c语言中continue语句
c语言中continue语句;执行continue语句后,循环体的剩余部分就会被跳过。
例子;
1、原始程序。输出矩形。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, j, height, width;
puts("please input the height and width.");
do
{
printf("height = "); scanf("%d", &height);
if (height <= 0)
puts("the range of height is > 0 ");
printf("width = "); scanf("%d", &width);
if (width <= 0)
puts("the range of width is > 0 ");
}
while (height <= 0 || width <= 0);
for (i = 1; i <= height; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= width; j++)
{
putchar('*');
}
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
当height和width都大于0时,程序正常输出矩形。
当height <= 0时,此时程序已经满足do语句重新执行的条件,但是任然执行width的输入,因此需要改进。以下使用break改进。
2、使用break
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, j, height, width;
puts("please input the height and width.");
do
{
printf("height = "); scanf("%d", &height);
if (height <= 0)
{
puts("the range of height is > 0 ");
break;
}
printf("width = "); scanf("%d", &width);
if (width <= 0)
puts("the range of width is > 0 ");
}
while (height <= 0 || width <= 0);
for (i = 1; i <= height; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= width; j++)
{
putchar('*');
}
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
当height和width都大于0时程序正常执行,但是当height小于等于0时,程序就直接退出了。 以下使用continue语句改进。
3、使用continue
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, j, height, width;
puts("please input the height and width.");
do
{
printf("height = "); scanf("%d", &height);
if (height <= 0)
{
puts("the range of height is > 0 ");
continue;
}
printf("width = "); scanf("%d", &width);
if (width <= 0)
puts("the range of width is > 0");
}
while (height <= 0 || width <= 0);
for (i = 1; i <= height; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= width; j++)
{
putchar('*');
}
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
当height小于等于0时,程序会跳过循环体的剩余部分。
执行continue语句后,循环体的剩余部分就会被跳过。
例子:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, j;
puts("please input an integer.");
printf("j = "); scanf("%d", &j);
for (i = 1; i <= j; i++)
{
if (i == 6)
break;
printf("%d ", i);
}
putchar('\n');
puts("xxxxxyyyyyy");
return 0;
}
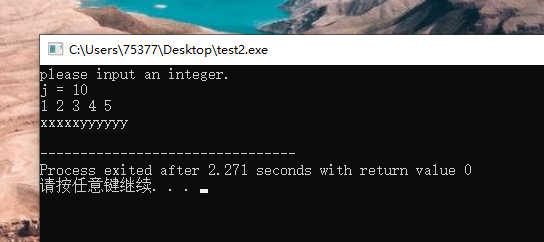
break语句会直接终止循环。
下面看continue。
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i, j;
puts("please input an integer.");
printf("j = "); scanf("%d", &j);
for (i = 1; i <= j; i++)
{
if (i == 6)
continue;
printf("%d ", i);
}
putchar('\n');
puts("xxxxxyyyyyy");
return 0;
}

continue语句则是仅仅跳出“6”的那一次执行过程。
分类:
c/c++






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律