GWAS分析中一般线性模型GML中snp的回归系数r2的计算
001、plink计算
root@PC1:/home/test# ls gwas_test.map gwas_test.ped root@PC1:/home/test# plink --file gwas_test --assoc 1> /dev/null root@PC1:/home/test# ls gwas_test.map gwas_test.ped plink.log plink.qassoc root@PC1:/home/test# head plink.qassoc ## 倒数第三列为r2 CHR SNP BP NMISS BETA SE R2 T P 1 snp1 2802 541 -8.911 8.344 0.002111 -1.068 0.286 1 snp2 2823 541 7.754 10.04 0.001104 0.772 0.4405 1 snp3 4512 541 9.264 9.814 0.00165 0.9439 0.3456 1 snp4 16529 541 -18.49 10.81 0.005401 -1.711 0.08769 1 snp5 16578 541 5.661 9.93 0.0006026 0.5701 0.5689 1 snp6 16579 541 -5.577 5.657 0.0018 -0.9858 0.3247 1 snp7 16635 541 2.985 8.717 0.0002176 0.3425 0.7321 1 snp8 20879 541 9.053 7.29 0.002853 1.242 0.2148 1 snp9 20908 541 9.278 6.695 0.00355 1.386 0.1664
002、R语言计算
root@PC1:/home/test# ls gwas_test.map gwas_test.ped root@PC1:/home/test# plink --file gwas_test --recode A 1> /dev/null root@PC1:/home/test# ls gwas_test.map gwas_test.ped plink.log plink.raw root@PC1:/home/test# cut -d " " -f 1,3-5 --complement plink.raw > num.raw root@PC1:/home/test# ls gwas_test.map gwas_test.ped num.raw plink.log plink.raw
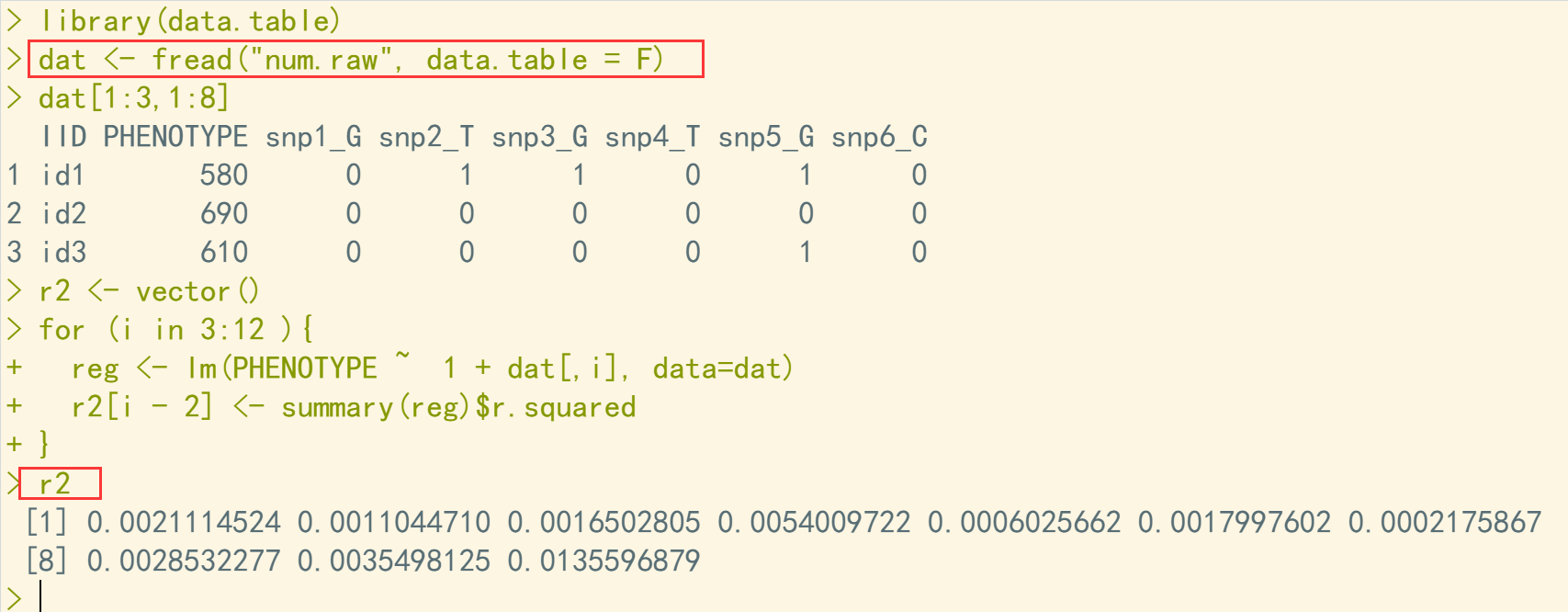
library(data.table) dat <- fread("num.raw", data.table = F) dat[1:3,1:8] r2 <- vector() for (i in 3:12 ){ reg <- lm(PHENOTYPE ~ 1 + dat[,i], data=dat) r2[i - 2] <- summary(reg)$r.squared } r2
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/yijiaobani/article/details/122093938?app_version=5.6.0&code=app_1562916241&csdn_share_tail=%7B%22type%22%3A%22blog%22%2C%22rType%22%3A%22article%22%2C%22rId%22%3A%22122093938%22%2C%22source%22%3A%22liujiaxin2019%22%7D&ctrtid=6XokY&uLinkId=usr1mkqgl919blen&utm_source=app






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
2021-07-27 c primer plus 3.11-2
2021-07-27 c primer plus 3.11
2021-07-27 c语言中如何处理整数值的上溢和下溢