c primer plus 8编程练习
1、
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main(void) { int ch; FILE * fp; char filename[128]; int sum = 0; printf("please input filename: "); scanf("%s", filename); fp = fopen(filename, "r"); if(fp == NULL) { printf("file failed opened!\n"); exit(1); } while((ch = getc(fp)) != EOF) { putchar(ch); sum++; } printf("\nsum: %d.\n", sum); return 0; }
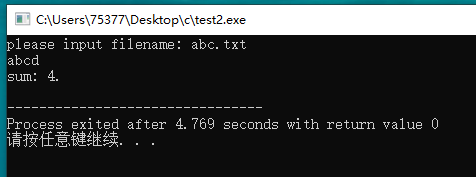
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char ch; int sum = 0; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { putchar(ch); sum++; } printf("sum: %d.\n", sum); return 0; }
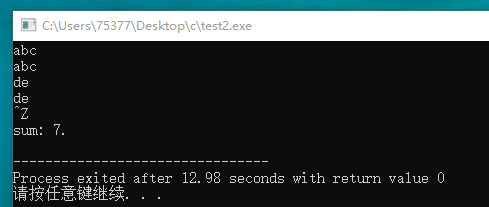
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char ch; int sum = 0; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { putchar(ch); if(ch > '\040') sum++; } printf("sum: %d.\n", sum); return 0; }
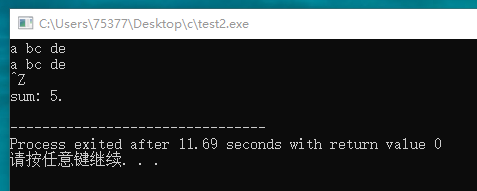
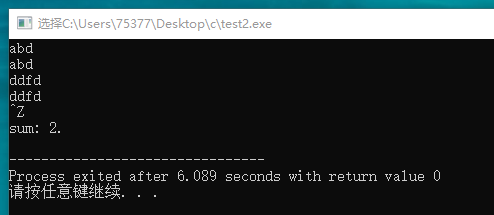
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char ch; int sum = 0; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { putchar(ch); if(ch == '\n') sum++; } printf("sum: %d.\n", sum); return 0; }
2、
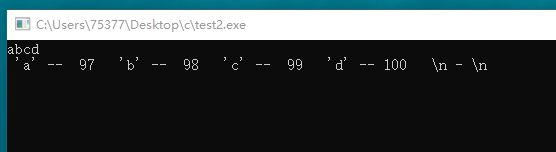
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int counter = 0; char ch; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(counter++ == 10) { printf("\n"); counter = 1; } if(ch >= '\040') { printf(" \'%c\'--%3d ", ch, ch); } else if(ch == '\n') { printf(" \\n--\\n "); counter = 0; } else if(ch == '\t') { printf(" \\t--\\t "); } else { printf(" \'%c\'--^%c ", ch, (ch + 64)); } } return 0; }
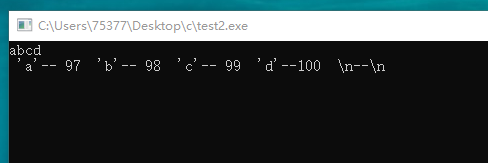
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int counter = 0; char ch; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(counter++ == 10) { printf("\n"); counter = 1; } if(ch >= '\040') { printf(" \'%c\' -- %3d ", ch, ch); } else if(ch == '\n') { printf(" \\n - \\n "); } else if(ch == '\t') { printf(" \\t -- \\t "); } else { printf(" %c -- %d. ", ch, (ch + 64)); } } return 0; }
3、
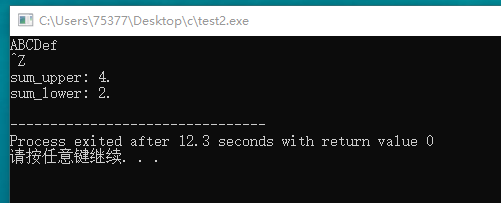
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> int main(void) { char ch; int sum_upper = 0; int sum_lower = 0; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(isupper(ch)) sum_upper++; if(islower(ch)) sum_lower++; } printf("sum_upper: %d.\n", sum_upper); printf("sum_lower: %d.\n", sum_lower); return 0; }
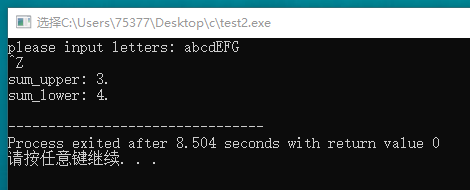
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char ch; int sum_upper = 0; int sum_lower = 0; printf("please input letters: "); while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') sum_lower++; if(ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') sum_upper++; } printf("sum_upper: %d.\n", sum_upper); printf("sum_lower: %d.\n", sum_lower); return 0; }
4、
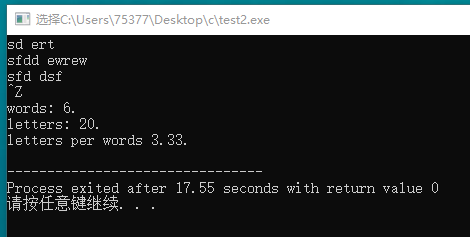
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char ch; int words = 0; int letters = 0; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(ch == ' ' || ch == '\n') words++; if(ch != ' ' && ch != '\n') letters++; } printf("words: %d.\n", words); printf("letters: %d.\n", letters); printf("average letters: %.2f\n", (double)letters/words); return 0; }
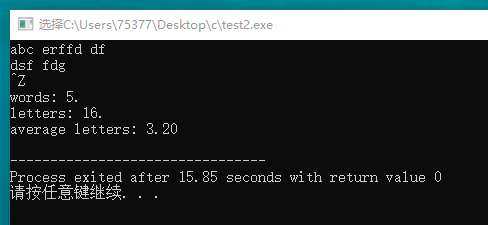
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdbool.h> #include <ctype.h> int main(void) { int ch; bool word = false; bool space = false; int words = 0; int letters = 0; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(!isspace(ch)) word = true; else space = true; if(word && space) { words++; word = false; space = false; } if(!word && space) space = false; // 消除连续空格的影响 if(isalpha(ch)) letters++; } printf("words: %d.\n", words); printf("letters: %d.\n", letters); printf("average letters per word: %.2f.\n"); return 0; }
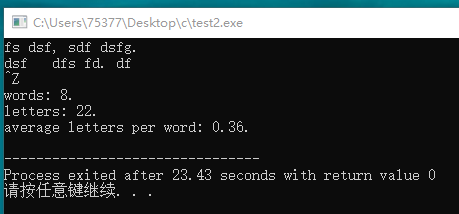
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> #include <stdbool.h> int main(void) { int ch; bool inword = false; int words = 0; int letters = 0; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(!isspace(ch) && !inword) { words++; inword = true; } if(isspace(ch) && inword) inword = false; if(isalpha(ch)) letters++; } printf("words: %d.\n", words); printf("letters: %d.\n", letters); printf("letters per words %.2f.\n", (float)letters/words); return 0; }
5、
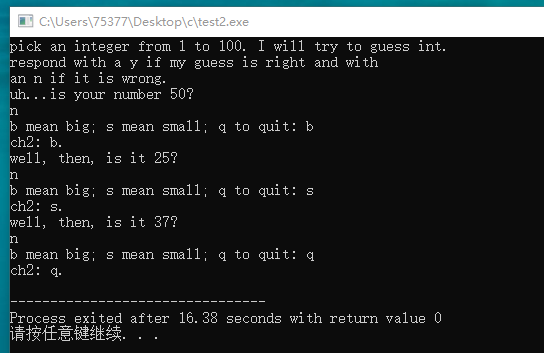
#include <stdio.h> char judge(void); int main(void) { int top = 100; int bottom = 0; int guess; char ch; char ch2; guess = (top - bottom) /2; int tmp; printf("pick an integer from 1 to 100. I will try to guess "); printf("int.\nrespond with a y if my guess is right and with"); printf("\nan n if it is wrong.\n"); printf("uh...is your number %d?\n", guess); while((ch = getchar()) != 'y') { if(ch == 'n') { while(getchar() != '\n') continue; ch2 = judge(); printf("ch2: %c.\n", ch2); if(ch2 == 'b') { top = guess; guess = guess - (guess - bottom)/2; } else if(ch2 == 's') { tmp = guess; guess = guess + (guess - bottom)/2; bottom = tmp; } else break; printf("well, then, is it %d?\n", guess); } else printf("you can only input n and y: "); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } if(ch2 != 'q') printf("i kenw i could do it!\n"); return 0; } char judge(void) { char ch; printf("b mean big; s mean small; q to quit: "); while((ch = getchar()) != 'q' && ch != 'b' && ch != 's') { printf("you can only input b, s and q, b mean big, s mean small, q to quit: "); } return ch; }
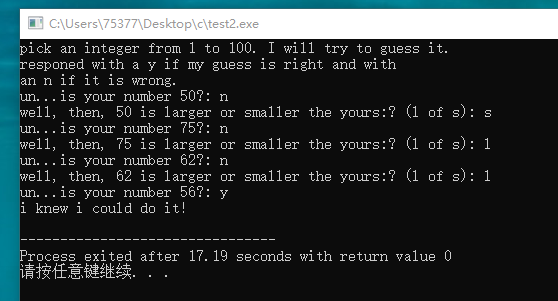
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int head = 1; int tail = 100; int guess = (head + tail) / 2; char ch; printf("pick an integer from 1 to 100. I will try to guess "); printf("it.\nresponed with a y if my guess is right and with"); printf("\nan n if it is wrong.\n"); do { printf("un...is your number %d?: ", guess); if(getchar() == 'y') break; printf("well, then, %d is larger or smaller the yours:? (l of s): ", guess); while((ch = getchar()) == '\n') continue; if(ch == 'l' || ch == 'L') { tail = guess - 1; guess = (head + tail) / 2; continue; } else if(ch == 's' || ch == 'S') { head = guess + 1; guess = (head + tail)/2; continue; } else continue; } while(getchar() != 'y'); printf("i knew i could do it!\n"); return 0; }
6、
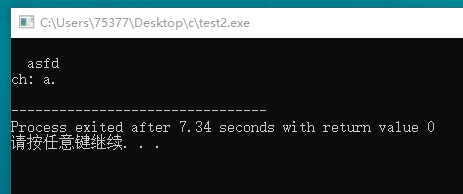
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> char get_first(void); int main(void) { int ch; ch = get_first(); printf("ch: %c.\n", ch); return 0; } char get_first(void) { int ch; while((ch = getchar()) != EOF) { if(!isspace(ch)) break; } while(getchar() != '\n') continue; return ch; }
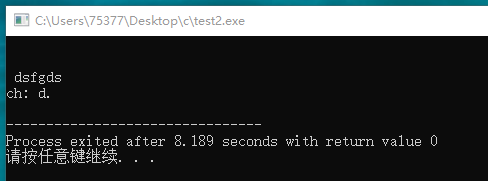
#include <stdio.h> #include <ctype.h> char get_first(void); int main(void) { char ch; ch = get_first(); printf("ch: %c.\n", ch); return 0; } char get_first(void) { char ch; do { ch = getchar(); } while(isspace(ch)); return ch; }
7、
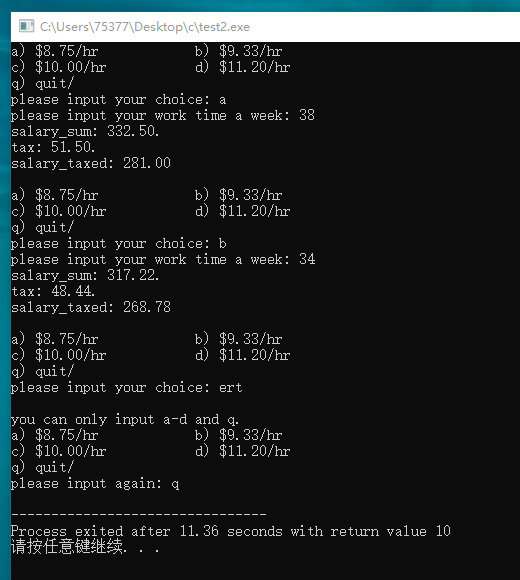
#include <stdio.h> #define OVER_WORK 1.5 #define BASE_TAX 0.15 #define EXTRA_TAX 0.2 #define EXCEED_TAX 0.25 char get_char(void); void calculat_salary(float time, float price); int main(void) { char ch; float work_time; float price; ch = get_char(); while(ch != 'q') { printf("please input your work time a week: "); scanf("%f", &work_time); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; switch(ch) { case 'a': price = 8.75; calculat_salary( work_time, price); break; case 'b': price = 9.33; calculat_salary( work_time, price); break; case 'c': price = 10.00; calculat_salary( work_time, price); break; case 'd': price = 11.20; calculat_salary( work_time, price); break; default: printf("program error.\n"); break; } putchar('\n'); ch = get_char(); } } char get_char(void) { char ch; printf("a) $8.75/hr b) $9.33/hr\n"); printf("c) $10.00/hr d) $11.20/hr\n"); printf("q) quit/\n"); printf("please input your choice: "); while((ch = getchar()) != 'q' && (ch < 'a' || ch > 'd')) { printf("\nyou can only input a-d and q.\n"); printf("a) $8.75/hr b) $9.33/hr\n"); printf("c) $10.00/hr d) $11.20/hr\n"); printf("q) quit/\n"); printf("please input again: "); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; } return ch; } void calculat_salary(float time, float price) { float salary_sum; float tax; float salary_taxed; if(time <= 40) { salary_sum = time * price; } else { time = 40 + (time - 40) * OVER_WORK; salary_sum = time * price; } if(salary_sum <= 300) { tax = salary_sum * BASE_TAX; } else if(salary_sum > 300 && salary_sum <= 450) { tax = 300 * BASE_TAX + (salary_sum - 300) * EXTRA_TAX; } else { tax = 300 * BASE_TAX + 150 * EXTRA_TAX + (salary_sum - 450) * EXCEED_TAX; } salary_taxed = salary_sum - tax; printf("salary_sum: %.2f.\n", salary_sum); printf("tax: %.2f.\n", tax); printf("salary_taxed: %.2f\n", salary_taxed); }
#include <stdio.h> #define WORK_OVERTIME 1.5 #define BASE_TAX 0.15 #define EXTRA_TAX 0.20 #define EXCEED_TAX 0.25 void memo(void); float get_time(void); void calculate(float time, float price); char get_char(void); int main(void) { float worktime; float price; char choice; do { memo(); choice = get_char(); switch(choice) { case 'a': price = 8.75; worktime = get_time(); calculate(worktime, price); break; case 'b': price = 9.33; worktime = get_time(); calculate(worktime, price); break; case 'c': price = 10.00; worktime = get_time(); calculate(worktime, price); break; case 'd': price = 11.20; worktime = get_time(); calculate(worktime, price); break; case 'q': break; default: printf("you can only input a-d and q.\n"); break; } } while(choice != 'q'); } void memo(void) { printf("The options are as bellow.\n"); printf("a) $8.75/hr b) $9.33/hr\n"); printf("c) $10.00/hr d) $11.20/hr\n"); printf("q) quit\n"); printf("please input your choice: "); } float get_time(void) { float time; char ch; printf("please input your work time: "); while(scanf("%f", &time) != 1) { while((ch = getchar()) != '\n') putchar(ch); printf(" is not num.\n"); printf("please input num: "); } while(getchar() != '\n') continue; return time; } char get_char(void) { char ch; ch = getchar(); while(getchar() != '\n') continue; return ch; } void calculate(float time, float price) { float salary_sum; float tax; float salary_taxed; if(time <= 40) { salary_sum = time * price; } else { time = 40 + (time - 40) * WORK_OVERTIME; salary_sum = time * price; } if(salary_sum <= 300) { tax = salary_sum * BASE_TAX; } else if(salary_sum > 300 && salary_sum <= 450) { tax = 300 * BASE_TAX + (salary_sum - 300) * EXTRA_TAX; } else { tax = 300 * BASE_TAX + 150 * EXTRA_TAX + (salary_sum - 450) * EXCEED_TAX; } salary_taxed = salary_sum - tax; printf("salary_sum: %.2f.\n", salary_sum); printf("tax: %.2f.\n", tax); printf("salary_taxed: %.2f\n\n", salary_taxed); }
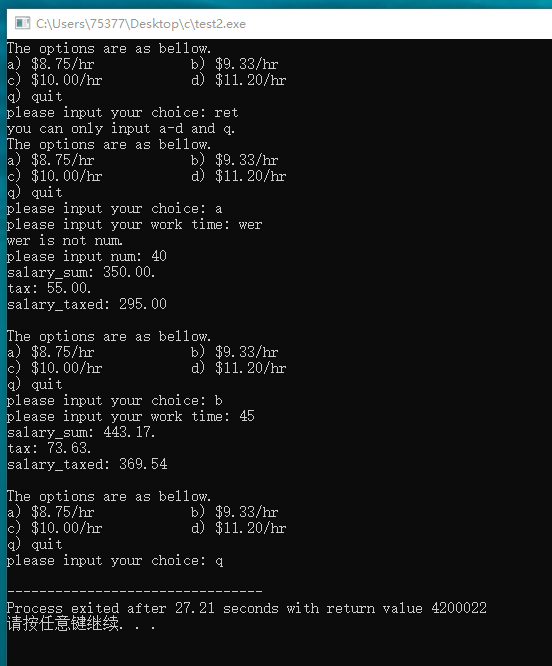
8、
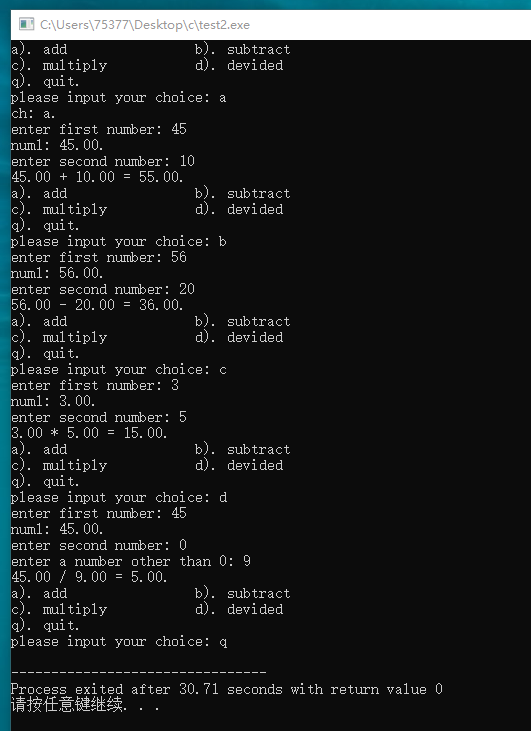
#include <stdio.h> float get_num(void); char get_char(void); int main(void) { char ch; float num1; float num2; ch = get_char(); printf("ch: %c.\n", ch); while(ch != 'q') { printf("enter first number: "); num1 = get_num(); printf("num1: %.2f.\n", num1); printf("enter second number: "); num2 = get_num(); while(ch == 'd' && num2 == 0) { printf("enter a number other than 0: "); num2 = get_num(); } switch(ch) { case 'a': printf("%.2f + %.2f = %.2f.\n",num1, num2, num1 + num2); break; case 'b': printf("%.2f - %.2f = %.2f.\n", num1, num2, num1 - num2); break; case 'c': printf("%.2f * %.2f = %.2f.\n", num1, num2, num1 * num2); break; case 'd': printf("%.2f / %.2f = %.2f.\n", num1, num2, num1 / num2); break; default: printf("programme error.\n"); break; } while(getchar() != '\n') continue; ch = get_char(); } return 0; } char get_char(void) { char ch; printf("a). add b). subtract\n"); printf("c). multiply d). devided\n"); printf("q). quit.\n"); printf("please input your choice: "); while((ch = getchar()) != 'q' && (ch < 'a' || ch > 'd')) { while(getchar() != '\n') continue; printf("you can only choose a-d and q: "); } return ch; } float get_num(void) { float num; char ch; while(scanf("%f", &num) != 1) { while((ch = getchar()) != '\n') putchar(ch); printf(" is not num.\n"); printf("please input again: "); } return num; }
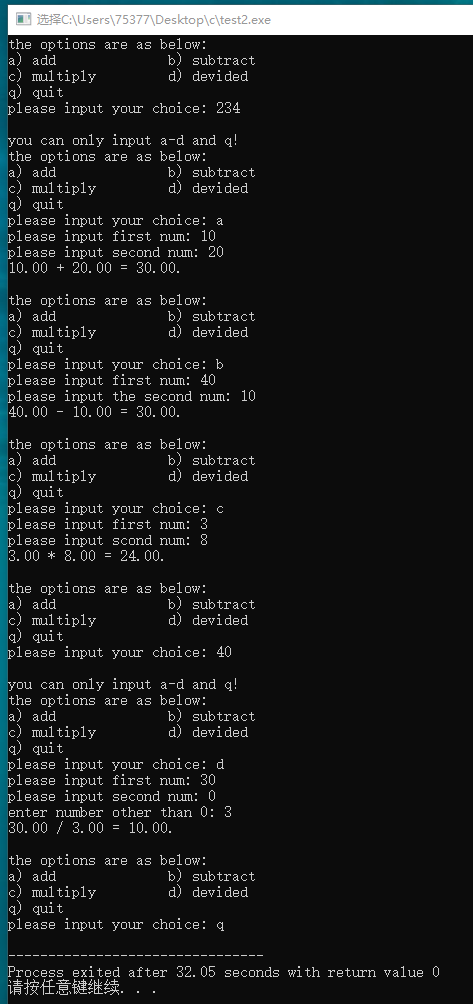
#include <stdio.h> void get_memo(void); float get_num(void); int main(void) { float first, second; char ch; do { get_memo(); ch = getchar(); switch(ch) { case 'a': printf("please input first num: "); first = get_num(); printf("please input second num: "); second = get_num(); printf("%.2f + %.2f = %.2f.\n\n", first, second, first + second); break; case 'b': printf("please input first num: "); first = get_num(); printf("please input the second num: "); second = get_num(); printf("%.2f - %.2f = %.2f.\n\n", first, second, first - second); break; case 'c': printf("please input first num: "); first = get_num(); printf("please input scond num: "); second = get_num(); printf("%.2f * %.2f = %.2f.\n\n", first, second, first * second); break; case 'd': printf("please input first num: "); first = get_num(); printf("please input second num: "); while((second = get_num()) == 0) { printf("enter number other than 0: "); } printf("%.2f / %.2f = %.2f.\n\n", first, second, first / second); break; case 'q': break; default: printf("\nyou can only input a-d and q! \n"); break; } while(getchar() != '\n'); continue; putchar('\n'); } while(ch != 'q'); return 0; } void get_memo(void) { printf("the options are as below: \n"); printf("a) add b) subtract\n"); printf("c) multiply d) devided\n"); printf("q) quit\n"); printf("please input your choice: "); } float get_num(void) { float num; char ch; while(scanf("%f", &num) != 1) { while((ch = getchar()) != '\n') putchar(ch); printf(" is not num.\n"); printf("please input num: "); } return num; }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律