kotlin中的集合学习
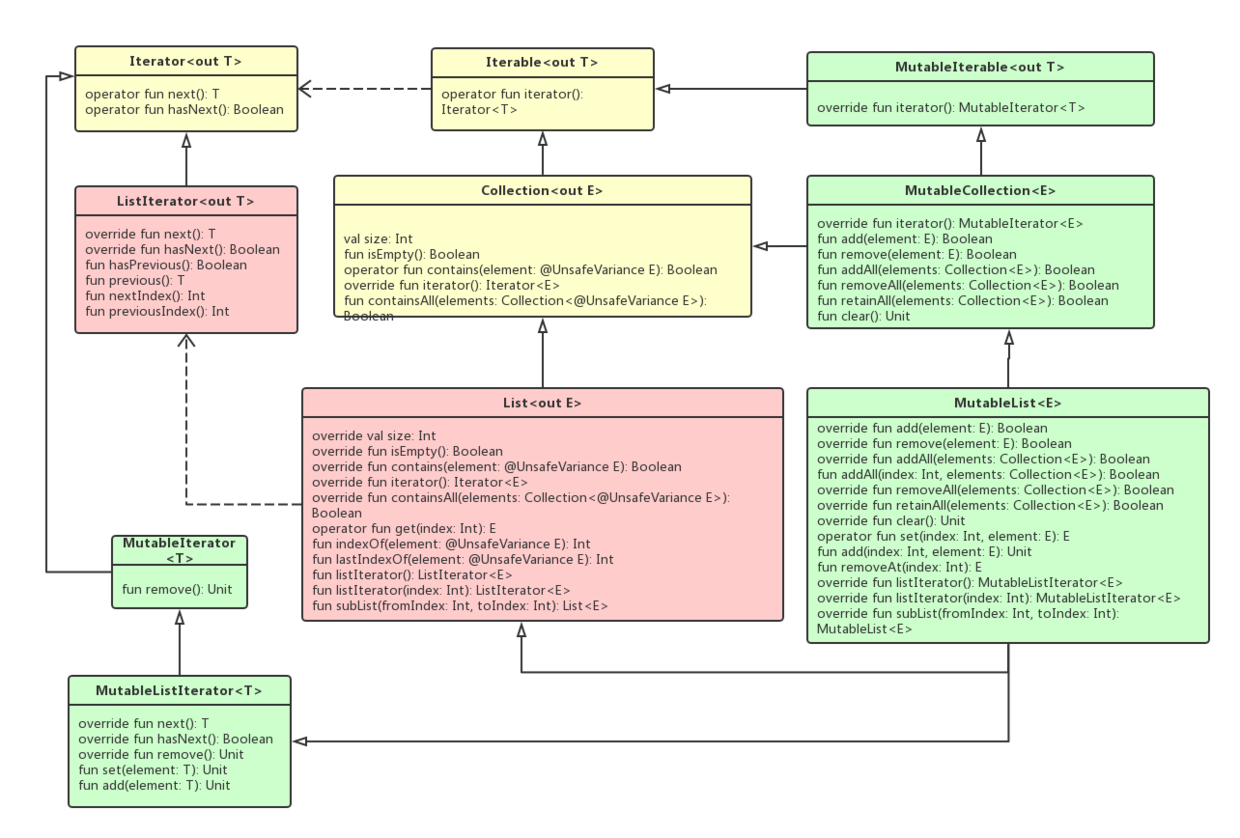
集合分为两类:可变集合类(Mutable)、不可变集合类(Immutable)
集合类型: List、set、map
list:数组、链表、堆栈、队列等
set:无序:set 、 有序set—>TreeSet
map: key-value键值对
直接使用java的结构:
@SinceKotlin("1.1") public actual typealias RandomAccess = java.util.RandomAccess
@SinceKotlin("1.1") public actual typealias ArrayList<E> = java.util.ArrayList<E>
@SinceKotlin("1.1") public actual typealias LinkedHashMap<K, V> = java.util.LinkedHashMap<K, V>
@SinceKotlin("1.1") public actual typealias HashMap<K, V> = java.util.HashMap<K, V>
@SinceKotlin("1.1") public actual typealias LinkedHashSet<E> = java.util.LinkedHashSet<E>
@SinceKotlin("1.1") public actual typealias HashSet<E> = java.util.HashSet<E>
下标操作类
-
contains —— 判断是否有指定元素
-
elementAt —— 返回对应的元素,越界会抛IndexOutOfBoundsException
-
firstOrNull —— 返回符合条件的第一个元素,没有 返回null
-
lastOrNull —— 返回符合条件的最后一个元素,没有 返回null
-
indexOf —— 返回指定元素的下标,没有 返回-1
-
singleOrNull —— 返回符合条件的单个元素,如有没有符合或超过一个,返回null
判断类
-
any —— 判断集合中 是否有满足条件 的元素
-
all —— 判断集合中的元素 是否都满足条件
-
none —— 判断集合中是否 都不满足条件,是则返回true
-
count —— 查询集合中 满足条件 的 元素个数
-
reduce —— 从 第一项到最后一项进行累计
过滤类
-
filter —— 过滤 掉所有 满足条件 的元素
-
filterNot —— 过滤所有不满足条件的元素
-
filterNotNull —— 过滤NULL
-
take —— 返回前 n 个元素
转换类
-
map —— 转换成另一个集合(与上面我们实现的 convert 方法作用一样);
-
mapIndexed —— 除了转换成另一个集合,还可以拿到Index(下标);
-
mapNotNull —— 执行转换前过滤掉 为 NULL 的元素
-
flatMap —— 自定义逻辑合并两个集合;
-
groupBy —— 按照某个条件分组,返回Map;
排序类
-
reversed —— 反序
-
sorted —— 升序
-
sortedBy —— 自定义排序
-
sortedDescending —— 降序
-
不可变List,listOf创建
/*
listOf()用于创建没有元素的空List
listOf(vararg elements: T)用于创建只有一个元素的List
listOf(element: T)用于创建拥有多个元素的List
*/
@kotlin.internal.InlineOnly
public inline fun <T> listOf(): List<T> = emptyList()
public fun <T> listOf(vararg elements: T): List<T> = if (elements.size > 0) elements.asList() else emptyList()
@JvmVersion
public fun <T> listOf(element: T): List<T> = java.util.Collections.singletonList(element)
其实是封装了Java的list和ArrayList,可以用arrayListOf生成一个java的ArrayList对象实例
-
创建可变集合MutableList
在MutableList中,除了继承List中的那些函数外,另外新增了add/addAll、remove/removeAll/removeAt、set、clear、retainAll等更新修改的操作函数。
//添加一个元素
override fun add(element: E): Boolean
//删除一个元素
override fun remove(element: E): Boolean
//将一个集合里的所有元素加入
override fun addAll(elements: Collection<E>): Boolean
//
fun addAll(index: Int, elements: Collection<E>): Boolean
//删除一个集合里的所有元素
override fun removeAll(elements: Collection<E>): Boolean
override fun retainAll(elements: Collection<E>): Boolean
override fun clear(): Unit
operator fun set(index: Int, element: E): E
fun add(index: Int, element: E): Unit
fun removeAt(index: Int): E
override fun listIterator(): MutableListIterator<E>
override fun listIterator(index: Int): MutableListIterator<E>
override fun subList(fromIndex: Int, toIndex: Int): MutableList<E>
-
迭代器
(1)调用iterator()函数,容器返回一个Iterator实例。iterator()函数是kotlin.collections.Iterable中的函数, 被Collection继承。 (2)调用hasNext()函数检查序列中是否还有元素。 (3)第一次调用Iterator的next()函数时,它返回序列的第一个元素。依次向后递推,使用next()获得序列中的下一个元素。
private open inner class IteratorImpl : Iterator<E> {
protected var index = 0
override fun hasNext(): Boolean = index < size
override fun next(): E {
if (!hasNext()) throw NoSuchElementException()
return get(index++)
}
}
//到这里,说明实现了iterator的类都有其对象,forEach实际上是调用了一遍for对每一个元素调用了action(in 其实是一个语法糖,也是调用了迭代器对象)
@kotlin.internal.HidesMembers
public inline fun <T> Iterable<T>.forEach(action: (T) -> Unit): Unit {
for (element in this) action(element)
}
一些基本运算函数:
-
any()
-
判断是否有元素
-
如果加了lambada,可以判断是否有符合条件的元素
public inline fun <T> Iterable<T>.any(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): Boolean {
for (element in this) if (predicate(element)) return true
return false
} -
-
all(predicate: (T) -> Boolean)
判断是否都满足条件
-
none()
-
判断集合是否无元素
public fun <T> Iterable<T>.none(): Boolean {
for (element in this) return false
return true
}
2.是否都不满足,与any类似
-
count
-
集合元素的个数
-
符合条件的个数
-
reduce
从第一项到最后一项进行累计运算,从这个源码可以看出,iterable从-1开始计数,与cursor类似
public inline fun <S, T: S> Iterable<T>.reduce(operation: (acc: S, T) -> S): S {
val iterator = this.iterator()
if (!iterator.hasNext()) throw UnsupportedOperationException("Empty collection can't be reduced.")
var accumulator: S = iterator.next()
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
accumulator = operation(accumulator, iterator.next())
}
return accumulator
}
-
reduceRight
从最后一项到第一项累计运算
-
fold
带有初始值的reduce
public inline fun <T, R> Iterable<T>.fold(initial: R, operation: (acc: R, T) -> R): R {
var accumulator = initial
for (element in this) accumulator = operation(accumulator, element)
return accumulator
}
-
forEachIndexed
public inline fun <T> Iterable<T>.forEachIndexed(action: (index: Int, T) -> Unit): Unit {
var index = 0
for (item in this) action(index++, item)
}
-
Max、Min
必须是可比较的类
-
MaxBy(selector: (T) -> R)、MinBy(selector: (T) -> R)
public inline fun <T, R : Comparable<R>> Iterable<T>.maxBy(selector: (T) -> R): T? {
val iterator = iterator()
if (!iterator.hasNext()) return null
var maxElem = iterator.next()
var maxValue = selector(maxElem)
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
val e = iterator.next()
val v = selector(e)
if (maxValue < v) {
maxElem = e
maxValue = v
}
}
return maxElem
}
-
SumBy(selector: (T) -> Int):Int
必须返回Int
-
Take(n:Int): List<T>
挑选前n个
-
takeWhile(predicate: (T) -> Boolean)
挑选满足条件的元素的子集合
-
takeLast
public fun <T> List<T>.takeLast(n: Int): List<T> {
require(n >= 0) { "Requested element count $n is less than zero." }
if (n == 0) return emptyList()
val size = size
if (n >= size) return toList()
if (n == 1) return listOf(last())
//注意 返回的是ArrayList
val list = ArrayList<T>(n)
if (this is RandomAccess) {
for (index in size - n .. size - 1)
list.add(this[index])
} else {
for (item in listIterator(n))
list.add(item)
}
return list
}
-
takeLastWhile(predicate: (T) -> Boolean)
从最后开始找出满足条件的值
public inline fun <T> List<T>.takeLastWhile(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): List<T> {
if (isEmpty())
return emptyList()
val iterator = listIterator(size)
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
if (!predicate(iterator.previous())) {
iterator.next()
val expectedSize = size - iterator.nextIndex()
if (expectedSize == 0) return emptyList()
return ArrayList<T>(expectedSize).apply {
while (iterator.hasNext())
add(iterator.next())
}
}
}
return toList()
}
-
drop(n: Int)
取出前n个元素返回剩下元素的子集合
-
dropWhile(predicate: (T) -> Boolean)
public inline fun <T> Iterable<T>.dropWhile(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): List<T> {
var yielding = false
val list = ArrayList<T>()
for (item in this)
if (yielding)
list.add(item)
else if (!predicate(item)) {
list.add(item)
yielding = true
}
return list
}
-
dropLast(n: Int)
去除最后n个元素
-
dropLastWhile(predicate: (T) -> Boolean)
public inline fun <T> List<T>.dropLastWhile(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): List<T> {
if (!isEmpty()) {
val iterator = listIterator(size)
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
if (!predicate(iterator.previous())) {
return take(iterator.nextIndex() + 1)
}
}
}
return emptyList()
}
-
Slice(indices: IntRange)
取下标置结束下标元素子集合
public fun <T> List<T>.slice(indices: IntRange): List<T> {
if (indices.isEmpty()) return listOf()
return this.subList(indices.start, indices.endInclusive + 1).toList()
}
-
Slice(indices: Iterable<Int>)
返回指定下标的元素子集合
public fun <T> List<T>.slice(indices: Iterable<Int>): List<T> {
val size = indices.collectionSizeOrDefault(10)
if (size == 0) return emptyList()
val list = ArrayList<T>(size)
for (index in indices) {
list.add(get(index))
}
return list
}
val list = listOf(1,2,3,4)
list.slice(listOf(1,3))//结果为2,4
-
filter(predicate:(T)-Boolean)
选出符合条件的元素
调用filterTo
-
filterTo(destination: C, predicate: (T) -> Boolean)
过滤满足 条件的元素并赋值给destination
-
map(transform: (T) -> R): list<R>
转化为另一个元素 存到另一个集合中
//调用mapTo
public inline fun <T, R> Iterable<T>.map(transform: (T) -> R): List<R> {
return mapTo(ArrayList<R>(collectionSizeOrDefault(10)), transform)
}
//将每一个元素都transform一遍
public inline fun <T, R, C : MutableCollection<in R>> Iterable<T>.mapTo(destination: C, transform: (T) -> R): C {
for (item in this)
destination.add(transform(item))
return destination
}
-
mapIndexed ( transform: (kotlin.Int, T) -> R)
带有下标参数的转换
-
mapNotNull
删除掉transform后的null元素
-
flatMap
Map每一个得到的结果都是一个新的list
flatMap只得到一个list
public inline fun <T, R> Iterable<T>.flatMap(transform: (T) -> Iterable<R>): List<R> {
return flatMapTo(ArrayList<R>(), transform)
}
//与map的区别主要是在transform函数上
public inline fun <T, R, C : MutableCollection<in R>> Iterable<T>.flatMapTo(destination: C, transform: (T) -> Iterable<R>): C {
for (element in this) {
val list = transform(element)
destination.addAll(list)
}
return destination
}
-
groupBy( keySelector: (T) -> K): Map<K, List<T> )
注意 返回的是选择后的类型作为key,符合一类条件的作为value
//其中map为LinkHashMap
public inline fun <T, K, M : MutableMap<in K, MutableList<T>>> Iterable<T>.groupByTo(destination: M, keySelector: (T) -> K): M {
for (element in this) {
val key = keySelector(element)
val list = destination.getOrPut(key) { ArrayList<T>() }
list.add(element)
}
return destination
}
-
groupBy(keySelector: (T) -> K, valueTransform: (T) -> V)
将分组之后值再次用valueTransform转换一遍
-
reversed(): List<T>
反转list
-
sorted / sortedDescending
升序和降序排序
-
sortBy / sortedByDescending
根据条件进行排序
public inline fun <T, R : Comparable<R>> MutableList<T>.sortBy(crossinline selector: (T) -> R?): Unit {
if (size > 1) sortWith(compareBy(selector))
}
public inline fun <T, R : Comparable<R>> MutableList<T>.sortByDescending(crossinline selector: (T) -> R?): Unit {
if (size > 1) sortWith(compareByDescending(selector))
}
-
zip(other: Iterable<R>): List<Pair<T, R>>
两个集合按照下标配对,组成新的pair作为新的list的元素返回,长度不一致取短的
-
unzip(): Pair<List<T>, List<R>>
作用在pair的集合上,将first和second分别作为两个列表返回
public fun <T, R> Iterable<Pair<T, R>>.unzip(): Pair<List<T>, List<R>> {
val expectedSize = collectionSizeOrDefault(10)
val listT = ArrayList<T>(expectedSize)
val listR = ArrayList<R>(expectedSize)
for (pair in this) {
listT.add(pair.first)
listR.add(pair.second)
}
return listT to listR
}
-
partition
分为两个集合,pair中的第一个符合条件,第二个不符合
public inline fun <T> Iterable<T>.partition(predicate: (T) -> Boolean): Pair<List<T>, List<T>> {
val first = ArrayList<T>()
val second = ArrayList<T>()
for (element in this) {
if (predicate(element)) {
first.add(element)
} else {
second.add(element)
}
}
return Pair(first, second)
}
-
plus()
将两个同类型集合相加返回一个新的集合
public operator fun <T> Iterable<T>.plus(elements: Iterable<T>): List<T> {
if (this is Collection) return this.plus(elements)
val result = ArrayList<T>()
result.addAll(this)
result.addAll(elements)
return result
}
-
plusElement(element: T): List<T>
@kotlin.internal.InlineOnly
public inline fun <T> Iterable<T>.plusElement(element: T): List<T> {
return plus(element)
}
Set
internal object EmptySet : Set<Nothing>, Serializable {
private const val serialVersionUID: Long = 3406603774387020532
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean = other is Set<*> && other.isEmpty()
override fun hashCode(): Int = 0
override fun toString(): String = "[]"
override val size: Int get() = 0
override fun isEmpty(): Boolean = true
override fun contains(element: Nothing): Boolean = false
override fun containsAll(elements: Collection<Nothing>): Boolean = elements.isEmpty()
override fun iterator(): Iterator<Nothing> = EmptyIterator
private fun readResolve(): Any = EmptySet
}
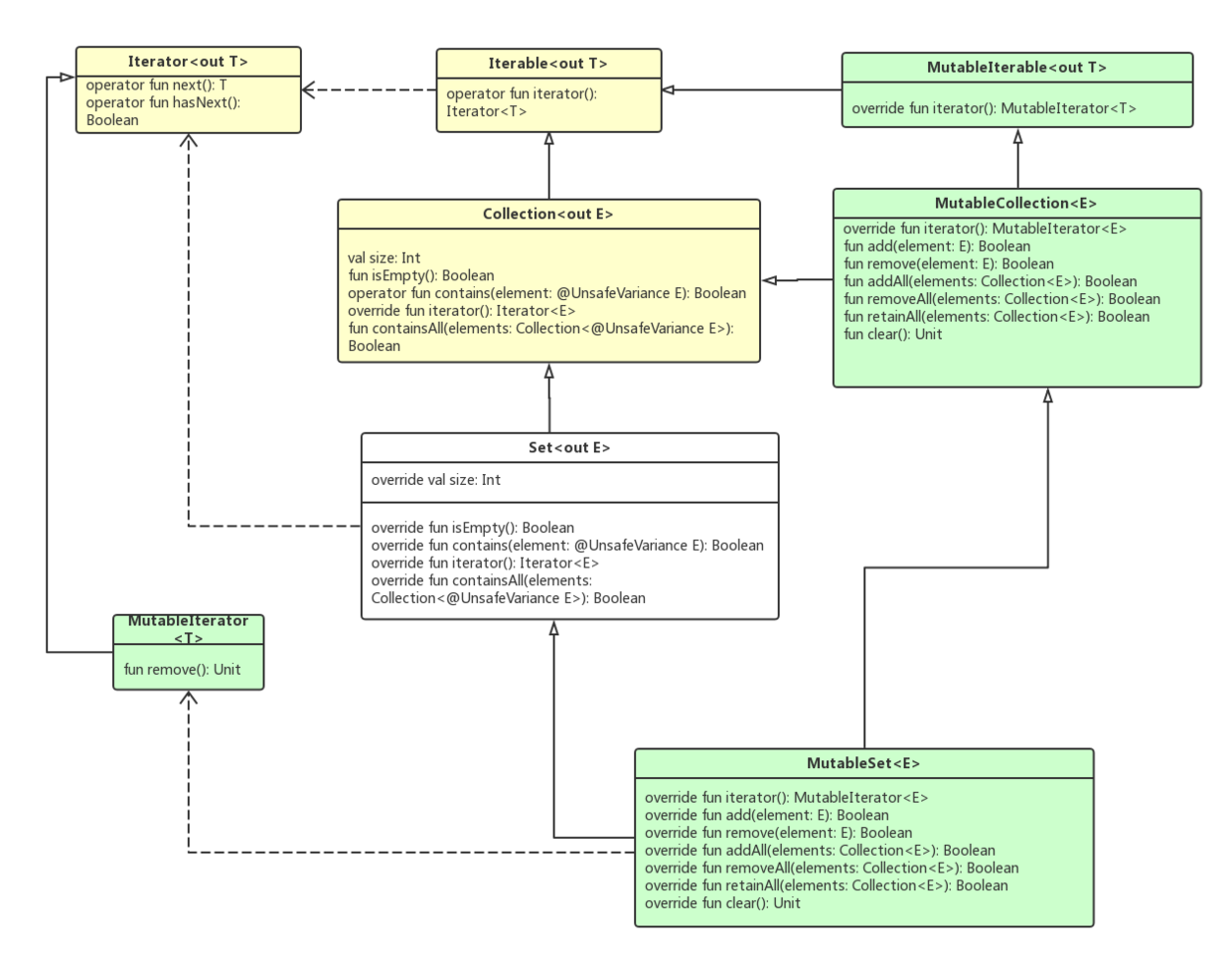
类似的,Kotlin中的Set也分为:不可变Set和支持增加和删除的可变MutableSet。
不可变Set同样是继承了Collection。MutableSet接口继承于Set, MutableCollection,同时对Set进行扩展,添加了对元素添加和删除等操作。
Set的类图结构如下:
空集
万物生于无。我们先来看下Kotlin中的空集:
internal object EmptySet : Set<Nothing>, Serializable { private const val serialVersionUID: Long = 3406603774387020532 override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean = other is Set<*> && other.isEmpty() override fun hashCode(): Int = 0 override fun toString(): String = "[]" override val size: Int get() = 0 override fun isEmpty(): Boolean = true override fun contains(element: Nothing): Boolean = false override fun containsAll(elements: Collection<Nothing>): Boolean = elements.isEmpty() override fun iterator(): Iterator<Nothing> = EmptyIterator private fun readResolve(): Any = EmptySet}
空集继承了Serializable,表明是可被序列化的。它的size是0, isEmpty()返回true,hashCode()也是0。
下面是创建一个空集的代码示例:
>>> val emptySet = emptySet<Int>()>>> emptySet[]>>> emptySet.size0>>> emptySet.isEmpty()true>>> emptySet.hashCode()0
创建Set
setOf
首先,Set中的元素是不可重复的(任意两个元素 x, y 都不相等)。这里的元素 x, y 不相等的意思是:
x.hashCode() != y.hashCode() !x.equals(y)
上面两个表达式值都为true 。
代码示例
>>> val list = listOf(1,1,2,3,3)>>> list[1, 1, 2, 3, 3]>>> val set = setOf(1,1,2,3,3)>>> set[1, 2, 3]
Kotlin跟Java一样的,判断两个对象的是否重复标准是hashCode()和equals()两个参考值,也就是说只有两个对象的hashCode值一样与equals()为真时,才认为是相同的对象。所以自定义的类必须要要重写hashCode()和equals()两个函数。作为Java程序员,这里一般都会注意到。
创建多个元素的Set使用的函数是
setOf(vararg elements: T): Set<T> = if (elements.size > 0) elements.toSet() else emptySet()
这个toSet()函数是Array类的扩展函数,定义如下
public fun <T> Array<out T>.toSet(): Set<T> { return when (size) { 0 -> emptySet() 1 -> setOf(this[0]) else -> toCollection(LinkedHashSet<T>(mapCapacity(size))) }}
我们可以看出,setOf函数背后实际上用的是LinkedHashSet构造函数。关于创建Set的初始容量的算法是:
@PublishedApiinternal fun mapCapacity(expectedSize: Int): Int { if (expectedSize < 3) { return expectedSize + 1 } if (expectedSize < INT_MAX_POWER_OF_TWO) { return expectedSize + expectedSize / 3 } return Int.MAX_VALUE // 2147483647, any large value}
也就是说,当元素个数n小于3,初始容量为n+1; 当元素个数n小于2147483647 / 2 + 1 , 初始容量为 n + n/3; 否则,初始容量为2147483647。
如果我们想对一个List去重,可以直接使用下面的方式
>>> list.toSet()[1, 2, 3]
上文我们使用emptySet<Int>()来创建空集,我们也可以使用setOf()来创建空集:
>>> val s = setOf<Int>()>>> s[]
创建1个元素的Set:
>>> val s = setOf<Int>(1)>>> s[1]
这个函数调用的是setOf(element: T): Set<T> = java.util.Collections.singleton(element), 也是Java的Collections类里的方法。
mutableSetOf(): MutableSet<T>
创建一个可变Set。
函数定义
@SinceKotlin("1.1")@kotlin.internal.InlineOnlypublic inline fun <T> mutableSetOf(): MutableSet<T> = LinkedHashSet()
这个LinkedHashSet()构造函数背后实际上是java.util.LinkedHashSet<E>, 这就是Kotlin中的类型别名。
使用Java中的Set类
包kotlin.collections下面的TypeAliases.kt类中,有一些类型别名的定义如下:
@file:kotlin.jvm.JvmVersionpackage kotlin.collections@SinceKotlin("1.1") public typealias RandomAccess = java.util.RandomAccess@SinceKotlin("1.1") public typealias ArrayList<E> = java.util.ArrayList<E>@SinceKotlin("1.1") public typealias LinkedHashMap<K, V> = java.util.LinkedHashMap<K, V>@SinceKotlin("1.1") public typealias HashMap<K, V> = java.util.HashMap<K, V>@SinceKotlin("1.1") public typealias LinkedHashSet<E> = java.util.LinkedHashSet<E>@SinceKotlin("1.1") public typealias HashSet<E> = java.util.HashSet<E>// also @SinceKotlin("1.1")internal typealias SortedSet<E> = java.util.SortedSet<E>internal typealias TreeSet<E> = java.util.TreeSet<E>
从这里,我们可以看出,Kotlin中的LinkedHashSet , HashSet, SortedSet, TreeSet 就是直接使用的Java中的对应的集合类。
对应的创建的方法是
hashSetOflinkedSetOfmutableSetOfsortedSetOf
代码示例如下:
>>> val hs = hashSetOf(1,3,2,7)>>> hs[1, 2, 3, 7]>>> hs::classclass java.util.HashSet>>> val ls = linkedSetOf(1,3,2,7)>>> ls[1, 3, 2, 7]>>> ls::classclass java.util.LinkedHashSet>>> val ms = mutableSetOf(1,3,2,7)>>> ms[1, 3, 2, 7]>>> ms::classclass java.util.LinkedHashSet>>> val ss = sortedSetOf(1,3,2,7)>>> ss[1, 2, 3, 7]>>> ss::classclass java.util.TreeSet
我们知道在Java中,Set接口有两个主要的实现类HashSet和TreeSet:
HashSet : 该类按照哈希算法来存取集合中的对象,存取速度较快。 TreeSet : 该类实现了SortedSet接口,能够对集合中的对象进行排序。 LinkedHashSet:具有HashSet的查询速度,且内部使用链表维护元素的顺序,在对Set元素进行频繁插入、删除的场景中使用。
Kotlin并没有单独去实现一套HashSet、TreeSet和LinkedHashSet。如果我们在实际开发过程中,需要用到这些Set, 就可以直接用上面的方法。
Set元素的加减操作 plus minus
Kotlin中针对Set做了一些加减运算的扩展函数, 例如:
operator fun <T> Set<T>.plus(element: T)plusElement(element: T)plus(elements: Iterable<T>)operator fun <T> Set<T>.minus(element: T)minusElement(element: T)minus(elements: Iterable<T>)
代码示例:
复制代码>>> val ms = mutableSetOf(1,3,2,7)>>> ms+10[1, 3, 2, 7, 10]>>> ms-1[3, 2, 7]>>> >>> ms + listOf(8,9)[1, 3, 2, 7, 8, 9]>>> ms - listOf(8,9)[1, 3, 2, 7]>>> ms - listOf(1,3)[2, 7]
Map
Map概述
Map是一种把键对象Key和值对象Value映射的集合,它的每一个元素都包含一对键对象和值对象(K-V Pair)。 Key可以看成是Value 的索引,作为key的对象在集合中不可重复(uniq)。
如果我们从数据结构的本质上来看,其实List就是Key是Int类型下标的特殊的Map。而Set也是Key为Int,但是Value值不能重复的特殊Map。
Kotlin中的Map与List、Set一样,Map也分为只读Map和可变的MutableMap。
Map没有继承于Collection接口。其类图结构如下:
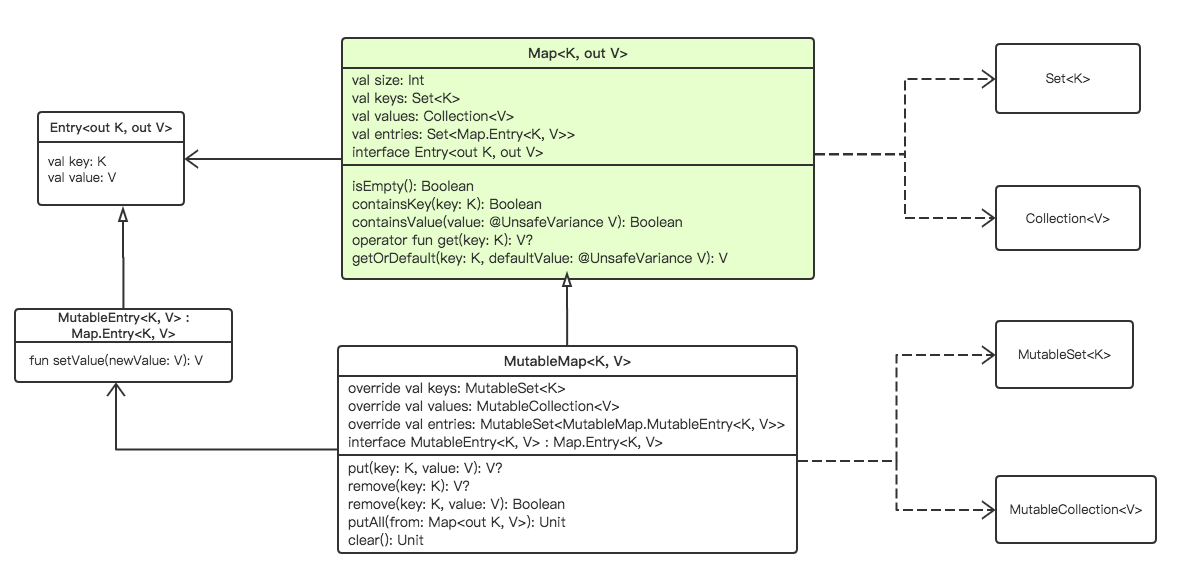
在接口interface Map<K, out V>中,K是键值的类型,V是对应的映射值的类型。这里的out V表示类型为V或V的子类。这是泛型的相关知识,我们将在下一章节中介绍。
其中,Entry<out K, out V>中保存的是Map的键值对。
创建Map
跟Java相比不同的是,在Kotlin中的Map区分了只读的Map和可编辑的Map(MutableMap、HashMap、LinkedHashMap)。
Kotlin没有自己重新去实现一套集合类,而是在Java的集合类基础上做了一些扩展。
我们知道在Java中,根据内部数据结构的不同,Map 接口通常有多种实现类。
其中常用的有:
-
HashMap
HashMap是基于哈希表(hash table)的 Map 接口的实现,以key-value的形式存在。在HashMap中,key-value是一个整体,系统会根据hash算法来来计算key-value的存储位置,我们可以通过key快速地存取value。它允许使用 null 值和 null 键。
另外,HashMap中元素的顺序,随着时间的推移会发生变化。
-
TreeMap
使用红黑二叉树(red-black tree)的 Map 接口的实现。
-
LinkedHashMap
还有继承了HashMap,并使用链表实现的LinkedHashMap。LinkedHashMap保存了记录的插入顺序,在用Iterator遍历LinkedHashMap时,先得到的记录是先插入的记录。简单说,LinkedHashMap是有序的,它使用链表维护内部次序。
我们在使用Kotlin创建Map的时候,实际上大部分都是调用Java的Map的方法。
下面我们就来介绍Map的创建以及基本操作函数。
mapOf()
创建一个只读空Map。
>>> val map1 = mapOf<String, Int>()>>> map1.size0>>> map1.isEmpty()true
我们还可以用另外一个函数创建空Map:
>>> val map2 = emptyMap<String, Int>()>>> map2.size0>>> map2.isEmpty()true
空Map都是相等的:
>>> map2==map1true
这个空Map是只读的,其属性和函数返回都是预定义好的。其代码如下:
private object EmptyMap : Map<Any?, Nothing>, Serializable { private const val serialVersionUID: Long = 8246714829545688274 override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean = other is Map<*,*> && other.isEmpty() override fun hashCode(): Int = 0 override fun toString(): String = "{}" override val size: Int get() = 0 override fun isEmpty(): Boolean = true override fun containsKey(key: Any?): Boolean = false override fun containsValue(value: Nothing): Boolean = false override fun get(key: Any?): Nothing? = null override val entries: Set<Map.Entry<Any?, Nothing>> get() = EmptySet override val keys: Set<Any?> get() = EmptySet override val values: Collection<Nothing> get() = EmptyList private fun readResolve(): Any = EmptyMap}
mapOf(pair: Pair<K, V>): Map<K, V>
使用二元组Pair创建一个只读Map。
>>> val map = mapOf(1 to "x", 2 to "y", 3 to "z")>>> map{1=x, 2=y, 3=z}>>> map.get(1)x>>> map.get(3)z>>> map.size3>>> map.entries[1=x, 2=y, 3=z]
这个创建函数内部是调用的LinkedHashMap构造函数,其相关代码如下:
pairs.toMap(LinkedHashMap(mapCapacity(pairs.size)))
如果我们想编辑这个Map, 编译器会直接报错
>>> map[1]="a"error: unresolved reference. None of the following candidates is applicable because of receiver type mismatch: @InlineOnly public operator inline fun <K, V> MutableMap<Int, String>.set(key: Int, value: String): Unit defined in kotlin.collections@InlineOnly public operator inline fun kotlin.text.StringBuilder /* = java.lang.StringBuilder */.set(index: Int, value: Char): Unit defined in kotlin.textmap[1]="a"^error: no set method providing array accessmap[1]="a" ^
因为在不可变(Immutable)Map中,根本就没有提供set函数。
mutableMapOf()
创建一个空的可变的Map。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf<Int, Any?>()>>> map.isEmpty()true>>> map[1] = "x">>> map[2] = 1>>> map{1=x, 2=1}
该函数直接是调用的LinkedHashMap()构造函数。
mutableMapOf(vararg pairs: Pair<K, V>): MutableMap<K, V>
创建一个可编辑的MutableMap对象。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf(1 to "x", 2 to "y", 3 to "z")>>> map{1=x, 2=y, 3=z}>>> map[1]="a">>> map{1=a, 2=y, 3=z}
另外,如果Map中有重复的key键,后面的会直接覆盖掉前面的:
>>> val map = mutableMapOf(1 to "x", 2 to "y", 1 to "z")>>> map{1=z, 2=y}
后面的1 to "z"直接把前面的1 to "x"覆盖掉了。
hashMapOf(): HashMap<K, V>
创建HashMap对象。Kotlin直接使用的是Java的HashMap。
>>> val map: HashMap<Int, String> = hashMapOf(1 to "x", 2 to "y", 3 to "z")>>> map{1=x, 2=y, 3=z}
linkedMapOf(): LinkedHashMap<K, V>
创建空对象LinkedHashMap。直接使用的是Java中的LinkedHashMap。
>>> val map: LinkedHashMap<Int, String> = linkedMapOf()>>> map{}>>> map[1]="x">>> map{1=x}
linkedMapOf(vararg pairs: Pair<K, V>): LinkedHashMap<K, V>
创建带二元组Pair元素的LinkedHashMap对象。直接使用的是Java中的LinkedHashMap。
>>> val map: LinkedHashMap<Int, String> = linkedMapOf(1 to "x", 2 to "y", 3 to "z")>>> map{1=x, 2=y, 3=z}>>> map[1]="a">>> map{1=a, 2=y, 3=z}
sortedMapOf(vararg pairs: Pair<K, V>): SortedMap<K, V>
创建一个根据Key升序排序好的TreeMap。对应的是使用Java中的SortedMap。
>>> val map = sortedMapOf(Pair("c", 3), Pair("b", 2), Pair("d", 1))>>> map{b=2, c=3, d=1}
访问Map的元素
entries属性
我们可以直接访问entries属性
val entries: Set<Entry<K, V>>
获取该Map中的所有键/值对的Set。这个Entry类型定义如下:
public interface Entry<out K, out V> { public val key: K public val value: V}
代码示例
>>> val map = mapOf("x" to 1, "y" to 2, "z" to 3)>>> map{x=1, y=2, z=3}>>> map.entries[x=1, y=2, z=3]
这样,我们就可以遍历这个Entry的Set了:
>>> map.entries.forEach({println("key="+ it.key + " value=" + it.value)})key=x value=1key=y value=2key=z value=3
keys属性
访问keys属性:
val keys: Set<K>
获取Map中的所有键的Set。
>>> map.keys[x, y, z]
values属性
访问val values: Collection<V>获取Map中的所有值的Collection。这个值的集合可能包含重复值。
>>> map.values[1, 2, 3]
size属性
访问val size: Int获取map键/值对的数目。
>>> map.size3
get(key: K)
我们使用get函数来通过key来获取value的值。
operator fun get(key: K): V?
对应的操作符是[]:
>>> map["x"]1>>> map.get("x")1
如果这个key不在Map中,就返回null。
>>> map["k"]null
如果不想返回null,可以使用getOrDefault函数
getOrDefault(key: K, defaultValue: @UnsafeVariance V): V
当为null时,不返回null,而是返回设置的一个默认值:
>>> map.getOrDefault("k",0)0
这个默认值的类型,要和V对应。类型不匹配会报错:
>>> map.getOrDefault("k","a")error: type mismatch: inferred type is String but Int was expectedmap.getOrDefault("k","a") ^
Map操作符函数
containsKey(key: K): Boolean
是否包含该key。
>>> val map = mapOf("x" to 1, "y" to 2, "z" to 3)>>> map.containsKey("x")true>>> map.containsKey("j")false
containsValue(value: V): Boolean
是否包含该value。
>>> val map = mapOf("x" to 1, "y" to 2, "z" to 3)>>> map.containsValue(2)true>>> map.containsValue(20)false
component1() component2()
Map.Entry<K, V>的操作符函数,分别用来直接访问key和value。
>>> val map = mapOf("x" to 1, "y" to 2, "z" to 3)>>> map.entries.forEach({println("key="+ it.component1() + " value=" + it.component2())})key=x value=1key=y value=2key=z value=3
这两个函数的定义如下:
@kotlin.internal.InlineOnlypublic inline operator fun <K, V> Map.Entry<K, V>.component1(): K = key@kotlin.internal.InlineOnlypublic inline operator fun <K, V> Map.Entry<K, V>.component2(): V = value
Map.Entry<K, V>.toPair(): Pair<K, V>
把Map的Entry转换为Pair。
>>> map.entries[x=1, y=2, z=3]>>> map.entries.forEach({println(it.toPair())})(x, 1)(y, 2)(z, 3)
getOrElse(key: K, defaultValue: () -> V): V
通过key获取值,当没有值可以设置默认值。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf<String, Int?>()>>> map.getOrElse("x", { 1 })1>>> map["x"] = 3>>> map.getOrElse("x", { 1 })3
getValue(key: K): V
当Map中不存在这个key,调用get函数,如果不想返回null,直接抛出异常,可调用此方法。
val map = mutableMapOf<String, Int?>()>>> map.get("v")null>>> map.getValue("v")java.util.NoSuchElementException: Key v is missing in the map. at kotlin.collections.MapsKt__MapWithDefaultKt.getOrImplicitDefaultNullable(MapWithDefault.kt:19) at kotlin.collections.MapsKt__MapsKt.getValue(Maps.kt:252)
getOrPut(key: K, defaultValue: () -> V): V
如果不存在这个key,就添加这个key到Map中,对应的value是defaultValue。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf<String, Int?>()>>> map.getOrPut("x", { 2 })2>>> map{x=2}
iterator(): Iterator<Map.Entry<K, V>>
这个函数返回的是 entries.iterator()。这样我们就可以像下面这样使用for循环来遍历Map:
>>> val map = mapOf("x" to 1, "y" to 2, "z" to 3 )>>> for((k,v) in map){println("key=$k, value=$v")}key=x, value=1key=y, value=2key=z, value=3
mapKeys(transform: (Map.Entry<K, V>) -> R): Map<R, V>
把Map的Key设置为通过转换函数transform映射之后的值。
>>> val map:Map<Int,String> = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> val mmap = map.mapKeys{it.key * 10}>>> mmap{10=a, 20=b, 30=c, -10=z}
注意,这里的it是Map的Entry。 如果不巧,有任意两个key通过映射之后相等了,那么后面的key将会覆盖掉前面的key。
>>> val mmap = map.mapKeys{it.key * it.key}>>> mmap{1=z, 4=b, 9=c}
我们可以看出,1 to "a"被-1 to "z"覆盖掉了。
mapValues(transform: (Map.Entry<K, V>) -> R): Map<K, R>
对应的这个函数是把Map的value设置为通过转换函数transform转换之后的新值。
>>> val map:Map<Int,String> = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> val mmap = map.mapValues({it.value + "$"})>>> mmap{1=a$, 2=b$, 3=c$, -1=z$}
filterKeys(predicate: (K) -> Boolean): Map<K, V>
返回过滤出满足key判断条件的元素组成的新Map。
>>> val map:Map<Int,String> = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map.filterKeys({it>0}){1=a, 2=b, 3=c}
注意,这里的it元素是Key。
filterValues(predicate: (V) -> Boolean): Map<K, V>
返回过滤出满足value判断条件的元素组成的新Map。
>>> val map:Map<Int,String> = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map.filterValues({it>"b"}){3=c, -1=z}
注意,这里的it元素是value。
filter(predicate: (Map.Entry<K, V>) -> Boolean): Map<K, V>
返回过滤出满足Entry判断条件的元素组成的新Map。
>>> val map:Map<Int,String> = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map.filter({it.key>0 && it.value > "b"}){3=c}
Iterable<Pair<K, V>>.toMap(destination: M): M
把持有Pair的Iterable集合转换为Map。
>>> val pairList = listOf(Pair(1,"a"),Pair(2,"b"),Pair(3,"c"))>>> pairList[(1, a), (2, b), (3, c)]>>> pairList.toMap(){1=a, 2=b, 3=c}
Map<out K, V>.toMutableMap(): MutableMap<K, V>
把一个只读的Map转换为可编辑的MutableMap。
>>> val map = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map[1]="x"error: unresolved reference. None of the following candidates is applicable ...error: no set method providing array accessmap[1]="x" ^>>> val mutableMap = map.toMutableMap()>>> mutableMap{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z}>>> mutableMap[1]="x">>> mutableMap{1=x, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z}
plus minus
Map的加法运算符函数如下:
operator fun <K, V> Map<out K, V>.plus(pair: Pair<K, V>): Map<K, V>operator fun <K, V> Map<out K, V>.plus(pairs: Iterable<Pair<K, V>>): Map<K, V>operator fun <K, V> Map<out K, V>.plus(pairs: Array<out Pair<K, V>>): Map<K, V>operator fun <K, V> Map<out K, V>.plus(pairs: Sequence<Pair<K, V>>): Map<K, V>operator fun <K, V> Map<out K, V>.plus(map: Map<out K, V>): Map<K, V>
代码示例:
>>> val map = mapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map+Pair(10,"g"){1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 10=g}>>> map + listOf(Pair(9,"s"),Pair(10,"w")){1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 9=s, 10=w}>>> map + arrayOf(Pair(9,"s"),Pair(10,"w")){1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 9=s, 10=w}>>> map + sequenceOf(Pair(9,"s"),Pair(10,"w")){1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 9=s, 10=w}>>> map + mapOf(9 to "s", 10 to "w"){1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 9=s, 10=w}
加并赋值函数:
inline operator fun <K, V> MutableMap<in K, in V>.plusAssign(pair: Pair<K, V>)inline operator fun <K, V> MutableMap<in K, in V>.plusAssign(pairs: Iterable<Pair<K, V>>)inline operator fun <K, V> MutableMap<in K, in V>.plusAssign(pairs: Array<out Pair<K, V>>)inline operator fun <K, V> MutableMap<in K, in V>.plusAssign(pairs: Sequence<Pair<K, V>>)inline operator fun <K, V> MutableMap<in K, in V>.plusAssign(map: Map<K, V>)
代码示例:
>>> val map = mutableMapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map+=Pair(10,"g")>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 10=g}>>> map += listOf(Pair(9,"s"),Pair(11,"w"))>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 10=g, 9=s, 11=w}>>> map += mapOf(20 to "qq", 30 to "tt")>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 10=g, 9=s, 11=w, 20=qq, 30=tt}
减法跟加法类似。
put(key: K, value: V): V?
根据key设置元素的value。如果该key存在就更新value;不存在就添加,但是put的返回值是null。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z}>>> map.put(10,"q")null>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 10=q}>>> map.put(1,"f")a>>> map{1=f, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 10=q}
putAll(from: Map<out K, V>): Unit
把一个Map全部添加到一个MutableMap中。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> val map2 = mapOf(99 to "aa", 100 to "bb")>>> map.putAll(map2)>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 99=aa, 100=bb}
如果有key重复的,后面的值会覆盖掉前面的值:
>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z, 99=aa, 100=bb}>>> map.putAll(mapOf(1 to "www",2 to "tttt"))>>> map{1=www, 2=tttt, 3=c, -1=z, 99=aa, 100=bb}
MutableMap<out K, V>.remove(key: K): V?
根据键值key来删除元素。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map.remove(-1)z>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c}>>> map.remove(100)null>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c}
MutableMap<K, V>.clear(): Unit
清空MutableMap。
>>> val map = mutableMapOf(1 to "a", 2 to "b", 3 to "c", -1 to "z")>>> map{1=a, 2=b, 3=c, -1=z}>>> map.clear()>>> map{}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号