文件1
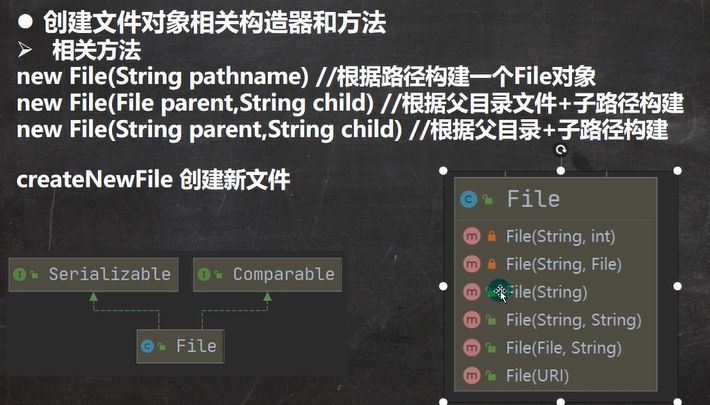
创建方法(3种)

public class FileCreate { public static void main(String[] args) { } //方式1 new File(String pathname) @Test public void create01() { String filePath = "e:\\news1.txt"; File file = new File(filePath); //这里的file对象,在java程序中,只是一个对象 try { file.createNewFile(); //只有执行了createNewFile 方法,才会真正的,在磁盘创建该文件 System.out.println("文件创建成功"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //方式2 new File(File parent,String child) //根据父目录文件+子路径构建 //e:\\news2.txt @Test public void create02() { File parentFile = new File("e:\\"); String fileName = "news2.txt"; //只有执行了createNewFile 方法,才会真正的,在磁盘创建该文件 File file = new File(parentFile, fileName); //这里的file对象,在java程序中,只是一个对象 try { file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功~"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //方式3 new File(String parent,String child) //根据父目录+子路径构建 @Test public void create03() { //String parentPath = "e:\\"; String parentPath = "e:\\"; String fileName = "news4.txt"; File file = new File(parentPath, fileName); try { file.createNewFile(); System.out.println("创建成功~"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //下面四个都是抽象类 // //InputStream //OutputStream //Reader //字符输入流 //Writer //字符输出流 }
获取文件的信息


public void info() { //先创建文件对象 File file = new File("e:\\news1.txt"); //调用相应的方法,得到对应信息 System.out.println("文件名字=" + file.getName()); //getName、getAbsolutePath、getParent、length、exists、isFile、isDirectory System.out.println("文件绝对路径=" + file.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent()); System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length()); System.out.println("文件是否存在=" + file.exists());//T System.out.println("是不是一个文件=" + file.isFile());//T System.out.println("是不是一个目录=" + file.isDirectory());//F }
字节流
读取文件1:单字节,(效率低,读1字节的 英文 符号 数字,不能读汉字 )

public void readFile01() { String filePath = "e:\\news1.txt"; int readData = 0; FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try { //创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath); //从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。 如果没有输入可用,此方法将阻止。 //如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕 while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) { System.out.print((char)readData);//转成char显示 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭文件流,释放资源. try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
读取文件2:X字节(自定义每次读取的字节数,提高效率)

public void readFile02() { String filePath = "e:\\news1.txt"; //字节数组 byte[] buf = new byte[9]; //一次读取8个字节. int readLen = 0; FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; try { //创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件 fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath); //从该输入流读取最多b.length字节的数据到字节数组。 此方法将阻塞,直到某些输入可用。 //如果返回-1 , 表示读取完毕 //如果读取正常, 返回实际读取的字节数 while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen));//显示 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭文件流,释放资源. try { fileInputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
写入文件

public void writeFile() { //创建 FileOutputStream对象 String filePath = "e:\\a.txt"; FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; try { //得到 FileOutputStream对象 对象 //老师说明 //1. new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式,当写入内容是,会覆盖原来的内容 //2. new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式,当写入内容是,是追加到文件后面 fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath, true); //写入一个字节 //fileOutputStream.write('H');// //写入字符串 String str = "杜甫01,hello,world!"; //str.getBytes() 可以把 字符串-> 字节数组 //fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes()); /* write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将 len字节从位于偏移量 off的指定字节数组写入此文件输出流 */ // fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(), 0, 3); fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { fileOutputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
文件拷贝

public static void main(String[] args) { //完成 文件拷贝,将 e:\\1648370.jpg 拷贝 c:\\ //思路分析 //1. 创建文件的输入流 , 将文件读入到程序 //2. 创建文件的输出流, 将读取到的文件数据,写入到指定的文件. String srcFilePath = "e:\\1648370.jpg"; String destFilePath = "e:\\Koala3.jpg"; FileInputStream fileInputStream = null; FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null; try { fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath); fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(destFilePath); //定义一个字节数组,提高读取效果 byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; int readLen = 0; while ((readLen = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1) { //读取到后,就写入到文件 通过 fileOutputStream //即,是一边读,一边写 fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, readLen);//一定要使用这个方法 } System.out.println("拷贝ok~"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { //关闭输入流和输出流,释放资源 if (fileInputStream != null) { fileInputStream.close(); } if (fileOutputStream != null) { fileOutputStream.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
字符流
读取文件的两种方法:单个字符+字符数组

/** * 单个字符读取文件 */ @Test public void readFile01() { String filePath = "e:\\story.txt"; FileReader fileReader = null; int data = 0; //1. 创建FileReader对象 try { fileReader = new FileReader(filePath); //循环读取 使用read, 单个字符读取 while ((data = fileReader.read()) != -1) { System.out.print((char) data); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (fileReader != null) { fileReader.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 字符数组读取文件 */ @Test public void readFile02() { System.out.println("~~~readFile02 ~~~"); String filePath = "e:\\story.txt"; FileReader fileReader = null; int readLen = 0; char[] buf = new char[8]; //1. 创建FileReader对象 try { fileReader = new FileReader(filePath); //循环读取 使用read(buf), 返回的是实际读取到的字符数 //如果返回-1, 说明到文件结束 while ((readLen = fileReader.read(buf)) != -1) { System.out.print(new String(buf, 0, readLen)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (fileReader != null) { fileReader.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
写入文件

public static void main(String[] args) { String filePath = "e:\\note.txt"; //创建FileWriter对象 FileWriter fileWriter = null; char[] chars = {'a', 'b', 'c'}; try { fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);//默认是覆盖写入 // 3) write(int):写入单个字符 fileWriter.write('H'); // 4) write(char[]):写入指定数组 fileWriter.write(chars); // 5) write(char[],off,len):写入指定数组的指定部分:韩顺平 fileWriter.write("韩顺平教育".toCharArray(), 0, 3); // 6) write(string):写入整个字符串 fileWriter.write(" 你好北京~"); fileWriter.write("风雨之后,定见彩虹"); // 7) write(string,off,len):写入字符串的指定部分 fileWriter.write("上海天津", 0, 2); //在数据量大的情况下,可以使用循环操作. } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { //fileWriter.flush(); //关闭文件流,等价 flush() + 关闭 fileWriter.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("程序结束..."); }
节点流和处理流

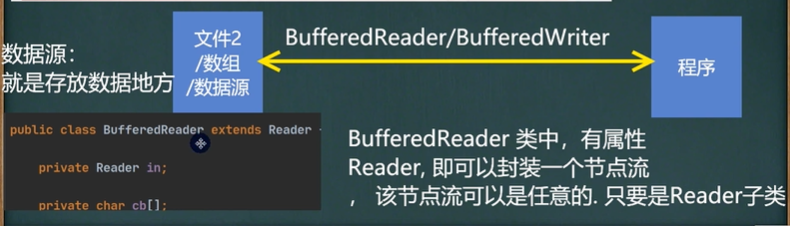

BufferedReader(可以按行读取)-字符

public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String filePath = "e:\\a.java"; //创建bufferedReader BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath)); //读取 String line; //按行读取, 效率高 //说明 //1. bufferedReader.readLine() 是按行读取文件 //2. 当返回null 时,表示文件读取完毕 while ((line = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } //关闭流, 这里注意,只需要关闭 BufferedReader ,因为底层会自动的去关闭 节点流 //FileReader。 /* public void close() throws IOException { synchronized (lock) { if (in == null) return; try { in.close();//in 就是我们传入的 new FileReader(filePath), 关闭了. } finally { in = null; cb = null; } } } */ bufferedReader.close(); }
BufferedWriter-字符

public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "e:\\ok.txt"; //创建BufferedWriter //说明: //1. new FileWriter(filePath, true) 表示以追加的方式写入 //2. new FileWriter(filePath) , 表示以覆盖的方式写入 BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath)); bufferedWriter.write("hello, 韩顺平教育!"); bufferedWriter.newLine();//插入一个和系统相关的换行 bufferedWriter.write("hello2, 韩顺平教育!"); bufferedWriter.newLine(); bufferedWriter.write("hello3, 韩顺平教育!"); bufferedWriter.newLine(); //说明:关闭外层流即可 , 传入的 new FileWriter(filePath) ,会在底层关闭 bufferedWriter.close(); }
Copy(字符)

public static void main(String[] args) { //老韩说明 //1. BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter 是安装字符操作 //2. 不要去操作 二进制文件[声音,视频,doc, pdf ], 可能造成文件损坏 //BufferedInputStream //BufferedOutputStream String srcFilePath = "e:\\a.java"; String destFilePath = "e:\\a2.java"; // String srcFilePath = "e:\\0245_韩顺平零基础学Java_引出this.avi"; // String destFilePath = "e:\\a2韩顺平.avi"; BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; String line; try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcFilePath)); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destFilePath)); //说明: readLine 读取一行内容,但是没有换行 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { //每读取一行,就写入 bw.write(line); //插入一个换行 bw.newLine(); } System.out.println("拷贝完毕..."); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭流 try { if(br != null) { br.close(); } if(bw != null) { bw.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Copy(字节)

public static void main(String[] args) { // String srcFilePath = "e:\\Koala.jpg"; // String destFilePath = "e:\\hsp.jpg"; // String srcFilePath = "e:\\0245_韩顺平零基础学Java_引出this.avi"; // String destFilePath = "e:\\hsp.avi"; String srcFilePath = "e:\\a.java"; String destFilePath = "e:\\a3.java"; //创建BufferedOutputStream对象BufferedInputStream对象 BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { //因为 FileInputStream 是 InputStream 子类 bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFilePath)); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFilePath)); //循环的读取文件,并写入到 destFilePath byte[] buff = new byte[1024]; int readLen = 0; //当返回 -1 时,就表示文件读取完毕 while ((readLen = bis.read(buff)) != -1) { bos.write(buff, 0, readLen); } System.out.println("文件拷贝完毕~~~"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭流 , 关闭外层的处理流即可,底层会去关闭节点流 try { if(bis != null) { bis.close(); } if(bos != null) { bos.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }







· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术