Spring Boot+Mybatis:实现数据库登录注册与两种properties配置参数读取
〇、参考资料
1、hutool介绍
https://blog.csdn.net/abst122/article/details/124091375
2、Spring Boot+Mybatis实现登录注册
https://www.cnblogs.com/wiki918/p/16221758.html
3、Spring Boot读取自定义配置文件
https://www.yisu.com/zixun/366877.html
4、Spring Boot读取properties配置文件的两种方式
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42352733/article/details/121830775
一、概述
1、技术栈
Spring Boot+Mybatis+Lombok+Hutool+Slf4j+thymeleaf
2、项目截图
二、登录注册(后台)
1、数据库设计
表结构:
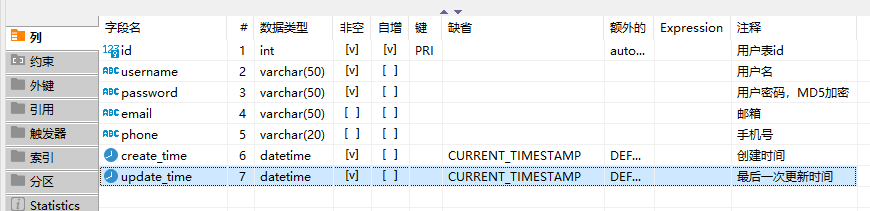
表数据:

建表语句:
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户表id',
`username` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`password` varchar(50) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户密码,MD5加密',
`email` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
`phone` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '最后一次更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=19 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci COMMENT='用户表'2、POJO(Entity)编写-UserBean.java
package com.boulderaitech.entity;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
@Data //提供了set、get方法及toString
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class UserBean implements Serializable {
private Integer id; //为什么用Integer,不用int
private String username;
private String password;
private String email;
private String phone;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-mm HH:mm:ss")
private Date create_time;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-mm HH:mm:ss")
private Date update_time;
}3、Controller编写-UserController.java
package com.boulderaitech.controller;
import cn.hutool.core.lang.Opt;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
import com.boulderaitech.entity.UserBean;
import com.boulderaitech.service.UserService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Slf4j
@Controller // 不能用@RestController
public class UserController {
//将Service注入Web层
@Autowired
UserService userService;
//用户测试
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping("/register")
public String register() {
return "signup";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String login(String username,String password) {
UserBean userBean = userService.login(username,password);
log.info("username:{}",username);
log.info("password:{}",password);
//hutool-core 核心,包括Bean操作、日期、各种Util等
if(StrUtil.isNotEmpty(username)) {
if(userBean != null) {
return "success";
//方法引用-遍历集合
//Opt.ofEmptyAble(userBean).ifPresent(System.out::println);
}
} else {
return "用户名不允许为空";
}
return "error";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/signup", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String signup(String username,String password) {
userService.insert(username,password);
return "success";
}
}4、Service编写-UserService.java
package com.boulderaitech.service;
import com.boulderaitech.entity.UserBean;
import com.boulderaitech.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class UserService {
//将dao层属性注入service层,为什么不用Autowired
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
public UserBean login(String username, String password) {
return userMapper.getInfo(username,password);
}
public void insert(String username, String password) {
userMapper.saveUser(username,password);
}
}5、Mapper编写-UserMapper.java
package com.boulderaitech.mapper;
import com.boulderaitech.entity.UserBean;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
@Mapper //添加Mapper注解,就不用写xml的mapper映射文件了
public interface UserMapper {
//多个参数要加@Param修饰
//思考:xml中的<include>代码片段怎么配
@Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE username=#{username} AND password= #{password}")
UserBean getInfo(@Param("username") String username,@Param("password") String password);
@Insert("INSERT INTO user(username,password) VALUE(#{username},#{password})")
void saveUser(@Param("username") String username,@Param("password") String password);
}6、配置文件编写-application.properties
# Spring Boot端口号
server.port=9088
# 数据源配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.password=qaz123
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.40.111:3306/visualization?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/7、启动类编写-KettleProcessorApplication.java
package com.boulderaitech;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* Spring Boot启动类,加Spring Boot注解,调用Spring的静态run方法
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class KettleProcessorApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KettleProcessorApplication.class);
}
}三、登录注册(前台)
1、登录页面-login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>login</title>
</head>
<body>
<form role="form" action = "/login" method="post">
账号:<input type="text" id="username" name = "username"> <br>
密码:<input type="password" id = "password" name = "password"> <br>
<input type="submit" id = "login" value = "登录">
</form>
<a href="/register">注册</a>
</body>
</html>2、注册页面-signup.html
<!--注册页面-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>注册</title>
</head>
<body>
<form role="form" action="/signup" method="post">
请输入姓名:<input type="text" name="username" id="name"><br>
请输入密码:<input type="password" name="password" id="password"><br>
<input type="submit" name="sign" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>3、成功页面-success.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>success</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>欢迎,恭喜登录成功/注册成功</h1>
</body>
</html>4、失败页面-error.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>error</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录失败!</h1>
</body>
</html>四、配置读取
1、配置编写-kettle.properties
# 读取properties的两种方式:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42352733/article/details/121830775
environment=xuelei-www
kettle.repository.type=database
kettle.repository.username=admin
kettle.repository.password=admin2、POJO(Entity)编写-KettleRepositoryBean.java
package com.boulderaitech.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "kettle.repository")
public class KettleRepositoryBean {
private String type;
private String username;
private String password;
}3、Controller编写-PropertiesController.java
package com.boulderaitech.controller;
import com.boulderaitech.entity.KettleRepositoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController //Controller和RestCOntroller的区别
@PropertySource("classpath:kettle.properties") //默认是application.properties
public class PropertiesController {
@Value("${environment}")
private String envName;
@Autowired
private KettleRepositoryBean kettleRepositoryBean;
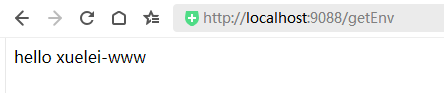
@RequestMapping("/getEnv")
public String getEnv() {
return "hello " + envName;
}
@RequestMapping("/getRepoInfo")
public String getRepoInfo() {
return "hello " + kettleRepositoryBean.toString();
}
}五、验证
1、登录

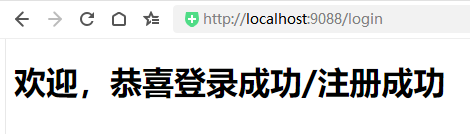
2、注册

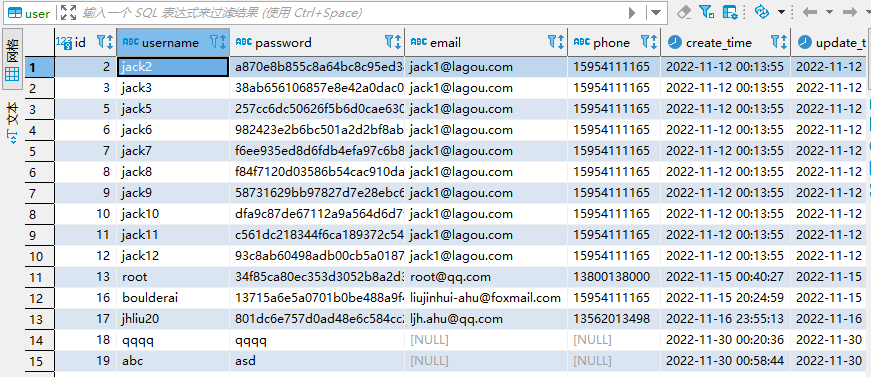
3、读取单个配置
4、读取实体类配置(多个)

本文来自博客园,作者:哥们要飞,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujinhui/p/16937229.html



