27-SpringMVC-3(视图解析+RESTful CRUD)
1. 视图解析#
1.1 使用#
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
// → Go to WebContent/hello.jsp
// 相对路径的写法
return "../../hello";
}
/*
* → Go to WebContent/hello.jsp
* forward: 转发到一个页面(有前缀的返回值独立解析,不由视图解析器拼串)
* /hello.jsp 当前项目下的hello.jsp(加'/', 不然就是相对路径,容易出错)
*/
@RequestMapping("/handle01")
public String handle01() {
System.out.println("handle01");
return "forward:/hello.jsp";
}
// 多次派发
@RequestMapping("/handle02")
public String handle02() {
System.out.println("handle02");
return "forward:/handle01"; // 2 次转发
}
/*
* 重定向前缀:redirect
* 同重定向一样,视图解析器不会为其拼串
* /hello.jsp 代表的就是从当前项目下开始,SpringMVC 会为路径自动拼接上项目名
*/
@RequestMapping("/handle03")
public String handle03() {
System.out.println("handle03");
return "redirect:/hello.jsp";
}
@RequestMapping("/handle04")
public String handle04() {
System.out.println("handle04");
return "redirect:/handle03"; // 2 次重定向
}
}
1.2 源码#
1.2.1 得到 View 对象#
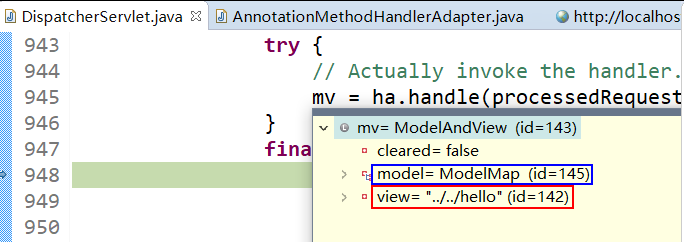
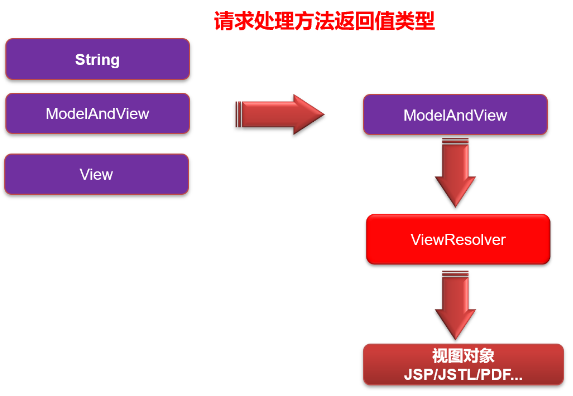
(1) 任何方法的返回值,最终都会被包装成 ModelAndView 对象。
(2) 来到页面的方法:processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException)
(3) 视图解析器得到 View 对象的流程:所有配置的视图解析器都来根据视图名(返回值)得到 View 对象。如果能得到,就返回;得不到就换下一个视图解析器来试试能不能得到。
<<DispatcherServlet>>
[1012] render(mv, request, response);
||
\/
[1204] view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model
, Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
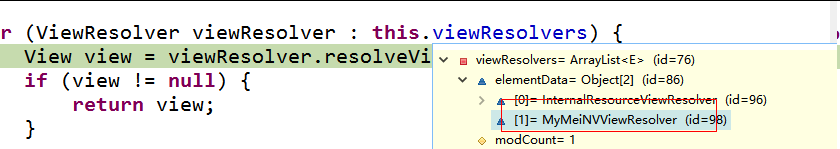
// 遍历所有的 ViewResolver(视图解析器)
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
// 视图解析器根据目标方法的返回值得到一个 View 对象
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
return null;
}
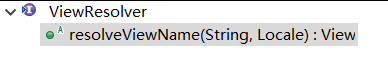
ViewResolver<I> 作用是根据视图名得到视图对象 View。
(4) InternalResourceViewResolver 的 resolveViewName 实现细节:
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
if (!isCache()) {
return createView(viewName, locale);
}
else {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(viewName, locale);
View view = this.viewAccessCache.get(cacheKey);
if (view == null) {
synchronized (this.viewCreationCache) {
view = this.viewCreationCache.get(cacheKey);
if (view == null) {
// Ask the subclass to create the View object.
// 创建 View 对象!
view = createView(viewName, locale);
if (view == null && this.cacheUnresolved) {
view = UNRESOLVED_VIEW;
}
if (view != null) {
this.viewAccessCache.put(cacheKey, view);
this.viewCreationCache.put(cacheKey, view);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Cached view [" + cacheKey + "]");
}
}
}
}
}
return (view != UNRESOLVED_VIEW ? view : null);
}
}
@Override
protected View createView(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
// If this resolver is not supposed to handle the given view,
// return null to pass on to the next resolver in the chain.
if (!canHandle(viewName, locale)) {
return null;
}
// Check for special "redirect:" prefix.
if (viewName.startsWith(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX)) {
String redirectUrl = viewName.substring(REDIRECT_URL_PREFIX.length());
RedirectView view = new RedirectView(redirectUrl
, isRedirectContextRelative(), isRedirectHttp10Compatible());
return applyLifecycleMethods(viewName, view);
}
// Check for special "forward:" prefix.
if (viewName.startsWith(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX)) {
String forwardUrl = viewName.substring(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX.length());
return new InternalResourceView(forwardUrl);
}
// Else fall back to superclass implementation: calling loadView.
// 如果没有前缀就使用父类默认创建一个 View
return super.createView(viewName, locale);
}
1.2.2 View 渲染视图#
View 和 ViewResolver
视图解析器只是为了得到视图对象,视图对象才能真正的渲染页面 // 转发(并将隐含模型中的数据放入请求域)或者重定向到页面
调用 View 对象的 render 方法:
@Override
public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request
, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view with name '" + this.beanName + "' with model "
+ model + " and static attributes " + this.staticAttributes);
}
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
// 渲染要给页面输出的所有数据
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, request, response);
}
InternalResourceView 的 renderMergedOutputModel 方法:
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(Map<String, Object> model
, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine which request handle to expose to the RequestDispatcher.
HttpServletRequest requestToExpose = getRequestToExpose(request);
// Expose the model object as request attributes !!!
// 将隐含模型中的数据放在请求域中
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, requestToExpose);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(requestToExpose);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
// 转发路径
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(requestToExpose, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
// 拿到转发器
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(requestToExpose, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(requestToExpose, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including resource [" + getUrl()
+ "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
rd.include(requestToExpose, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to resource [" + getUrl()
+ "] in InternalResourceView '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
// 请求转发
rd.forward(requestToExpose, response);
}
}
为什么隐含模型中的数据能在 request 域中取出?
protected void exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(Map<String, Object> model
, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : model.entrySet()) {
String modelName = entry.getKey();
Object modelValue = entry.getValue();
if (modelValue != null) {
request.setAttribute(modelName, modelValue);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Added model object '" + modelName
+ "' of type [" + modelValue.getClass().getName()
+"] to request in view with name '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
}
else {
request.removeAttribute(modelName);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Removed model object '" + modelName +
"' from request in view with name '" + getBeanName() + "'");
}
}
}
}
1.3 视图和视图解析器#
- 请求处理方法执行完成后,最终返回一个 ModelAndView 对象。对于那些返回 String,View 或 ModelMap 等类型的处理方法,Spring MVC 也会在内部将它们装配成一个 ModelAndView 对象,它包含了逻辑名和模型对象的视图。
- Spring MVC 借助视图解析器(ViewResolver)得到最终的视图对象(View),最终的视图可以是 JSP ,也可能是 Excel、JFreeChart 等各种表现形式的视图。
- 对于最终究竟采取何种视图对象对模型数据进行渲染,处理器并不关心,处理器工作重点聚焦在生产模型数据的工作上,从而实现 MVC 的充分解耦。
1.3.1 视图#
- 视图的作用是渲染模型数据,将模型里的数据以某种形式呈现给客户。
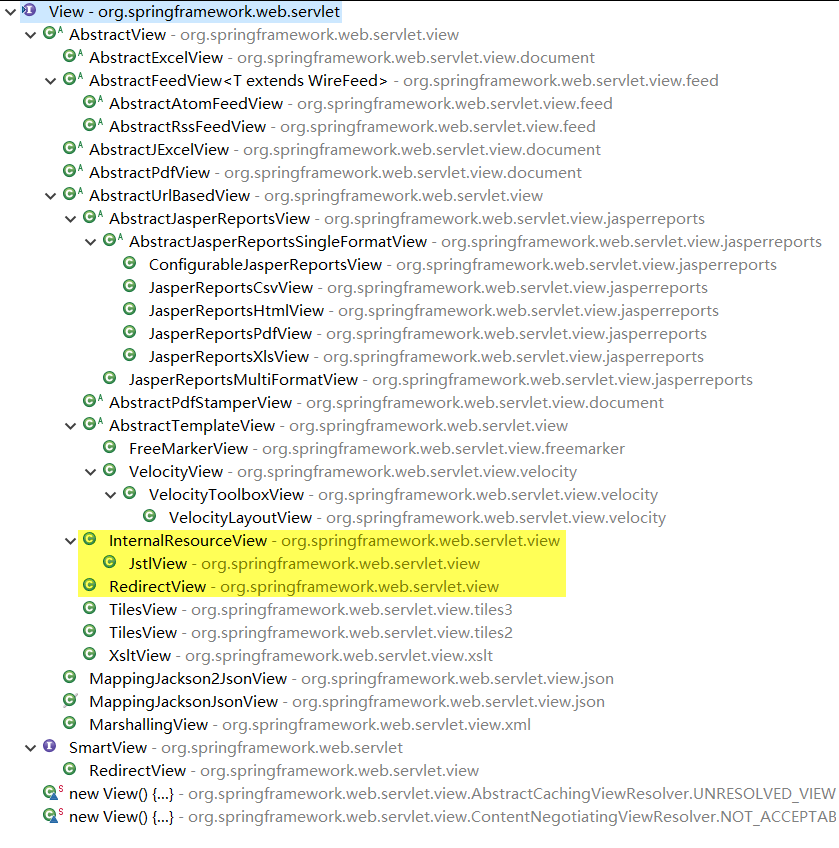
- 为了实现视图模型和具体实现技术的解耦,Spring 在 org.springframework.web.servlet 包中定义了一个高度抽象的 View 接口。
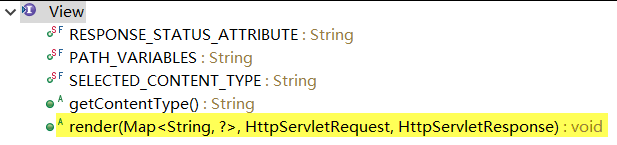
- 视图对象由视图解析器负责实例化。由于视图是无状态的,所以他们不会有线程安全的问题。
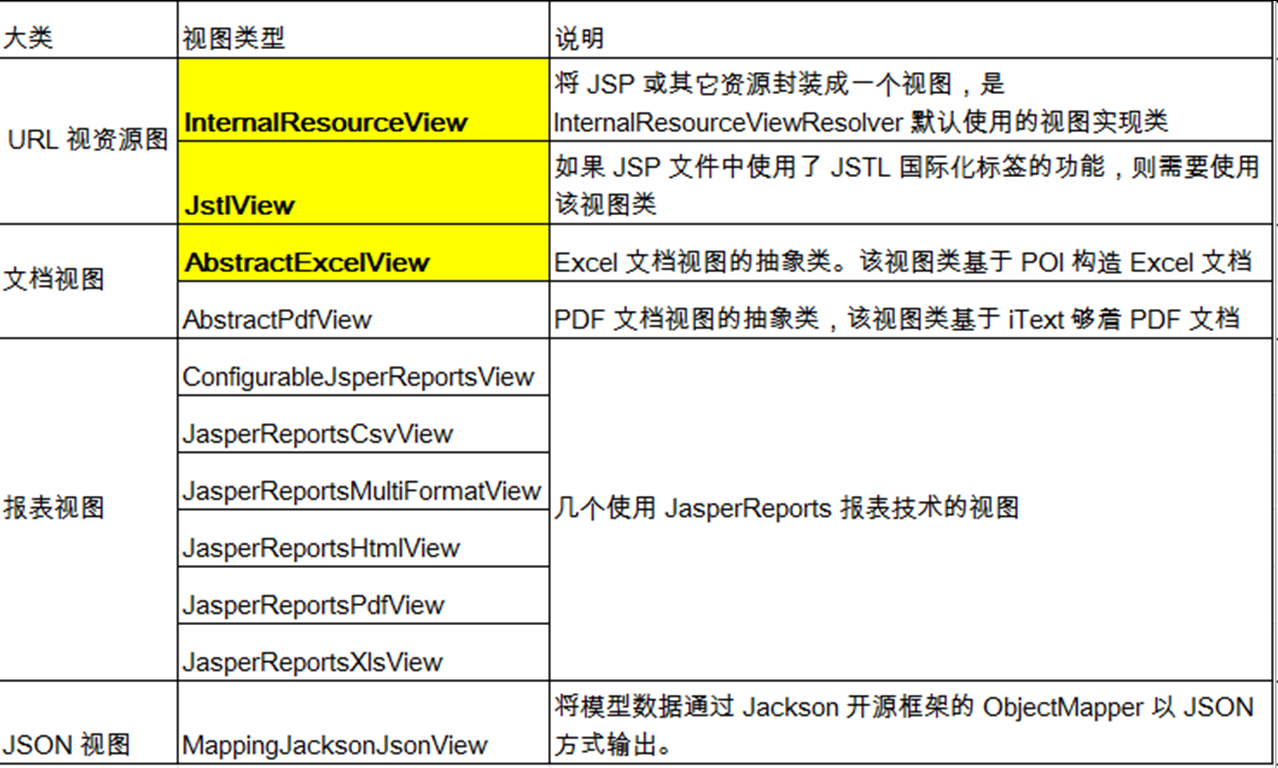
- 常用的视图实现类
1.3.2 视图解析器#
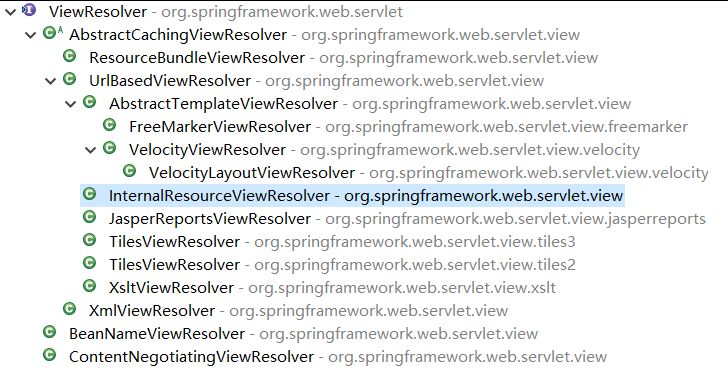
- 视图解析器的作用比较单一:将逻辑视图解析为一个具体的视图对象。
- 所有的视图解析器都必须实现 ViewResolver 接口。SpringMVC 为逻辑视图名的解析提供了不同的策略,可以在 Spring WEB 上下文中配置一种或多种解析策略,并指定他们之间的先后顺序。每一种映射策略对应一个具体的视图解析器实现类。
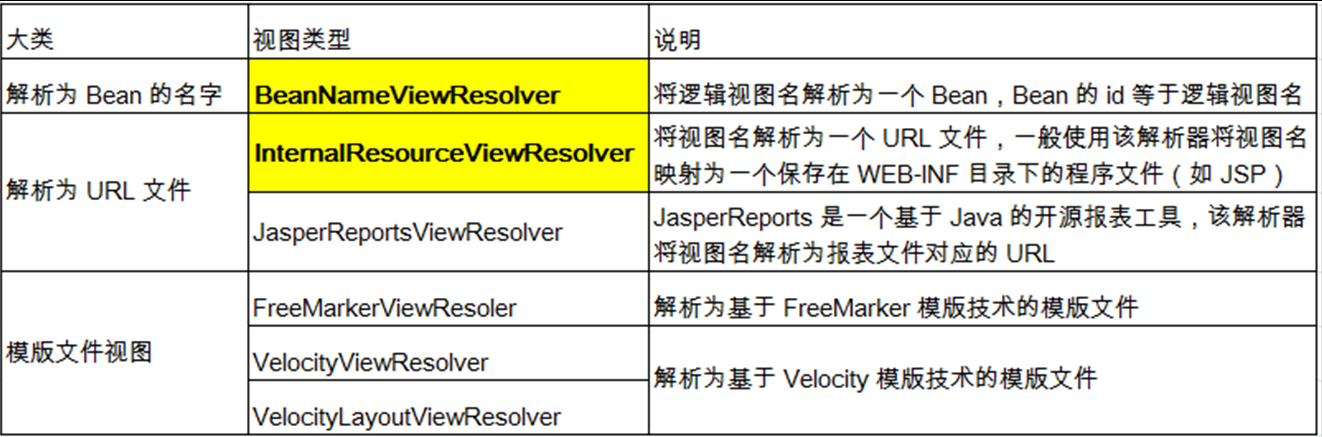
- 常用的视图解析器实现类
- 程序员可以选择一种视图解析器或混用多种视图解析器。
- 每个视图解析器都实现了 Ordered 接口并开放出一个 order 属性,可以通过 order 属性指定解析器的优先顺序,order 越小优先级越高。
- SpringMVC 会按视图解析器的优先顺序对逻辑视图名进行解析,直到解析成功并返回视图对象,否则将抛出 ServletException 异常。
1.3.3 JstlView#
- 若项目中使用了 JSTL,则 SpringMVC 会自动把视图由 InternalResourceView 转为 JstlView
- 若使用 JSTL 的 fmt 标签则需要在 SpringMVC 的配置文件中配置国际化资源文件
<!--让 SpringMVC 管理国际化资源文件;配置一个资源文件管理器 --> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <!-- basename 指定基础名--> <property name="basename" value="i18n"></property> </bean> - 直接去页面使用
<fmt:message><h1><fmt:message key="welcomeinfo"/></h1> <form action="#"> <fmt:message key="username"/>:<input /><br/> <fmt:message key="password"/>:<input /><br/> <input type="submit" value='<fmt:message key="loginBtn"/>'/> </form> - 请求一定要过 SpringMVC 的视图解析流程,人家会创建一个 JstlView 帮你快速国际化(也不能写
forward:)if (viewName.startsWith(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX)) { String forwardUrl = viewName.substring(FORWARD_URL_PREFIX.length()); return new InternalResourceView(forwardUrl); } - 若希望直接响应通过 SpringMVC 渲染的页面,可以使用
<mvc:view-controller>标签实现<!-- 发送一个请求("toLoginPage") 直接来到 WEB-INF 下的 login.jsp path 指定哪个请求 view-name 指定映射给哪个视图 ······························· 走了 SpringMVC 的整个流程:视图解析 ... 提供国际化 ... ······························· 副作用:其他请求就不好使了 → [解决方案] 开启 MVC 注解驱动模式 <mvc:annotation-driven /> --> <mvc:view-controller path="/toLoginPage" view-name="login">
1.3.4 自定义视图和视图解析器#
- Tips
- 视图解析器根据方法的返回值得到视图对象
- 多个视图解析器都会尝试能否得到视图对象
- 视图对象不同就可以具有不同功能
- 自定义视图和视图解析器
- 编写自定义视图解析器和视图实现类(为了让自定义的视图解析器先执行,还要让解析器类实现 Ordered 接口)
- 视图解析器必须放在 IOC 容器中,让其工作,能创建出我们的自定义视图对象;
<bean class="cn.edu.nuist.view.MyMeiNvViewResolver"> <property name="order" value="1"></property> </bean> - 视图对象自定义渲染逻辑
2. Restful-CRUD#
2.1 思路#
- CRUD 的 URL 地址:/资源名/资源标识
- /emp/1 GET:查询 id 为 1 的员工
- /emp/1 PUT:更新 id 为 1 的员工
- /emp/1 DELETE:删除 id 为 1 的员工
- /emp POST:新增员工
- /emp GET:员工列表
- 功能
- 员工列表
-> 访问 index.jsp,直接发送 /emp[GET] -> 控制器收到请求,查询所有员工,放入 request域 -> 转发带到 list.jsp 做展示 - 员工添加
-> 在 list.jsp 点击 ADD 发送 /toAddPage 请求 -> 控制器查出所有部门信息(部门下拉框表单项),存放到 request 域 -> 转发到 add.jsp 显示表单项 -> 输入信息后,表单提交到 /emp[POST] -> 控制器收到请求,保存新添加员工信息 -> 重定向到 list.jsp - 员工修改
-> list.jsp 为每条记录追加一个超链接 EDIT,发送 /toEditPage -> 处理器查出所有部门信息和要修改员工的原信息,存放到请求域 -> 转发带到修改页面 edit.jsp 做回显 -> 输入员工数据(不可修改 name,别用隐藏域带,用 @ModelAttribute 提前查出来) -> 点击提交,处理器收到请求,保存员工 -> 完毕后,重定向到员工列表页面做展示 - 员工删除
-> 在 list.jsp 添加一个表单,实现 DELETE 方式提交 -> 为 每条记录后的 DELETE 超链接绑定点击事件 -> 将 {超链接href} 赋值给 {表单action} -> 取消超链接默认行为 -> 处理器删除员工后,重定向到员工列表页面做展示
- 员工列表
2.2 代码实现#
2.2.1 springMVC.xml#
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.edu.nuist"></context:component-scan>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
<!--
前端控制器配置的'/',意为拦截除 Jsp 外所有请求,所以 JS 请求 404
而关于静态资源的请求,都是 tomcat 的 DefaultServlet 在负责处理。
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/> 不能处理的请求交给 tomcat
副作用:静态是可以访问了,动态映射的完蛋了
-->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<!-- 保证动态|静态请求都能访问 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
2.2.2 EmpController#
@Controller
public class EmpController {
@Autowired
EmployeeDao empDao;
@Autowired
DepartmentDao deptDao;
@RequestMapping(value="emp", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String selectAll(Model model) {
Collection<Employee> emps = empDao.getAll();
model.addAttribute("emps", emps);
return "list";
}
@RequestMapping(value="toAddPage")
public String toAddPage(Model model) {
Collection<Department> depts = deptDao.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("depts", depts);
/* model.addAttribute("employee", new Employee(null, "张三"
, "123@163.com", 1, deptDao.getDepartment(103))); */
model.addAttribute("employee", new Employee());
return "add";
}
@RequestMapping(value="emp", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public String addEmp(Employee emp) {
System.out.println("要添加的员工:" + emp);
empDao.save(emp);
return "redirect:/emp";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{id}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String toEditPage(Model model, @PathVariable("id")Integer id) {
model.addAttribute("employee", empDao.get(id));
model.addAttribute("depts", deptDao.getDepartments());
return "edit";
}
@ModelAttribute
public void getUpdateEmpInfo(Model model
, @RequestParam(value="id", required = false)Integer id) {
System.out.println("@ModelAttribute: getUpdateEmpInfo");
/*
* 不能从 @PathVariable("id") 中拿, @ModelAttribute 注解会在所有目标方法执
* 行前执行,而且,该注解只有一个 value 属性,如果请求没带该属性,则会抛异常。
* ·····························
* 所以,使用 @RequestParam 给形参赋值,并可设置该注解的 required 为 false
*/
if(id != null) model.addAttribute("employee", empDao.get(id));
}
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{id}", method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateEmp(@ModelAttribute("employee")Employee emp) {
System.out.println(emp);
empDao.save(emp);
return "redirect:/emp";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/emp/{id}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteEmp(@PathVariable("id")Integer id) {
empDao.delete(id);
return "redirect:/emp";
}
}
2.2.3 页面#
index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!-- 访问项目就要展示员工列表页面 -->
<jsp:forward page="/emp"></jsp:forward>
list.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>员工列表页面</title>
<script src="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/scripts/jquery-1.9.1.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>LASTNAME</th>
<th>EMAIL</th>
<th>GENDER</th>
<th>DEPARTMENT</th>
<th>OPTION<a href="toAddPage">(ADD)</a></th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${emps }" var="emp">
<tr>
<td>${emp.id }</td>
<td>${emp.lastName }</td>
<td>${emp.email }</td>
<td>${emp.gender==1 ? '男' : '女' }</td>
<td>${emp.department.departmentName }</td>
<td>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/emp/${emp.id}">EDIT</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/emp/${emp.id}" class="del">DELETE</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<form method="POST" id="delForm"><input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE"/></form>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function() {
$(".del").click(function() {
// 1. 改变表单的 action,并提交表单
$("#delForm").attr("action", this.href).submit();
// 2. 禁止超链接默认行为
return false;
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
add.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>添加员工</title>
<!--
[SpringMVC表单标签] 将模型数据中的属性和HTML表单元素相绑定,以实现表单数据更便捷编辑和表单值的回显。
[可能抛出的异常] IllegalStateException: Neither BindingResult nor plain
target object for bean name 'command' available as request attribute.
1. SpringMVC 认为,表单数据的每一项最终都是要回显的,path 指定的是一
个属性,这个属性是从隐含模型(请求域)中取出的某个对象中的属性。
2. path 指定的每一个属性,请求域中必须有一个对象,拥有这个属性。默认去
请求域中找一个叫 'command' 对应的对象。
3. 可通过 modelAttribute 属性来修改这个对象名,而不是去找 command
-->
</head>
<body>
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/emp"
method="POST" modelAttribute="employee">
<!--
path:
1. 当作原生 input~name
2. 会自动回显隐含模型中某个对象对应的同名属性的值
-->
lastName: <form:input path="lastName"/><br/>
email: <form:input path="email" /><br/>
gender: 男<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="1"/>
女<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="0"/><br/>
<!--
itmes: 指定要遍历的集合;自动遍历;遍历出的每一个元素都是一个 Department 对象
itemLabel 指定一个属性,遍历到的对象的哪个属性作为 option(提示信息)
itemValue 指定一个属性,遍历到的对象的哪个属性作为 value(提交信息)
-->
dept: <form:select path="department.id" items="${depts }"
itemLabel="departmentName" itemValue="id"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="保存" />
</form:form>
<%-- <form>
lastName: <input type="text" name="lastName"/><br/>
email: <input type="text" name="email"/><br/>
gender: 男<input type="radio" name="gender" value="1"/>
女<input type="radio" name="gender" value="0"/><br/>
部门:<select name="department.id">
<c:forEach items="${depts }" var="dept">
<!-- 标签体是在页面的提示选项信息,value值才是真正提交的值 -->
<option value="${dept.id }">${dept.departmentName }</option>
</c:forEach>
</select><br/>
<input type="submit" value="添加" />
</form> --%>
</body>
</html>
edit.jsp
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/emp/${employee.id }"
method="PUT" modelAttribute="employee">
<%-- <form:hidden path="lastName"/> --%>
<form:hidden path="id" />
email: <form:input path="email"/><br/>
gender: 男<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="1"/>
女<form:radiobutton path="gender" value="0"/><br/>
department: <form:select path="department.id" items="${depts }"
itemLabel="departmentName" itemValue="id"></form:select><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" />
</form:form>
分类:
服务端开发



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?