C#学习之C#3.0语言功能
1. 隐式类型局部变量
使用var声明变量,编译器会根据初始化局部变量的初始值推断变量的类型。
控制台程序:
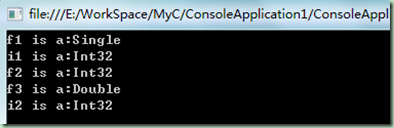
static void ImplicitVar() { //隐式声明几部变量:var 变量名称=初始值 float f1 = 0; int i1 = 0; var f2 = 0; var f3 = 0.0; var i2 = 0; Console.WriteLine("f1 is a:{0}", f1.GetType().Name); Console.WriteLine("i1 is a:{0}", i1.GetType().Name); Console.WriteLine("f2 is a:{0}", f2.GetType().Name); Console.WriteLine("f3 is a:{0}", f3.GetType().Name); Console.WriteLine("i2 is a:{0}", i2.GetType().Name); Console.ReadLine(); }
1.1 var在foreach语句中的使用
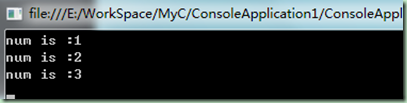
static void VarInForeach() { var numbers = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; foreach (int num in numbers)//使用强类型 Int32 //foreach (var num in numbers)//使用var { Console.WriteLine("num is :{0}", num); } Console.ReadLine(); }
1.2 隐式类型变量限制
- 不能使用var定义返回值、参数的类型或类型的数据成员。
- var声明的变量必须在声明时赋值,且不能为null。
1.3 隐式类型局部数组
static void ImplicitArray() { var a = new[] { 1, 2, 3 }; Console.WriteLine("a is a:{0}", a.ToString()); var b = new[] { "a", "b" }; Console.WriteLine("b is a:{0}", b.ToString()); }
1.4 隐式类型数据是强类型数据
2. 自动属性
class Car { //标准属性语法 //private string carName = string.Empty; //public string PetName //{ // get { return carName; } // set { carName = value; } //} //自动属性语法 public string PetName { get; set; } }
2.1 限制自动属性的访问
public string PetName { get; protected set; }
2.2 有关自动属性和默认值
使用自动属性封装布尔或数值类型,隐藏的支持字段被设置为一个可直接使用的安全的默认值。如包装引用类型,默认值为null。
3. 扩展方法
使用扩展方法,可为预编译的类型添加功能。扩展方法需在顶级静态类中定义。
限制:1)必须把方法定义在静态类中,每一个扩展方法也必须声明成静态的;2)第一个参数需用this修饰;3)扩展方法只能被内存中正确的实例调用,或通过所处的静态类被调用。
3.1 扩展方法定义与调用
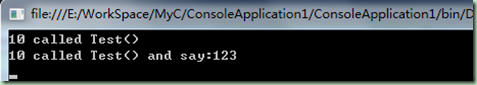
static class TestClass { public static void Test(this int i) { Console.WriteLine("{0} called Test()", i); } public static void Test(this int i,string Msg)//仅需第一个参数使用 this 修饰 { Console.WriteLine("{0} called Test() and say:{1}", i,Msg); } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //通过实例调用 int i = 10; i.Test(); i.Test("123"); //静态调用 TestClass.Test(20); TestClass.Test(20, "321"); Console.ReadLine(); } }
3.2 扩展方法作用域
扩展方法不能直接访问它扩展的类型的成员,但可使用this限定的参数来访问要扩展类型所有公共成员。
class Car { public int speed; public int speedup() { return ++speed; } } static class TestCar { public static int speeddown(this Car c) { return --c.speed; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Car c = new Car(); c.speed = 1; c.speedup(); Console.WriteLine("now speed is {0}", c.speed); c.speeddown(); Console.WriteLine("now speed is {0}", c.speed); Console.ReadLine(); } }
3.3 导入定义了扩展方法的类型
扩展方法受限于所在的命名空间,其他命名空间使用需要显示的引入。
3.4 扩展方法的智能感知
“向下”箭头标注的方法为扩展方法。
3.5 构建和使用扩展库
创建扩展库dll,在其他项目中引用该dll即可使用。
3.6 通过扩展方法来扩展接口类型
interface IBasicMath { int Add(int x, int y); } class MyCalc : IBasicMath { public int Add(int x, int y) { return x + y; } } static class MathTest { //扩展IBasicMath方法及其实现 //说明:接口只提供定义,不提供实现,然而此处必须这样定义 public static int sub(this IBasicMath ibm, int x, int y) { return x - y; } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MyCalc c = new MyCalc(); Console.WriteLine("1+2={0}", c.Add(1, 2)); Console.WriteLine("1-2={0}", c.sub(1, 2)); //强制转化成 IBasicMath 来调用 sub 扩展方法 Console.WriteLine("1-2={0}", ((IBasicMath)c).sub(1, 2)); Console.ReadLine(); }
4. 分部方法(partial)
允许在一个文件中定义方法原型,在另外一个文件中是实现。使用分部方法定义轻量级事件,开发人员可以实现或不实现,轻量级事件方法使用0n前缀。
注意点:1)分部方法只能定义在分部类中;2)分部方法必须返回viod;3)分部方法可以是静态的或实例级别的;4)分部方法可以有参数(包括被this、ref或params修饰的参数,但不能有out修饰符);5)分部方法总是隐式私有。
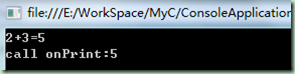
//program.cs using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { partial class PartTest { public void add(int x, int y) { Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}", x, y, x + y); onPrint(x + y); } partial void onPrint(int i);//整个项目对该分部方法未进行实现,编译时会屏蔽此方法 } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { PartTest pt = new PartTest(); pt.add(2, 3); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
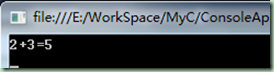
//codeFile1.cs using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { partial class PartTest { partial void onPrint(int i)//进行分部方法实现 { Console.WriteLine("call print:{0}", i); } } }
5. 对象初始化器
5.1 使用初始化语法
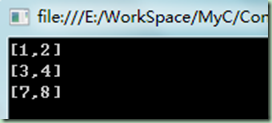
public class Point { private int x, y; public Point() { x = -1; y = -2; } public Point(int x1, int y1) { x = x1; y = y1; } public int x1 { get { return x; } set { x = value; } } public int y1 { get { return y; } set { y = value; } } public override string ToString() { return string.Format("[{0},{1}]", x, y); } }
static void Main(string[] args) { Point p1 = new Point { x1 = 1, y1 = 2 };//隐式调用构造函数 Point p2 = new Point() { x1 = 3, y1 = 4 };//显示调用构造函数 Point p3 = new Point(5, 6) { x1 = 7, y1 = 8 };//调用自定义构造函数 Console.WriteLine(p1.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(p2.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(p3.ToString()); Console.ReadLine(); }
6. 匿名类型
使用var创建匿名类型。
匿名类型直接继承System.Object,并且重写方法Equals()、GetHashCode()、ToString()。
限制:1)没有控制你们类型的名称;2)匿名类型继承System.Object;3)匿名类型不支持事件、自定义方法、自定义运算符和自定义重写;4)匿名类型是隐式封闭的(sealed);5)匿名类型的实例创建只使用默认构造函数。
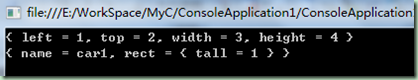
static void Main(string[] args) { var Rect = new { left = 1, top = 2, width = 3, height = 4 }; Console.WriteLine(Rect.ToString()); //包含匿名类型的匿名类型 var Car = new { name = "car1", rect = new { tall = 1 } }; Console.WriteLine(Car.ToString()); Console.ReadLine(); }