【Java SE进阶】Day10 缓冲流、转换流、序列化流 、打印流
一、缓冲流
1、概述
- 比普通流更强大的IO流,可以增加读写的效率
- 组成
- 缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream、BufferedReader
- 缓冲输出流:BufferedOutputStream、BufferedWriter
1、字节缓冲输出流(构造传递具体输出流)
- BufferedOutputStream
public class Demo01BufferOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建FileOutputStream对象,构造方法中绑定输出的目的地 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\a.txt"); //2.创建BufferedOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileOutputStream对象,提高FileOutputStream对象效率 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.使用BufferedOutputStream对象中的方法write,把数据写入到内部缓冲区中 bos.write("我把数据写入到内部缓冲区中".getBytes()); bos.flush(); bos.close(); } }
2、字节缓冲输入流
- BufferedInputStream
public class Demo02BufferedInputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建FileInputStream对象,构造方法中绑定要读取的数据源 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\a.txt"); //2.创建BufferedInputStream对象,构造方法中传递FileInputStream对象,提高FileInputStream对象的读取效率 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis); //3.使用BufferedInputStream对象中的read方法,读取文件 //int read()从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节 /*int len=0;//记录每次读取到的字节 while((len=bis.read())!=-1){ System.out.println(len); }*/ //int read(byte[] b) byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];//数组长度表示一次能读取的最大字节数 int len=0;//每次读取的有效字节个数 while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len)); } bis.close(); } }
- 效率测试
- 缓冲流+数组>缓冲流+单字节>普通流+数组>普通流+单字节
4、字符缓冲输出流
- BufferedWriter
public class Demo04BufferedWriter { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建字符缓冲输出流对象,构造方法中传递字符输出流 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\d.txt")); //2.调用字符缓冲输出流中的方法write,把数据写入到内存缓冲区中 for (int i=0;i<10;i++){ bw.write("传智播客"); bw.newLine(); bw.write("\n\r"); //sout调用的方法就是newLine } //3.调用字符缓冲输出流中的方法flush,把内存缓冲区的数据刷新到文件中 bw.flush(); //4.释放资源 bw.close(); } }
5、字符缓冲输入流
- BufferedReader
public class Demo05BufferedReader { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建字符缓冲输入流对象BufferedReader,构造方法中传递字符输入流 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\d.txt")); //2.使用字符输入流对象中的方法read和readLine读取文本 String line; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(line); } //3.释放资源 br.close(); } }
6、练习:对文本的内容进行排序
- HashMap会自动按照键的顺序进行排序
public class Demo06TestSort { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建一个HashMap集合对象,可以存储每行文本的学号,value存储每行的文本 HashMap<String,String> map=new HashMap<>();//【HashMap输入数据后会自动排序】 //2.创建字符缓冲输入流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输入流 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\in.txt")); //3.创建字符缓冲输出流对象,构造方法中绑定字符输出流 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\out.txt")); //4.使用字符缓冲输入流中的方法readline,逐行读取文本 String line; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ //5.对读取到的文本进行切割,获取行中的序号和文本内容 String[] arr=line.split("\\.");//转义字符 //6.将切割好的序号和文本中的内容存储到HashMap集合中(key是有序的,会自动排序) map.put(arr[0],arr[1]); } //7.遍历HashMap集合,获取每一个键值对 for (String key:map.keySet()){ String value = map.get(key); //8.将每一个键值对,转换为一个文本行 line= key +"."+ value; //9.将拼接好的文本,使用字符缓冲输出流中的方法write,写入到文件中 bw.write(line); bw.newLine();//写的时候不会把换行符写进去 } //10.释放资源 bw.close(); br.close(); } }
二、转换流
1、字符编码和字符集
- 字符编码
- 编码:字符按规则存储为二进制数
- 解码:将二进制数按规则解析显示
- 编码表:文字与二进制的对应规则
- 字符集Charset(编码表)
- ASCII
- GBK字符集:双字节编码
- Unicode字符集(UTF-8等):中文3个字节编码
2、编解码引出的问题
- IDEA默认以UTF-8编码,而windows默认为GBK编码
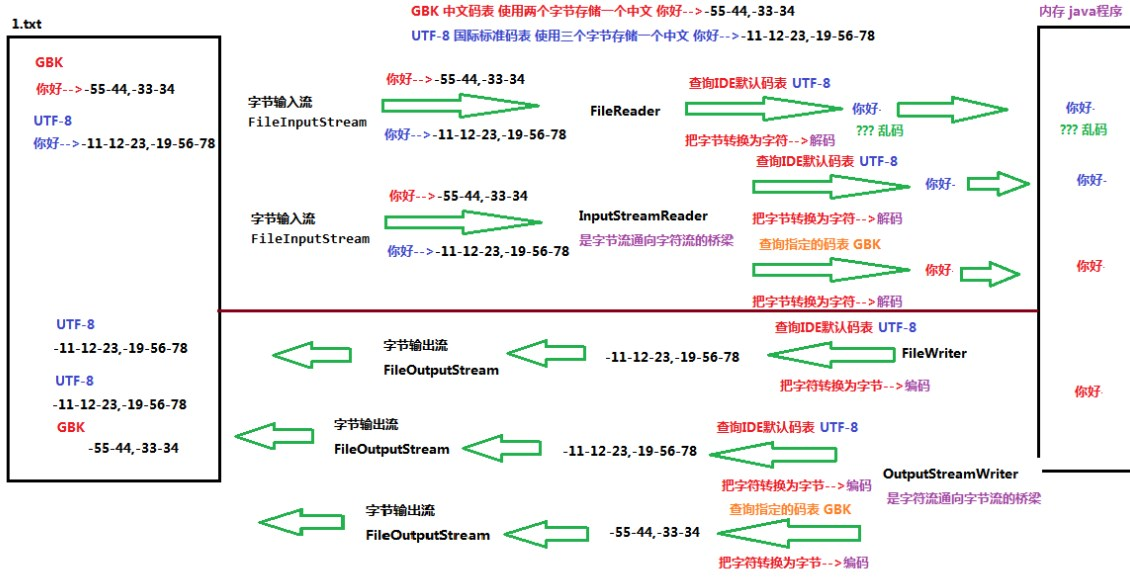
- 转换流的原理
- 包括转换输入流InputStreamReader和转换输出流OutputStreamWriter
-
- 字符输入流FileReader先通过FileInputStream读入默认编码的二进制码,再通过字符输入流FileReader查询默认编码表,将其解码为对应的字符,放至内存
- 字符输出流FileWriter先通过FileOutputStream查询默认码表,将字符转换为二进制编码字节,再通过字符输出流FileWriter将其解码为对应的字符,存入硬盘
- 转换输入流InputStreamReader先通过FileInputStream读入默认编码的二进制码,再通过转换流InputStreamReader按指定的编码表解码为对应的字符,放至内存
- 转换输出流OutputStreamWriter先通过FileOutputStream查询指定的编码表,将字符编码为对应的二进制字节,在通过字符输出流FileWriter将其解码为对应的字符,存入硬盘
3、OutputStreamWriter
- 是Writer的子类
/* 使用转换流OutputStreamWriter写UTF-8格式的文件 * */ private static void write_utf_8() throws IOException { //1、创建一个OutputStreamWriter对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流和指定的编码表名【默认是UTF-8格式编码】6字节 OutputStreamWriter osw =new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\utf_8.txt"),"utf-8"); //2、使用OutputStreamWriter对象中的方法write,将字符转换为字节存储缓冲区中【编码】 osw.write("你好"); //3、使用OutputStreamWriter对象中的方法flush,把内存缓冲区中的字节刷新到文件中(使用字节流写字节的过程) osw.flush(); //4、释放资源 osw.close(); }
4、InputStreamReader
- 是Reader的子类
/* 使用InputStreamReader读取UTF-8格式的文件 * */ private static void read_utf_8() throws IOException { //1、创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流和指定的字节编码表名称,默认就是UTF-8,可以不指定 InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\utf_8.txt"),"utf-8"); //2、使用InputStreamReader对象中的方法read读取文件 int len=0; while((len=isr.read())!=-1){ System.out.print((char)len); } //3、释放资源 isr.close(); }
5、练习:转换文件编码(GBK转UTF-8)
public class Demo10Practice { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建InputStreamReader对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流和指定的编码表名称GBK InputStreamReader isr =new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\gbk.txt"),"gbk"); //2.创建OutputStreamWriter对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流和指定的编码表名称UTF-8 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\utf8.txt"),"utf-8"); //3.使用InputStreamReader对象中的方法read读取文件 int len=0; while((len=isr.read())!=-1){ //4.使用OutputStreamWriter对象中的方法write,把读取的数据写入到文件中 osw.write(len); } //5.释放资源 osw.close(); isr.close(); } }
三、序列化
1、概述
-
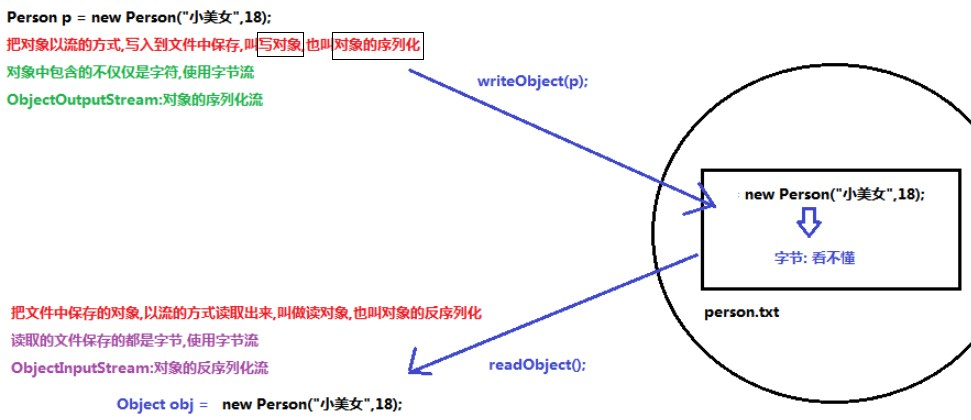
序列化:将对象写入到硬盘,以流的方式,名称为ObjectOutputStream.writeObject()
-
反序列化:从硬盘中读取对象,流名称为ObjectInputStream.readObject(),返回给Object类型对象
2、序列化流ObjectOutputStream
public class Demo11ObjectOutputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //1.创建一个ObjectOutputStream对象,构造方法中传递字节输出流 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt")); //2.调用ObjectOutputStream对象中的方法writeObject(),把对象写入到文件中 oos.writeObject(new Person("小美女",18)); //抛出NotSerializableException异常/未被序列化异常 /* * java.io.NotSerializableException 当实例需要具有序列化接口时,抛出此异常。序列化运行时或实例的类会抛出此异常。 * Serializable为序列化接口,类通过实现 java.io.Serializable 接口以启用其序列化功能。未实现此接口的类将无法使其任何状态序列化或反序列化。 * */ //3.释放资源 oos.close(); } }
3、反序列化流ObjectInputStream
public class Demo12ObjectInputStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException ,ClassNotFoundException { //1、创建一个ObjectInputStream对象,构造方法中传递字节输入流 ObjectInputStream ois =new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt")); //2、使用ObjectInputStream对象中的方法readObject,读取保存对象的文件 Person p = (Person)ois.readObject();//不转型也可以 //readObject方法声明抛出了ClassNotFoundException(.class文件找不到异常) //当不存在对象的class文件时,抛出此异常 //反序列化的前提: //1.类必须事先Serializable接口 //2.必须存在类对应的class 文件 //3、释放资源 ois.close(); //4、使用读取出来的对象 System.out.println(p); } }
4、瞬态关键字
- transient关键字修饰的成员变量,不能被序列化。序列化再反序列化后输出的是默认值0
- static优先于非静态,被static修饰的成员变量不能被序列化,能序列化的都是对象
5、InvalidClassException
- 原因:序列化后,class文件发生了修改,反序列化就会失败
- 解决方式:显式声明serialVersionUID字段
public class Person implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public String name; // private int age; private transient int age; public Person() { } public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; }
6、练习:序列化集合
public class Demo13SeriSet { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { //1、定义一个存储Person对象的ArrayList集合 ArrayList<Person> list=new ArrayList<>(); //2、在ArrayList集合中存储Person对象 list.add(new Person("张三",13)); list.add(new Person("李四",14)); list.add(new Person("王五",15)); //3、创建一个序列化流ObjectOutputStream对象 ObjectOutputStream oos =new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt")); //4、使用ObjectOutputStream对象中的方法writeObject,对集合进行序列化 oos.writeObject(list); //5、创建一个反序列化ObjectInputStream对象 ObjectInputStream ois =new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src\\com\\liujinhui\\Day1107BufferStream\\person.txt")); //6、使用ObjectInputStream对象中的方法readObject读取文件中保存的集合 Object o = ois.readObject(); //7、把Object类型的集合转换为ArrayList类型 ArrayList<Person> list2=(ArrayList<Person>)o; //8、遍历ArrayList集合 for (Person p : list2) { System.out.println(p); } //9、释放资源 ois.close(); oos.close(); } }
四、打印流
1、默认打印到文件
public class Demo14PrintStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { System.out.println("helloWorld"); //out就是一个打印流printStream //print和println是打印流的方法 //创建打印流PrintStream对象,构造方法中绑定要输出的目的地 PrintStream ps=new PrintStream("c:\\a.txt"); //如果使用继承自父类的write方法写数据,查看数据的时候会查询编码表 97-->a ps.write(97); ps.println(97); ps.println(8.8); ps.println("aaa"); ps.println(true); ps.println(2L); //释放资源 ps.close(); } }
2、改变输出流的目的地(打印到文件)
- System.setOut(PrintStream)改变输出语句的目的地,重新分配标准输出流
public class Demo15PrintStream { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException { System.out.println("我在控制台输出"); PrintStream ps =new PrintStream("C:\\a.txt"); System.setOut(ps); System.out.println("我在打印流的目的地中输出"); ps.close(); } }
本文来自博客园,作者:哥们要飞,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujinhui/p/14833766.html



