【重难点】反射
一、概念
1、反射:将类的各个组成部分封装为其他对象,这就是反射机制
- 反射是框架设计的灵魂
- 框架:半成品软件。可以在框架的基础上进行软件开发,简化编码
2、代码在计算机中经历的三个阶段
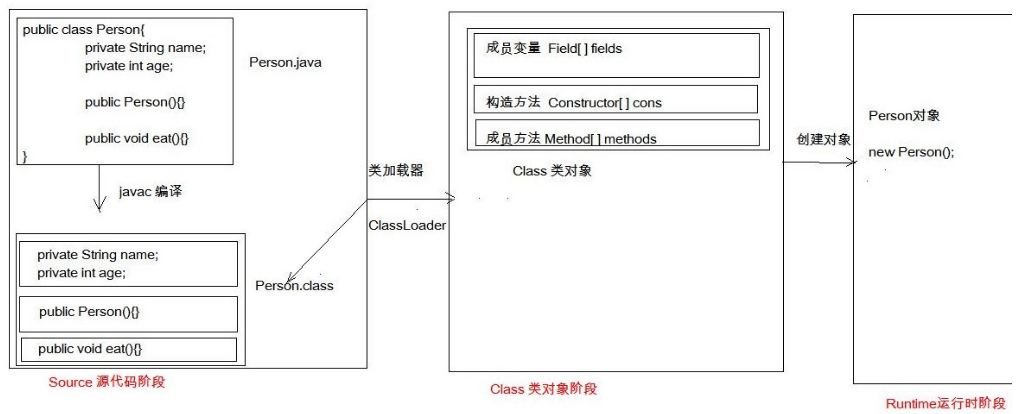
第一个阶段(源代码阶段):源文件.java--->目标文件.class:源代码阶段,代码还在硬盘上
第二个阶段(Class类对象阶段):通过类加载器对象ClassLoader把字节码文件加载进内存
内存中有一个对象描述字节码文件,该对象叫Class类对象
描述所有字节码的共同特征:成员变量(拿到值,设置值)--封装为Field对象---很多个Field[] field
构造方法(创建对象)--封装为Constructor对象--Constructor[] constructor数组描述所有的构造方法
成员方法(其他功能)--封装为Method对象--Method[] method
第三个阶段(运行时阶段):调用 Person对象,属于第三个阶段(运行时阶段)
3、好处
1.可以在程序运行过程中去操作这些对象。获取、执行等,在运行过程中很重要
例如:展示method对象数组的成员
- 2.解耦(降低耦合性和紧密程度),来提高程序的 可扩展性
二、常用操作
1、获取字节码Class对象的三种方式
源代码阶段(1)Class.forName("全类名(包名.类名)"):将字节码文件加载进内存,返回Class对象【写全类名常用于配置文件,读取文件,加载类】
类对象阶段(2)类名.class:通过类名的属性class获取【多用于参数的传递】
运行时阶段(3)对象.getClass():getClass() 返回此 Object的运行时类【多用于对象的获取字节码方式】
1 package com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.reflect; 2 import com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person; 3 import com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Student; 4 5 public class ReflectDemo1 { 6 /* 7 获取class的三种方式 8 源代码阶段(1)Class.forName("全类名(包名.类名)"):将字节码文件加载进内存,返回Class对象 9 【只有字节码文件,没有进内存,需要手动将其加载到内存,使用forName这种手动加载方式】 10 类对象阶段(2)类名.class:通过类名的属性class获取 11 【字节码已经加载到内存,不需要再加载,只需要获取,没有对象通过类名的属性获取该对象】 12 运行时阶段(3)对象.getClass():getClass() 返回此 Object的运行时类,在Object类中定义 13 【已经有对象,可以通过对象的方法进行获取类对象,封装在Object中的方法】 14 * */ 15 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 16 //1.Class.forName("全类名(包名.类名)") 17 //Class类的静态方法static Class<?> forName(String className) 返回与给定字符串名称的类或接口相关联的 Class对象。 18 Class<?> cls1 = Class.forName("com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person"); 19 //如果遇到ClassNotFoundClass,是自定义,则说明,类名写错了,需要重写类名 20 System.out.println(cls1);//class com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person 21 //2.类名.class 22 Class cls2 = Person.class;//删掉泛型 23 System.out.println(cls2); 24 //3.对象.getClass(): 25 Person p=new Person(); 26 Class cls3 = p.getClass(); 27 System.out.println(cls3); 28 //打印形式一样,直接使用==比较三个对象是否相等 29 //==比较的是对象的内存地址 30 System.out.println(cls1==cls2); 31 System.out.println(cls2==cls3); 32 //true 33 Class c = Student.class; 34 System.out.println(c==cls1);//每个字节码文件的物理文件对应的class类对象都不相同 35 } 36 }
2、Class对象的功能
1.获取成员变量们Field[]对象
Field[] getFields() 获取所有public修饰的成员变量
Field getField(String name)
Field[] getDeclaredFields() 获取所有的成员变量,不考虑修饰符
Field getDeclaredField(String name)
2.获取成员方法们Method[]
Method[] getMethods()
Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
3.获取构造方法们Constructor[]
Constructor<?>[] getConstructors()
Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes)
Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors()
Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes)
4.获取类名
String getName()
String getPackageName()
3、Field[]对象(成员变量)
操作:
1.设置值void set(Object obj, Object value)
2.获取值Object get(Object obj),根据成员变量找到对应的对象
3.忽略访问权限的安全检查d.setAccessible(true);//暴力反射
1 package com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain; 2 3 public class Person { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 public String a; 7 protected String b; 8 String c; 9 private String d; 10 11 public Person() { 12 } 13 14 public Person(String name, int age) { 15 this.name = name; 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 19 public String getName() { 20 return name; 21 } 22 23 public void setName(String name) { 24 this.name = name; 25 } 26 27 public int getAge() { 28 return age; 29 } 30 31 public void setAge(int age) { 32 this.age = age; 33 } 34 35 @Override 36 public String toString() { 37 return "Person{" + 38 "name='" + name + '\'' + 39 ", age=" + age + 40 ", a='" + a + '\'' + 41 ", b='" + b + '\'' + 42 ", c='" + c + '\'' + 43 ", d='" + d + '\'' + 44 '}'; 45 } 46 }
package com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.reflect; import com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person; import java.lang.reflect.Field; public class ReflectDemo2 { /* 1.获取成员变量们Field[]对象 Field[] getFields():获取所有public修饰的成员变量 Field getField(String name) Field[] getDeclaredFields()获取所有的成员变量,不考虑修饰符 Field getDeclaredField(String name) 2.获取成员方法们Method[] Method[] getMethods() Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) Method[] getDeclaredMethods() Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) 3.获取构造方法们Constructor[] Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors() Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) 4.获取类名 String getName() String getPackageName() * */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //1.获取Person的Class对象 Class personClass = Person.class; //Field[] getFields() Field[] fields = personClass.getFields(); for (Field field : fields) { /* public String a; protected String b; String c; private String d; * */ } //遍历可以输入.for或iter for (Field field : fields) { //一个都没有打印,应该是有两个成员变量的 System.out.println(field); } System.out.println("================"); Field a = personClass.getField("a"); System.out.println(a);//public java.lang.String com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person.a Person p = new Person(); Object value = a.get(p);//成员变量new之后是有初始值null的,局部变量没有初始值 System.out.println(value); //设置a的值 a.set(p,"张三"); System.out.println(p);//Person{name='null', age=0, a='张三', b='null', c='null', d='null'} System.out.println("================"); //Field[] getDeclaredFields() Field[] declaredFields = personClass.getDeclaredFields();//获取所有的成员变量,不考虑修饰符 for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) { System.out.println(declaredField); } /* private java.lang.String com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person.name private int com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person.age public java.lang.String com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person.a protected java.lang.String com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person.b java.lang.String com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person.c private java.lang.String com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person.d * */ //Field getDeclaredField(String name) //使用非public修饰的变量时,需要忽略访问权限修饰符的安全检查 Field d = personClass.getDeclaredField("d"); d.setAccessible(true);//暴力反射 Object value2 = d.get(p);//p是一个Person对象,根据成员变量找到对应的对象 System.out.println(value2);//会抛异常 //暴力反射后打印null } }
4、Constructor对象
创建对象
T newInstance(Object... initargs)
如果使用空参数的构造方法创建对象,操作可以简化,简化到class对象中的T newInstance()
Object o = personClass.newInstance();
1 package com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.reflect; 2 import com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person; 3 import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 5 public class ReflectDemo3 { 6 /* 7 获取构造方法们Constructor[] 8 Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() 9 Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) 10 Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors() 11 Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) 12 * */ 13 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 14 //1.获取Person的Class对象 15 Class personClass = Person.class; 16 /* 17 获取构造方法们Constructor[] 18 Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() 19 Constructor<T> getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) 20 Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors() 21 Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) 22 * */ 23 Constructor constructor = personClass.getConstructor(String.class, int.class); 24 System.out.println(constructor);//public com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person(java.lang.String,int) 25 //创建对象 26 Object person = constructor.newInstance("张三", 23); 27 System.out.println(person);//Person{name='张三', age=23, a='null', b='null', c='null', d='null'} 28 System.out.println("============="); 29 //创建空参数的构造器 30 Constructor constructor1 = personClass.getConstructor(); 31 constructor1.setAccessible(true);//也可以使用暴力反射 32 Object person1 = constructor1.newInstance(); 33 System.out.println(person1);//Person{name='null', age=0, a='null', b='null', c='null', d='null'} 34 //如果使用空参数的构造方法创建对象,操作可以简化,简化到class对象中的T newInstance() 35 Object o = personClass.newInstance(); 36 System.out.println(o); 37 } 38 }
5、Method对象(成员方法)
操作:
执行方法Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
获取方法名称String getName()
1 package com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.reflect; 2 import com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person; 3 4 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 5 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 6 public class ReflectDemo4 { 7 /* 8 获取成员方法们Method[] 9 Method[] getMethods() 10 Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) 11 Method[] getDeclaredMethods() 12 Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) 13 * */ 14 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 15 //1.获取Person的Class对象 16 Class personClass = Person.class; 17 /* 18 获取成员方法们Method[] 19 Method[] getMethods() 20 Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)获取指定名称的方法 21 Method[] getDeclaredMethods() 22 Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes) 23 * */ 24 Method eat_method = personClass.getMethod("eat"); 25 //执行方法,传递对象 26 Person p=new Person(); 27 eat_method.invoke(p);//执行p对象对应的eat方法 28 //有参数方法 29 Method eat_method2 = personClass.getMethod("eat", String.class); 30 eat_method2.invoke(p,"饭"); 31 //获取所有public修饰的方法 32 Method[] methods = personClass.getMethods(); 33 for (Method method : methods) { 34 method.setAccessible(true);//也可以设置暴力反射 35 System.out.println(method);//会打印父类隐藏的一些方法 36 String name = method.getName(); 37 System.out.println(name); 38 } 39 //获取类名 40 String className = personClass.getName(); 41 System.out.println(className);//打印全类名com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Person 42 } 43 }
三、案例
1、需求
写一个“框架”,不能改变该类的任何代码前提下,可以创建任意类的对象并执行任意类的方法
2、配置文件className=com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain.Student
methodName=sleep
3、步骤
1.将需要创建的对象的全类名和需要执行的方法定义在配置文件中
2.在程序中加载读取配置文件
3.使用反射技术来加载类文件进内存
4.创建对象
5.执行方法
4、代码
1 package com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.domain; 2 3 public class Student { 4 public void sleep(){ 5 System.out.println("sleep..."); 6 } 7 }
1 package com.liujinhui.Day1209BaseEnhance.reflect; 2 import java.io.InputStream; 3 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 4 import java.util.Properties; 5 /* 6 假设的框架类 7 改配置文件使程序的扩展性更强,配置文件中使用了全类名,则使用了反射机制 8 * */ 9 public class ReflectTest { 10 /** 11 * @author: Liu Jinhui 12 * @description: 创建任意对象 13 * @date: 2020/12/9 20:42 14 * @return * @param null 15 */ 16 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ 17 //可以创建任意类的对象,可以执行任意方法 18 /* 19 前提:不能改变该类的任何代码,可以创建任意类的对象,可以执行任意方法 20 * */ 21 //1.加载配置文件 22 //1.1.创建Properties对象 23 Properties pro=new Properties(); 24 //1.2加载配置文件,转换为一个双列map集合 25 //1.2.1获取class目录下配置文件的方式,使用类加载器完成 26 ClassLoader classLoader = ReflectTest.class.getClassLoader(); 27 //得到该类下的配置文件流 28 InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("pro.properties"); 29 //加载属性流 30 pro.load(is); 31 //2.获取配置文件中定义的数据 32 String className = pro.getProperty("className"); 33 String methodName = pro.getProperty("methodName"); 34 //3.加载该类进内存 35 Class cls = Class.forName(className); 36 //4.创建对象 37 Object obj = cls.newInstance(); 38 //5.获取方法对象 39 Method method = cls.getMethod(methodName); 40 //6.执行方法 41 method.invoke(obj); 42 } 43 }
本文来自博客园,作者:哥们要飞,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/liujinhui/p/14288009.html

