12-EndWithEstore
1. ThreadLocal#
使用方法很简单:
ThreadLocal<T> local = new ThreadLocal<T>();
local.set(...);
local.get();
ThreadLocal 而是一个线程内部的存储类,可以在指定线程内存储数据,数据存储以后,只有指定线程可以得到存储数据,官方解释如下。
This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., a user ID or Transaction ID).
大致意思就是 ThreadLocal 提供了线程内存储变量的能力,这些变量不同之处在于每一个线程读取的变量是对应的互相独立的。通过 get 和 set 方法就可以得到当前线程对应的值。
做个不恰当的比喻,从表面上看 Thread 相当于维护了一个 Map,key 就是当前的 ThreadLocal,value 就是需要存储的对象。
这里的这个比喻是不恰当的,实际上是 ThreadLocal 的静态内部类 ThreadLocalMap 为每个 Thread 都维护了一个 table[],ThreadLocal 确定了一个数组下标,而这个下标对应数组中的位置存储的就是 value。
public class Thread implements Runnable {
// 每个线程持有一个 ThreadLocalMap 对象
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
...
}
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
public ThreadLocal() {}
// 每一个 Thread 都会实例化 ThreadLocalMap 并赋值给成员变量 threadLocals
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
// 设置并获取初始化值
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
}
1.1 ThreadLocalMap#
// Entry 为 ThreadLocalMap 静态内部类,对 ThreadLocal 的弱引用
// 同时让 ThreadLocal 和 value 形成 key-value 的关系
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
// ThreadLocalMap 构造器
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
// 内部成员数组,INITIAL_CAPACITY 值为 16 的常量
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
// 位运算,结果与取模相同,计算出需要存放的位置
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
通过上面的代码不难看出在实例化 ThreadLocalMap 时创建了一个长度为 16 的 Entry[]。通过 hashCode 与 length 位运算确定出一个索引值 i,这个 i 就是被存储在 table 中的位置。
前面讲过每个线程 Thread 持有一个 ThreadLocalMap 类型的实例 threadLocals,结合此处的构造方法可以理解成每个线程 Thread 都持有一个 Entry 型的数组 table,而一切的读取过程都是通过操作这个数组 table 完成的。
显然 table 是 set 和 get 的焦点,在看具体的 set 和 get 方法前,先看下面这段代码。
// 在某一线程声明了 ABC 三种类型的 ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal<A> sThreadLocalA = new ThreadLocal<A>();
ThreadLocal<B> sThreadLocalB = new ThreadLocal<B>();
ThreadLocal<C> sThreadLocalC = new ThreadLocal<C>();
由前面我们知道对于一个 Thread 来说只能持有一个 ThreadLocalMap,所以 A、B、C 对应同一个 ThreadLocalMap 对象。为了管理 A、B、C,于是将他们存储在一个数组的不同位置,而这个数组就是上面提到的 Entry 型的数组 table。
1.2 set 方法#
那么问题来了,A、B、C 在 table 中的位置是如何确定的?为了能正常够正常的访问对应的值,肯定存在一种方法计算出确定的索引。如下是 ThreadLocalMap 的 set 方法:
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 获取索引值,这个地方是比较特别的地方
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
// 遍历 tab 如果已经存在则更新值
for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
// 如果上面没有遍历成功则创建新值
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
// 满足条件数组扩容x2
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
// 开放寻址冲突解决方法之线性探测法
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
在 ThreadLocalMap 中的 set 方法与构造方法能看到以下代码片段。
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
简而言之就是将 threadLocalHashCode 进行一个位运算(取模)得到索引 i,threadLocalHashCode 代码如下。
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
// The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at zero.
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode = new AtomicInteger();
/**
* The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns
* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread
* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.
*/
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
// Returns the next hash code.
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT); // 自增
}
因为 static 的原因,在每次 new ThreadLocal 时因为 threadLocalHashCode 的初始化,会使 threadLocalHashCode 值自增一次,增量为 0x61c88647。
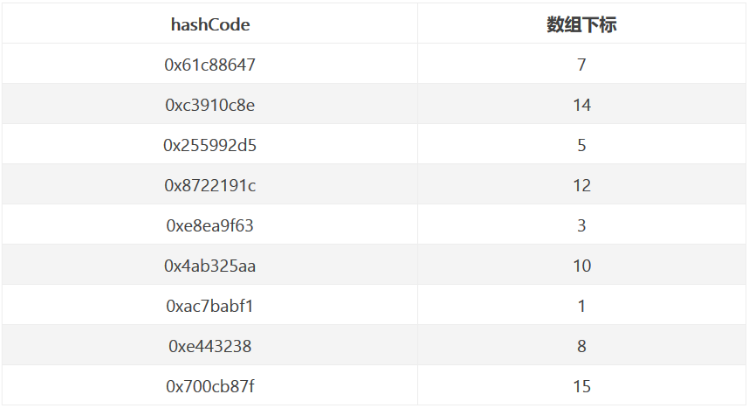
0x61c88647 是斐波那契散列乘数,它的优点是通过它散列(hash) 出来的结果分布会比较均匀,可以很大程度上避免hash冲突,已初始容量 16 为例,hash 并与 15 位运算计算数组下标结果如下:
总结如下:
- 对于某一 ThreadLocal 来讲,它的索引值 i 是确定的,在不同线程之间访问时访问的是不同的 table 数组的同一位置即都为 table[i],只不过这个不同线程之间的 table 是独立的。
- 对于同一线程的不同 ThreadLocal 来讲,这些 ThreadLocal 实例共享一个 table 数组,然后每个 ThreadLocal 实例在 table 中的索引 i 是不同的。
1.3 get 方法#
// ThreadLocal 中 get 方法
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
// ThreadLocalMap 中 getEntry 方法
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) return e; // find it!
if (k == null) { // 说明待查找元素不在其中
expungeStaleEntry(i);
} else { // 散列冲突 → 开放寻址法
i = nextIndex(i, len);
}
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
// 开放寻址冲突解决方法之线性探测法
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
理解了 set 方法,get 方法也就清楚明了,无非是通过计算出索引直接从数组对应位置读取即可。
ThreadLocal 实现主要涉及 Thread、ThreadLocal、ThreadLocalMap 这三个类。关于 ThreadLocal 的实现流程正如上面写的那样,实际代码还有许多细节处理的部分并没有在这里写出来。
ThreadLocal 和 synchronized 都是为了解决多线程中相同变量的访问冲突问题,不同的点是:
- Synchronized 是通过线程等待,牺牲时间来解决访问冲突;
- ThreadLocal 是通过每个线程单独一份存储空间,牺牲空间来解决冲突,并且与 synchronized 相比,ThreadLocal 具有线程隔离的效果,只有在线程内才能获取到对应的值,线程外则不能访问到想要的值。
正因为 ThreadLocal 的线程隔离特性,使他的应用场景相对来说更为特殊一些。在 Android 中 Looper、ActivityThread 以及 AMS 中都用到了 ThreadLocal。当某些数据是以线程为作用域并且不同线程具有不同的数据副本的时候,就可以考虑采用 ThreadLocal。
2. InheritableThreadLocal#
InheritableThreadLocal 是 Java 中的一个特殊类型的 ThreadLocal,它允许子线程从父线程那里继承值。普通的 ThreadLocal 在子线程中无法访问父线程设置的值,而 InheritableThreadLocal 则解决了这个问题,使得子线程可以获取父线程设置的值。
(1)出现原因
InheritableThreadLocal 的出现主要是为了解决在多线程环境中,特别是涉及线程嵌套或者线程池中的场景下,子线程无法访问到父线程设置的 ThreadLocal 值的问题。例如,某些情况下需要在父线程设置一些上下文信息,子线程也需要获取这些信息进行后续处理,此时就需要使用 InheritableThreadLocal。
(2)使用方法
使用 InheritableThreadLocal 类似于使用普通的 ThreadLocal,但有一些注意点:
- 初始化:通过创建 InheritableThreadLocal 实例来定义线程本地变量。
- 设置值:通过 set() 方法设置当前线程的局部变量值。
- 获取值:通过 get() 方法获取当前线程的局部变量值。
- 清理:使用完毕后,可以调用 remove() 方法清除当前线程的局部变量值。
public class InheritableThreadLocalExample {
private static final InheritableThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set value in parent thread
threadLocal.set("Parent Thread Value");
// Create a child thread
Thread childThread = new Thread(() -> {
// Child thread can access parent thread's value
String value = threadLocal.get();
System.out.println("Child Thread Value: " + value); // Outputs "Parent Thread Value"
});
childThread.start();
}
}
(3)适用场景
- 线程池中的任务:当使用线程池执行任务时,子任务可能会在不同的线程中执行,但需要共享父任务中设置的某些上下文信息。
- Web 请求上下文:在 Web 应用中,可能会将一些请求信息存储在 InheritableThreadLocal 中,以便于后续异步处理或线程池中执行的任务能够获取这些信息。
- 跨层级调用:在复杂的系统中,可能存在多层次的调用关系,需要一些共享的上下文信息在整个调用链中传递。
(4)实现原理
InheritableThreadLocal 的实现原理主要是基于 Thread 类的 inheritableThreadLocals 字段。当一个线程创建子线程时,子线程会继承父线程的 inheritableThreadLocals。具体流程包括:
- 当父线程创建子线程时,子线程的 inheritableThreadLocals 会从父线程复制一份。
- 当父线程的 inheritableThreadLocals 发生变化时(通过 set() 方法设置新值),子线程的 inheritableThreadLocals 不会受到影响,保持独立性。
- 子线程通过 get() 方法可以获取到父线程设置的值,实现了上下文的继承和传递。
需要注意的是,虽然 InheritableThreadLocal 提供了父线程到子线程的值传递机制,但过度依赖 InheritableThreadLocal 也可能会导致上下文信息的混乱和不可控性,因此在使用时需要谨慎考虑设计和使用场景。
3. Estore 项目难点#
1. ThreadLocal + @Annotation → 事务管理
- 反射注解:通过反射注解,来确定某个类的方法上是否有注解从而控制程序的流转;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.METHOD) public @interface Trans {} - 利用动态代理,使 DAO 中不需要区分是否开启过事务;
public class TransactionManager { private TransactionManager() {} private static DataSource source = new ComboPooledDataSource(); // private static Connection conn = DaoUtils.getConn(); private static ThreadLocal<Boolean> flag_local = new ThreadLocal<Boolean>() { protected Boolean initialValue() { return false; }; }; /* conn_local: 需要事务管理的业务可能会在这同一个 Connection 上执行多次SQL,为防止 QueryRunner 执行完每一次操作之后 close 该连接,故为此连接做代理,让 proxySource 每次 getConnection() 时,返回这个 proxyConnection realConn_local: 但迟早是要关的,所以还要保存真实的 Connection 的引用到此 ThreadLocalMap */ private static ThreadLocal<Connection> conn_local = new ThreadLocal<Connection>(); private static ThreadLocal<Connection> realConn_local = new ThreadLocal<Connection>(); public static void startTran() throws SQLException { flag_local.set(true); final Connection conn = source.getConnection(); conn.setAutoCommit(false); realConn_local.set(conn); Connection proxyConn = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance( conn.getClass().getClassLoader(), conn.getClass() .getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if("close".equals(method.getName())) return null; else return method.invoke(conn, args); } }); conn_local.set(proxyConn); } public static void commit() { DbUtils.commitAndCloseQuietly(conn_local.get()); } public static void rollback() { DbUtils.rollbackAndCloseQuietly(conn_local.get()); } /* public static Connection getConn() { return conn_local.get(); } ---------------------------------------- 若无须事务控制,QueryRunner 构造器里传 DataSource;需要事务控制,update 方法里传 getConn() 这么做无疑是和 Service 层耦合了。应统一起来,均在 QueryRunner 构造器里传 DataSource,只不过: > 如果 Service 没有开启事务,则返回普通数据源 > 如果 Service 已经开启事务,则返回改造过 getConnection() 的数据源 ,该数据源每次返回的都是同一个开启过事务的 Connection */ public static DataSource getSource() throws SQLException { if(flag_local.get()) { // 开启过事务,返回改造过的 DataSource return (DataSource) Proxy.newProxyInstance(source.getClass().getClassLoader() , source.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if("getConnection".equals(method.getName())) { return conn_local.get(); } else { // 没开启事务,返回普通的 DataSource return method.invoke(source, args); } } }); } else { return source; } } public static void release() { try { realConn_local.get().close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } realConn_local.remove(); conn_local.remove(); flag_local.remove(); } }
2. 工厂类 + 动态代理 → 面向切面编程(service层)
public class BasicFactory {
private static BasicFactory factory = new BasicFactory();
private static Properties prop = new Properties();
static {
try {
prop.load(BasicFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.properties"));
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private BasicFactory() {}
public static BasicFactory getFactory() {
return factory;
}
/*
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getInstance(Class<T> clazz) {
String key = clazz.getSimpleName();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
try {
return (T) Class.forName(value).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T extends Dao> T getDao(Class<T> clazz) {
String key = clazz.getSimpleName();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
try {
return (T) Class.forName(value).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T extends Service> T getService(Class<T> clazz) {
String key = clazz.getSimpleName();
String value = prop.getProperty(key);
try {
final T service = (T) Class.forName(value).newInstance();
T proxyService = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(service.getClass().getClassLoader()
, service.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Trans.class)) {
try {
TransactionManager.startTran();
Object obj = method.invoke(service, args);
TransactionManager.commit();
return obj;
} catch(InvocationTargetException e) {
TransactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e.getTargetException());
} catch(Exception e) {
TransactionManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
TransactionManager.release();
}
} else {
return method.invoke(service, args);
}
}
});
return proxyService;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?