【算法题型总结】--6、链表
一、目录
- 反转链表
- 链表中的节点,每k个一组翻转
- 移除链表元素
- 两两交换链表中的节点
- 删除链表的倒数第n个节点
- 链表相交
- 环形链表的入口
二、题目
1、反转链表、链表反转
注意:边界条件
解法1:双指针
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
解法2:递归
// 递归
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(null, head);
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return prev;
}
ListNode temp = null;
temp = cur.next;// 先保存下一个节点
cur.next = prev;// 反转
// 更新prev、cur位置
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
return reverse(prev, cur);
}
}

解法:先除以k双层循环,再对剩余的反转
//借助Stack,每放进k个,就pop()出来 public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) { // write code here Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>(); ListNode newNode=new ListNode(0); ListNode temp=newNode; ListNode cur=head; int len=0; while(cur!=null){ len++; cur=cur.next; } int time=len/k; for(int i=0;i<time;i++){ for(int j=0;j<k;j++){ stack.push(head.val); head=head.next; } while(!stack.isEmpty()){ temp.next=new ListNode(stack.pop()); temp=temp.next; } } while(head!=null){ temp.next=head; temp=temp.next; head=head.next; } return newNode.next; }
3、移除链表元素
题意:删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
输出:[1,2,3,4,5]
考虑虚拟节点--头节点的值即为
/**
* 添加虚节点方式
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 因为删除可能涉及到头节点,所以设置dummy节点,统一操作
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
/**
* 不添加虚拟节点方式
* 时间复杂度 O(n)
* 空间复杂度 O(1)
* @param head
* @param val
* @return
*/
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
while (head != null && head.val == val) {
head = head.next;
}
// 已经为null,提前退出
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 已确定当前head.val != val
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return head;
}

解法1:递归
// 递归版本
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// base case 退出提交
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// 获取当前节点的下一个节点
ListNode next = head.next;
// 进行递归
ListNode newNode = swapPairs(next.next);
// 这里进行交换
next.next = head;
head.next = newNode;
return next;
}
}
解法2:虚拟头节点
// 虚拟头结点
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummyNode;
while (prev.next != null && prev.next.next != null) {
ListNode temp = head.next.next; // 缓存 next
prev.next = head.next; // 将 prev 的 next 改为 head 的 next
head.next.next = head; // 将 head.next(prev.next) 的next,指向 head
head.next = temp; // 将head 的 next 接上缓存的temp
prev = head; // 步进1位
head = head.next; // 步进1位
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
进阶:你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
解法:建立虚拟头节点
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode slow = dummy;
ListNode fast = dummy;
while (n-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
// 记住 待删除节点slow 的上一节点
ListNode prev = null;
while (fast != null) {
prev = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
// 上一节点的next指针绕过 待删除节点slow 直接指向slow的下一节点
prev.next = slow.next;
// 释放 待删除节点slow 的next指针, 这句删掉也能AC
slow.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
}
6、链表相交
方法:引用完全相同-计算链表长度之差,从长度相等的位置往后找
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode curA = headA;
ListNode curB = headB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
while (curA != null) { // 求链表A的长度
lenA++;
curA = curA.next;
}
while (curB != null) { // 求链表B的长度
lenB++;
curB = curB.next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
// 让curA为最长链表的头,lenA为其长度
if (lenB > lenA) {
//1. swap (lenA, lenB);
int tmpLen = lenA;
lenA = lenB;
lenB = tmpLen;
//2. swap (curA, curB);
ListNode tmpNode = curA;
curA = curB;
curB = tmpNode;
}
// 求长度差
int gap = lenA - lenB;
// 让curA和curB在同一起点上(末尾位置对齐)
while (gap-- > 0) {
curA = curA.next;
}
// 遍历curA 和 curB,遇到相同则直接返回
while (curA != null) {
if (curA == curB) {
return curA;
}
curA = curA.next;
curB = curB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
7、环形链表的入口
题意: 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
判断有环:可以使用快慢指针法, 分别定义 fast 和 slow指针,从头结点出发,fast指针每次移动两个节点,slow指针每次移动一个节点,如果 fast 和 slow指针在途中相遇 ,说明这个链表有环。
找到入口:从头结点出发一个指针,从相遇节点也出发一个指针,这两个指针每次只走一个节点, 那么当这两个指针相遇的时候就是 环形入口的节点。
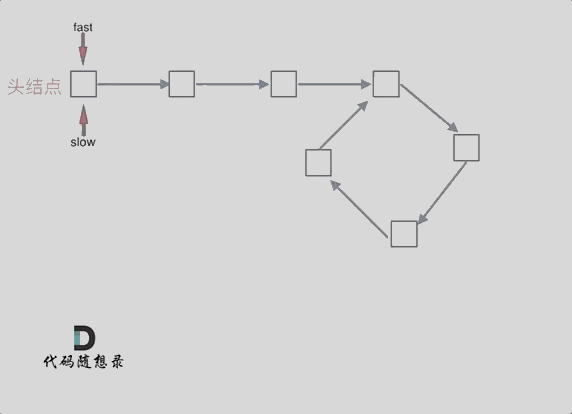
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {// 有环
ListNode index1 = fast;
ListNode index2 = head;
// 两个指针,从头结点和相遇结点,各走一步,直到相遇,相遇点即为环入口
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1.next;
index2 = index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}
本文来自博客园,作者:哥们要飞,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujinhui/p/15240640.html



