java继承与多态课后作业
1.运行 TestInherits.java 示例,观察输出,注意总结父类与子类之间构造方法的调用关系修改Parent构造方法的代码,显式调用GrandParent的另一个构造函数,注意这句调用代码是否是第一句,影响重大!
class Grandparent { public Grandparent() { System.out.println("GrandParent Created."); } public Grandparent(String string) { System.out.println("GrandParent Created.String:" + string); } } class Parent extends Grandparent { public Parent() { //super("Hello.Grandparent."); System.out.println("Parent Created"); // super("Hello.Grandparent."); } } class Child extends Parent { public Child() { System.out.println("Child Created"); } } public class test1 { public static void main(String args[]) { Child c = new Child(); } }
Parent Created
Child Created
结论: 通过 super 调用基类构造方法,必须是子类构造方法中的第一个语句。
2.为什么子类的构造方法在运行之前,必须调用父类的构造方法?能不能反过来?为什么不能反过来?构造函数的主要作用是什么?
构造方法是用来初始化变量的,子类继承了父类的变量,如果不调用父类构造方法,则有些变量未初始化。
若先调用子类构造方法,父类里并没有子类的变量,会导致出错
3.
class A{ } public class part1{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println(new A()); } }
运行结果为:
exercise.A@15db9742
初始化时调用了object类中的构造方法,返回输出该对象的哈希值,并用16进制表示
4.
方法覆盖要求子类与父类的方法一模一样,否则就是方法重载(overload)!
请自行编写代码测试以下特性(动手动脑): 在子类中,若要调用父类中被覆盖的方法,可以使用super关键字。
class Father { public void show() { System.out.println("父类"); } } class Son extends Father { public void show() { super.show(); System.out.println("子类"); } } public class test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Son s=new Son(); s.show(); } }
结果:
父类
子类
5.
public class ParentChildTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent=new Parent(); parent.printValue(); Child child=new Child(); child.printValue(); parent=child; parent.printValue(); parent.myValue++; parent.printValue(); ((Child)parent).myValue++; parent.printValue(); } } class Parent{ public int myValue=100; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Parent.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } } class Child extends Parent{ public int myValue=200; public void printValue() { System.out.println("Child.printValue(),myValue="+myValue); } }
1. 左边的程序运行结果是什么?
2. 你如何解释会得到这样的输出?
3. 计算机是不会出错的,之所以得 到这样的运行结果也是有原因的, 那么从这些运行结果中,你能总 结出Java的哪些语法特性?
猜测结果
Parent.printValue(),myValue=100
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=200
Child.printValue(),myValue=201
Child.printValue(),myValue=201
结果
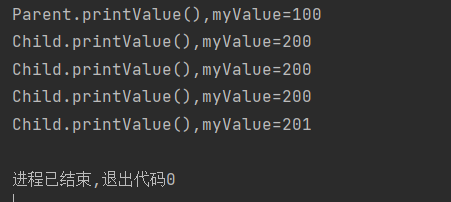
当把子类对象赋给父类对象后,父类对象调用的方法全是子类中的方法,
此时parent.myValue++所改变的数值只是父类中myValue的值,所以结果仍是子类中myValue的数值200,
而((Child)parent).myValue++改变的则是子类中myValue的值,所以输出201





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人