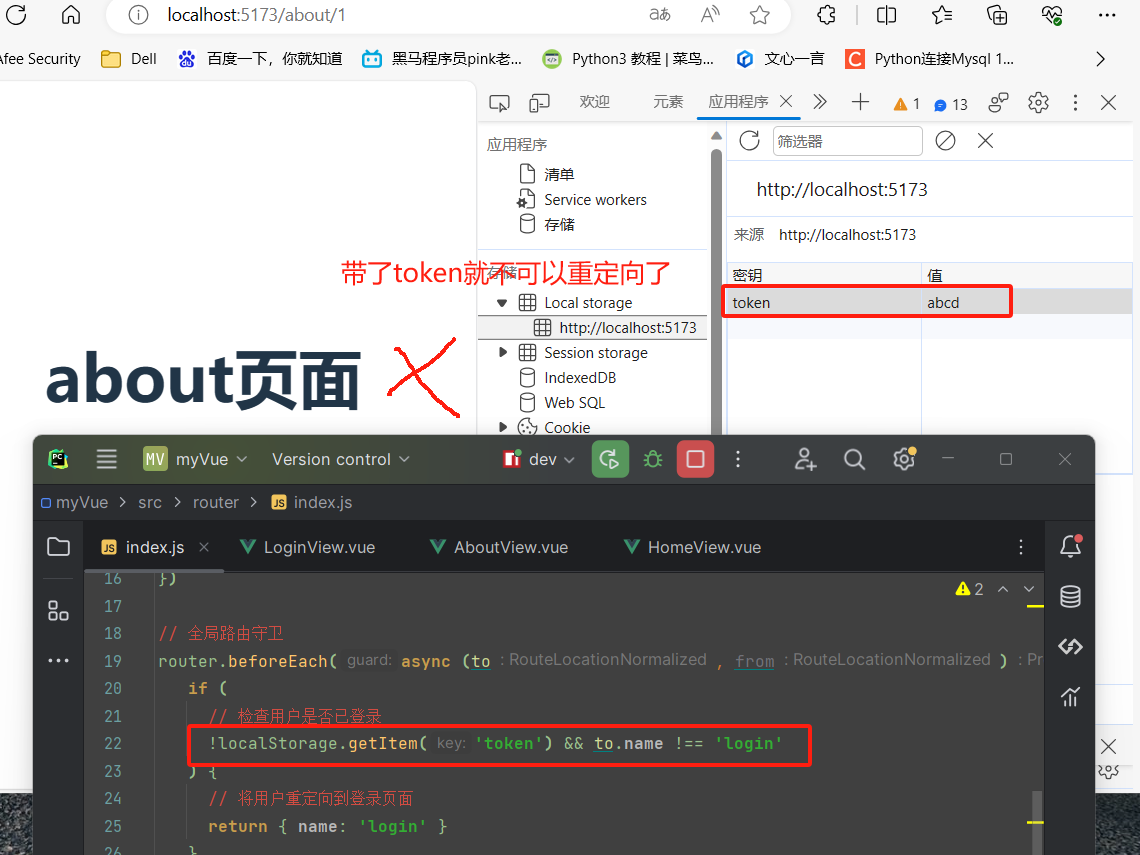
1 import {createRouter, createWebHashHistory, createWebHistory} from "vue-router"; 2 import HomeView from "../view/HomeView.vue"; 3 import AboutView from "../view/AboutView.vue"; 4 import LoginView from "../view/LoginView.vue"; 5 6 const routes = [ 7 {path: '/', name: 'home', component: HomeView}, 8 {path: '/about/:id', name: 'about', component: AboutView}, 9 {path: '/login', name: 'login', component: LoginView}, 10 ] 11 12 const router = createRouter({ 13 14 history: createWebHistory(), 15 routes, 16 }) 17 18 // 全局路由守卫 19 router.beforeEach(async (to, from) => { 20 if ( 21 // 检查用户是否已登录 22 !localStorage.getItem('token') && to.name !== 'login' 23 ) { 24 // 将用户重定向到登录页面 25 return { name: 'login' } 26 } 27 }) 28 export default router
。
。
【pinia】
状态管理器,统一状态管理,组件间通信
state、getter 和 action,我们可以假设这些概念相当于组件中的 data、 computed 和 methods
使用步骤: 1 安装 npm install pinia
2 在store/xx.js,写入代码,可以定义多个
3 main.js中使用插件
4 在组件中使用pinia的数据
store/counter.js
1 import {defineStore} from 'pinia' 2 3 export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', { 4 //1 定义变量 5 state: () => { 6 return { 7 count: 0, 8 hobby: '篮球' 9 } 10 }, 11 //2 这里面写方法,与后端交互或逻辑判断,再操作数据 12 actions: { 13 increment(id) { 14 // 跟后端交互--》把good_id--》真正加购物车 15 this.count++ 16 }, 17 changeHobby(hobby) { 18 this.hobby = hobby 19 } 20 }, 21 //3 getter-->获取数据 22 getters: { 23 getCount() { 24 return this.count 25 }, 26 }, 27 })
main.js
import {createPinia} from 'pinia'
const pinia = createPinia()
createApp(App).use(router).use(pinia).mount('#app')
goodsList组件
1 <script setup> 2 import {reactive} from "vue"; 3 import ShoppingCard from "./ShoppingCard.vue"; 4 //1.引入pinia的store/counter.js 5 import {useCounterStore} from "../store/counter"; 6 7 let counter = useCounterStore() 8 9 //2.页面渲染数据,都通过counter对象来操作State、getter、action 10 const goodsList = reactive([ 11 {id: 1, name: '钢笔', price: 100}, 12 {id: 2, name: '毛笔', price: 20}, 13 {id: 3, name: '铅笔', price: 10}, 14 {id: 4, name: '圆珠笔', price: 15}, 15 ]) 16 17 //点击按钮修改 18 function handleAdd(id) { 19 console.log('加入购物车', id) 20 // counter.count++ 21 counter.increment() 22 // counter.getCount() 23 } 24 25 //测试pinia中的changeHobby 26 function changeHobby() { 27 counter.hobby = '打羽毛球' 28 } 29 </script> 30 31 <template> 32 <h2>商品</h2> 33 <ShoppingCard/> 34 <hr> 35 <div> 36 <div v-for="item in goodsList"> 37 <span>商品名:{{ item.name }}</span> 38 <span>价格:{{ item.price }}</span> 39 <button @click="handleAdd(item.id)">加入购物车</button> 40 </div> 41 <button @click="changeHobby">点我变pinia中的hobby</button> 42 </div> 43 </template> 44 45 <style scoped> 46 47 </style>
shoppingCar组件
1 <script setup> 2 //1.引入pinia的store/counter.js 3 import {useCounterStore} from "../store/counter"; 4 5 let counter = useCounterStore() 6 </script> 7 8 <template> 9 <h2>购物车</h2> 10 <p>数量:{{ counter.getCount }}</p> 11 <p>爱好修改:{{ counter.hobby }}</p> 12 </template>
。
。
【elementui-plus】
# 0 ant-design :https://www.antdv.com/components/message-cn # 1 官网:https://element-plus.org/zh-CN/#/zh-CN # 2 安装 cnpm install element-plus --save # 3 main.js中注册 import ElementPlus from 'element-plus' import 'element-plus/dist/index.css' createApp(App).use(router).use(pinia).use(ElementPlus).mount('#app') # 4 组件中使用 <script setup> import { ElMessage } from 'element-plus' const open2 = () => { ElMessage({ message: '恭喜您成功了', type: 'success', }) } </script> <template> <div class="mb-4"> <el-button>Default</el-button> <el-button type="primary">Primary</el-button> <el-button type="success">Success</el-button> <el-button type="info">Info</el-button> <el-button type="warning">Warning</el-button> <el-button type="danger">Danger</el-button> </div> <div> <el-card style="max-width: 480px"> <template #header>Yummy hamburger</template> <img src="https://shadow.elemecdn.com/app/element/hamburger.9cf7b091-55e9-11e9-a976-7f4d0b07eef6.png" style="width: 100%" /> </el-card> </div> <div> <el-button :plain="true" @click="open2">Message</el-button> </div> </template> <style scoped> </style>



