《构建之法》之第四次作业
| 作业要求链接 | 作业地址 |
|---|---|
| 伙伴博客 | 李涵 |
| Github地址 | github |
一、
(1)PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 770 | 720 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 300 | 240 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 30 | 20 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 30 | 20 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 15 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 30 | 30 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 300 | 315 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 30 | 40 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 30 | 40 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 150 | 120 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 60 | 45 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 30 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 60 | 45 |
| 合计 | 950 | 900 |
(2)代码规范:
命名规范:1.类名首字母要大写,使用能够反映类功能的名词或名词短语命名类。
2.类成员变量首单词小写,变量名前可加_前缀。
3.方法名第一个字符要大写,且应使用动词或动词短语。
4.参数首字符小写,采用描述性参数名称。
5.接口名称要有意义,接口修饰符只能用public和internal。
6.每条语句至少占一行,过长语句断为两行显示。
7.语句嵌套不超过3层。
详细代码规范见:代码规范
(3)结对过程:非摆拍讨论、结对编程照片:
线下分工、讨论、结对编程;工作日时细小问题线上解决。
二、
(4)解题思路及关键代码展示:
大体功能结构图:
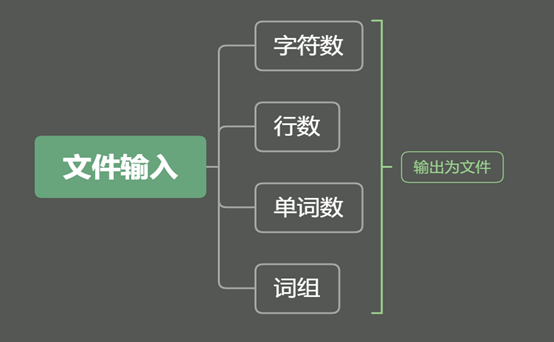
统计字符数、单词数、行数模块:
public long charactersnumber = 0; //字符数
public long wordsnumber = 0; //单词数
public long linesnumber = 0; //行数
//数据统计
public void Calculate(string dataline, WordTrie wtrie)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(dataline)) return;
string word = null;
for (int i = 0, len = dataline.Length; i < len; i++)
{
char unit = dataline[i];
if (unit >= 65 && unit <= 90){
unit = (char)(unit + 32);
} //大写转小写
if ((unit >= 48 && unit <= 57) || (unit >= 97 && unit <= 122)){
word = String.Concat(word, unit);
}
else{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(word)){ //判断是否为词尾后的字符
if (word[0] >= 97 && word[0] <= 122){ //首字符是否为字母
wtrie.Insert(word);
}
word = null;
}
}
}
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(word)) //判断行尾是否有单词
{
if (word[0] >= 97 && word[0] <= 122){ //首字符是否为字母
wtrie.Insert(word);
}
word = null;
}
this.linesnumber++; //统计行数
this.wordsnumber = wtrie.CountSum; //统计单词数
this.charactersnumber += dataline.Length; //统计字符数
}
词频排序:
public List<ListUnit> Sort()
{
TrieNode node = _Root;
List<ListUnit> WordList = new List<ListUnit>();
WordList = WordPreOrder(node, WordList);
//按词频降序排列,若词频相等按字典序排列
WordList.Sort((a, b) =>
{
if (a.WordNum.CompareTo(b.WordNum) != 0)
return -a.WordNum.CompareTo(b.WordNum);
else
return a.Word.CompareTo(b.Word);
});
return WordList;
}
单词表生成:
private List<ListUnit> WordPreOrder(TrieNode node, List<ListUnit> WordList)
{
if (node.PrefixNum == 0) { return WordList; }
if (node.WordNum != 0)
{
ListUnit unit = new ListUnit();
unit.Word = node.Word;
unit.WordNum = node.WordNum;
WordList.Add(unit);
}
foreach (char key in node.Sons.Keys)
{
WordList = WordPreOrder(node.Sons[key], WordList);
}
return WordList;
}
读取并统计文件:
public string pathIn;
public string pathOut;
//按行读取输入文件并统计
public WordCalculate Input(WordCalculate datanumber, WordTrie wtrie)
{
FileStream fs = null;
StreamReader sr = null;
String dataline = String.Empty;
try
{
fs = new FileStream(this.pathIn, FileMode.Open);
sr = new StreamReader(fs);
while ((dataline = sr.ReadLine()) != null)
{
datanumber.Calculate(dataline, wtrie); //按行统计数据
}
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("文档读取失败!");
}
finally
{
if (sr != null) { sr.Close(); }
if (fs != null) { fs.Close(); }
}
return datanumber;
}
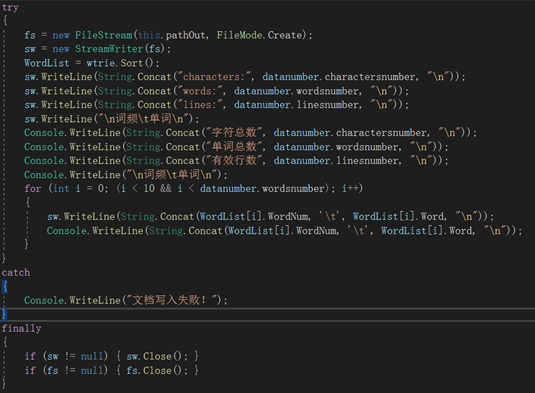
将结果输出文件:
//将统计数据写到输出文件
public void Output(WordCalculate datanumber, WordTrie wtrie)
{
FileStream fs = null;
StreamWriter sw = null;
List<WordTrie.ListUnit> WordList = new List<WordTrie.ListUnit>();
try
{
fs = new FileStream(this.pathOut, FileMode.Create);
sw = new StreamWriter(fs);
WordList = wtrie.Sort();
sw.WriteLine(String.Concat("characters:", datanumber.charactersnumber, "\n"));
sw.WriteLine(String.Concat("words:", datanumber.wordsnumber, "\n"));
sw.WriteLine(String.Concat("lines:", datanumber.linesnumber, "\n"));
sw.WriteLine("\n词频\t单词\n");
Console.WriteLine(String.Concat("字符总数", datanumber.charactersnumber, "\n"));
Console.WriteLine(String.Concat("单词总数", datanumber.wordsnumber, "\n"));
Console.WriteLine(String.Concat("有效行数", datanumber.linesnumber, "\n"));
Console.WriteLine("\n词频\t单词\n");
for (int i = 0; (i < 10 && i < datanumber.wordsnumber); i++)
{
sw.WriteLine(String.Concat(WordList[i].WordNum, '\t', WordList[i].Word, "\n"));
Console.WriteLine(String.Concat(WordList[i].WordNum, '\t', WordList[i].Word, "\n"));
}
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("文档写入失败!");
}
finally
{
if (sw != null) { sw.Close(); }
if (fs != null) { fs.Close(); }
}
}
代码较多,只展示部分代码,完整代码已提交。
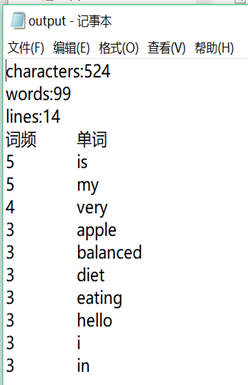
运行结果:输入文件

输出结果:
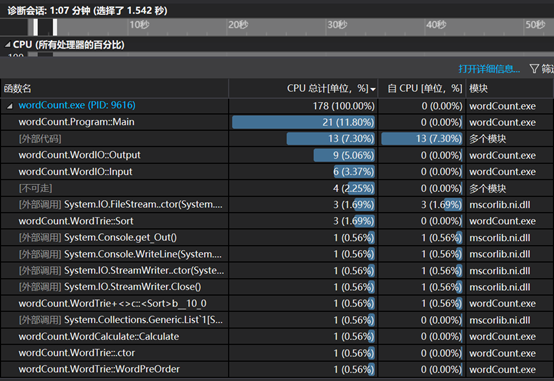
(5)性能分析及改进:
初期第一版我们所有功能代码写在一个Main函数中,意在与功能独立、松耦合后进行性能对比,Main函数资源占比巨大。
第二版本实现基础功能独立后生成性能分析报告:
三、
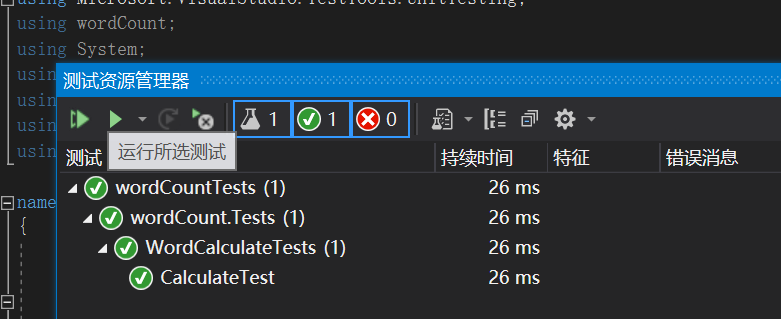
(6)单元测试:详情见队友
(7)异常处理:
代码中的异常处理机制:进行文档读取、写入的异常机制处理

(8)附加功能:
.-m 参数设定统计的词组长度
.-n参数设定输出的单词数量
.-i 参数设定读入的文件路径
.-o 参数设定生成文件的存储路径
多参数的混合使用等新增功能的实现,使用了commandline程序

(9)代码复审:
两人结对编程,编程过程中两人互相监督,且共同查阅相关资料,参考的文章也大抵相同。因而在代码复审过程中并未发现诸如结构、功能性问题等大问题。但复审还是发现了不少小问题,诸如相关代码规范执行的并不完全到位,有多处代码冗余情况。互通代码时路径问题也没沟通好,但都进行了及时修改。
四、
(10)个人感悟:
两人结对编程效率确实比一个人高,当遇到问题时何以相互探讨,一起查阅资料;一人在写代码时会同时有两双眼睛进行监督、纠错、思考;即使遇到困难心里也不会太慌张,一般通过讨论、百度即可解决。体验最真实,结对编程1+1确实是>2的
同时对结对编程流程、C#语言有了更深入的了解,自身的编程素质有了很大提高。通过本次实验作业收获良多。




