深度滤波器(4)——单目稠密重建的流程
各位泡芙们,大家好!
经过前两天的理论铺垫,相信你对深度滤波器有了一个感性的认识,今天,我们就通过流程图的方式来帮大家梳理一下单目稠密重建的代码。
主函数:
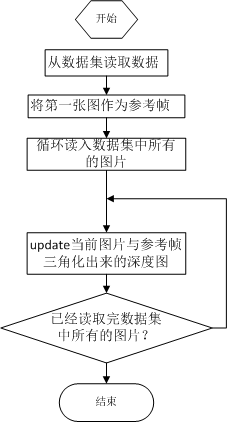
update:
1 bool update(const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, const SE3& T_C_R, Mat& depth, Mat& depth_cov ) 2 { 3 #pragma omp parallel for 4 for ( int x=boarder; x<width-boarder; x++ ) 5 #pragma omp parallel for 6 for ( int y=boarder; y<height-boarder; y++ ) 7 { 8 // 遍历每个像素 9 if ( depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x] < min_cov || depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x] > max_cov ) // 深度已收敛或发散 10 continue; 11 // 在极线上搜索 (x,y) 的匹配 12 Vector2d pt_curr; 13 bool ret = epipolarSearch ( 14 ref, 15 curr, 16 T_C_R, 17 Vector2d(x,y), 18 depth.ptr<double>(y)[x], 19 sqrt(depth_cov.ptr<double>(y)[x]), 20 pt_curr 21 ); 22 23 if ( ret == false ) // 匹配失败 24 continue; 25 26 // 取消该注释以显示匹配 27 // showEpipolarMatch( ref, curr, Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr ); 28 29 // 匹配成功,更新深度图 30 updateDepthFilter( Vector2d(x,y), pt_curr, T_C_R, depth, depth_cov ); 31 } 32 }
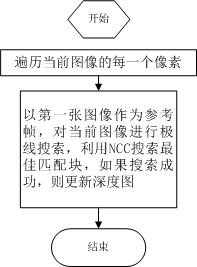
极线搜索:

1 // 极线搜索 2 // 方法见书 13.2 13.3 两节 3 bool epipolarSearch( 4 const Mat& ref, const Mat& curr, 5 const SE3& T_C_R, const Vector2d& pt_ref, 6 const double& depth_mu, const double& depth_cov, 7 Vector2d& pt_curr ) 8 { 9 Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pt_ref ); 10 f_ref.normalize(); 11 Vector3d P_ref = f_ref*depth_mu; // 参考帧的 P 向量 12 13 Vector2d px_mean_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*P_ref ); // 按深度均值投影的像素 14 double d_min = depth_mu-3*depth_cov, d_max = depth_mu+3*depth_cov; 15 if ( d_min<0.1 ) d_min = 0.1; 16 Vector2d px_min_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*(f_ref*d_min) ); // 按最小深度投影的像素 17 Vector2d px_max_curr = cam2px( T_C_R*(f_ref*d_max) ); // 按最大深度投影的像素 18 19 Vector2d epipolar_line = px_max_curr - px_min_curr; // 极线(线段形式) 20 Vector2d epipolar_direction = epipolar_line; // 极线方向 21 epipolar_direction.normalize(); 22 double half_length = 0.5*epipolar_line.norm(); // 极线线段的半长度 23 if ( half_length>100 ) half_length = 100; // 我们不希望搜索太多东西 24 25 // 取消此句注释以显示极线(线段) 26 // showEpipolarLine( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_min_curr, px_max_curr ); 27 28 // 在极线上搜索,以深度均值点为中心,左右各取半长度 29 double best_ncc = -1.0; 30 Vector2d best_px_curr; 31 for ( double l=-half_length; l<=half_length; l+=0.7 ) // l+=sqrt(2) 32 { 33 Vector2d px_curr = px_mean_curr + l*epipolar_direction; // 待匹配点 34 if ( !inside(px_curr) ) 35 continue; 36 // 计算待匹配点与参考帧的 NCC 37 double ncc = NCC( ref, curr, pt_ref, px_curr ); 38 if ( ncc>best_ncc ) 39 { 40 best_ncc = ncc; 41 best_px_curr = px_curr; 42 } 43 } 44 if ( best_ncc < 0.85f ) // 只相信 NCC 很高的匹配 45 return false; 46 pt_curr = best_px_curr; 47 return true; 48 }
深度滤波器:

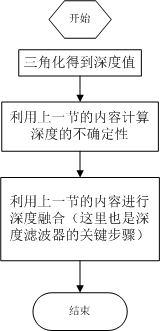
bool updateDepthFilter( const Vector2d& pt_ref, const Vector2d& pt_curr, const SE3& T_C_R, Mat& depth, Mat& depth_cov ) { // 我是一只喵 // 不知道这段还有没有人看 // 用三角化计算深度 SE3 T_R_C = T_C_R.inverse(); Vector3d f_ref = px2cam( pt_ref ); f_ref.normalize(); Vector3d f_curr = px2cam( pt_curr ); f_curr.normalize(); // 方程 // d_ref * f_ref = d_cur * ( R_RC * f_cur ) + t_RC // => [ f_ref^T f_ref, -f_ref^T f_cur ] [d_ref] = [f_ref^T t] // [ f_cur^T f_ref, -f_cur^T f_cur ] [d_cur] = [f_cur^T t] // 二阶方程用克莱默法则求解并解之 Vector3d t = T_R_C.translation(); Vector3d f2 = T_R_C.rotation_matrix() * f_curr; Vector2d b = Vector2d ( t.dot ( f_ref ), t.dot ( f2 ) ); double A[4]; A[0] = f_ref.dot ( f_ref ); A[2] = f_ref.dot ( f2 ); A[1] = -A[2]; A[3] = - f2.dot ( f2 ); double d = A[0]*A[3]-A[1]*A[2]; Vector2d lambdavec = Vector2d ( A[3] * b ( 0,0 ) - A[1] * b ( 1,0 ), -A[2] * b ( 0,0 ) + A[0] * b ( 1,0 )) /d; Vector3d xm = lambdavec ( 0,0 ) * f_ref; Vector3d xn = t + lambdavec ( 1,0 ) * f2; Vector3d d_esti = ( xm+xn ) / 2.0; // 三角化算得的深度向量 double depth_estimation = d_esti.norm(); // 深度值 // 计算不确定性(以一个像素为误差) Vector3d p = f_ref*depth_estimation; Vector3d a = p - t; double t_norm = t.norm(); double a_norm = a.norm(); double alpha = acos( f_ref.dot(t)/t_norm ); double beta = acos( -a.dot(t)/(a_norm*t_norm)); double beta_prime = beta + atan(1/fx); double gamma = M_PI - alpha - beta_prime; double p_prime = t_norm * sin(beta_prime) / sin(gamma); double d_cov = p_prime - depth_estimation; double d_cov2 = d_cov*d_cov; // 高斯融合 double mu = depth.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ]; double sigma2 = depth_cov.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ]; double mu_fuse = (d_cov2*mu+sigma2*depth_estimation) / ( sigma2+d_cov2); double sigma_fuse2 = ( sigma2 * d_cov2 ) / ( sigma2 + d_cov2 ); depth.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = mu_fuse; depth_cov.ptr<double>( int(pt_ref(1,0)) )[ int(pt_ref(0,0)) ] = sigma_fuse2; return true; }
相信有了上面的流程图,加上前面几章的理论铺垫,你能够比较轻松地看懂这些代码了。祝你阅读代码愉快!
posted on 2017-05-03 21:39 Brad_Lucas 阅读(1752) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报




