设计模式(一)
什么是设计模式?
设计模式,在软件工程中是对软件设计过程中普遍存在的问题,所提出的解决方案。
设计模式分类
GoF设计模式一共23种,分为三大类:创建型模式、结构型模式、行为型模式。
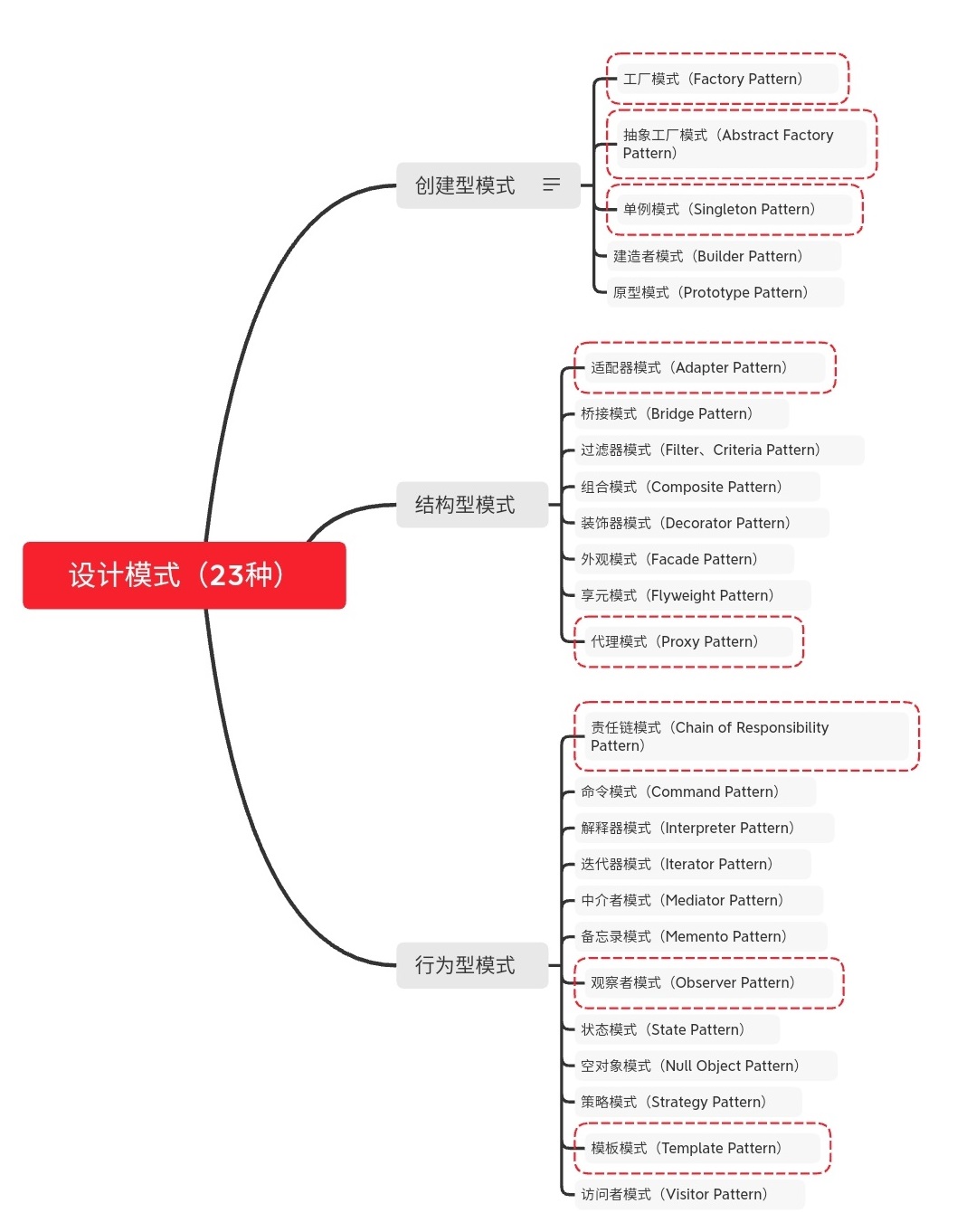
常用的设计模式
1.工厂模式(Factory Pattern)
工厂模式是Java中最常用的设计模式之一。这种设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
在工厂模式中,创建对象时不会对客户暴露创建逻辑,并且是通过使用一个共同的接口来指向新创建的对象。
实例:
1 2 3 | // 接口<br>public interface Shape { void draw();} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // 实现类public class Circle implements Shape{ public void draw() { System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method."); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | // 实现类public class Square implements Shape { public void draw() { System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method."); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | // 工厂类public class ShapeFactory { public Shape getShape(String shapeType){ if( "Square".equals(shapeType)){ return new Square(); }else if("Circle".equals(shapeType)){ return new Circle(); }else { return null; } }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | // Demopublic class FactoryPatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {<br> ShapeFactory factory = new ShapeFactory(); Shape square = factory.getShape("Square"); Shape circle = factory.getShape("Circle"); square.draw(); circle.draw(); }} |
1 2 3 | // 程序输出结果Inside Square::draw() method.Inside Circle::draw() method. |
2.抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory Pattern)
抽象工厂模式是围绕一个超级工厂创建其他的工厂。该超级工厂又称为其他工厂的工厂。
这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
在抽象工厂模式中,接口是负责创建一个相关对象的工厂,不需要显示指定他们的类,每个生成的工厂都能按照工厂模式提供对象。
实例:
1 2 3 | // 接口<br>public interface Shape { void draw();} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // 实现类public class Circle implements Shape{ public void draw() { System.out.println("Inside Circle::draw() method."); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | // 实现类public class Square implements Shape { public void draw() { System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method."); }} |
1 2 3 | public interface Color { void fill();} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 | public class Red implements Color { public void fill() { System.out.println("Inside Red::fill() method."); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 | public class Blue implements Color { public void fill() { System.out.println("Inside Blue::fill() method."); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public abstract class AbstractFactory { public abstract Shape getShape(String shape) ; public abstract Color getColor(String color) ;} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class ShapeFactory extends AbstractFactory{ public Shape getShape(String shapeType){ if( "Square".equals(shapeType)){ return new Square(); }else if("Circle".equals(shapeType)){ return new Circle(); }else { return null; } } public Color getColor(String color) { return null; }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class ColorFactory extends AbstractFactory{ public Color getColor(String color){ if( "Red".equals(color)){ return new Red(); }else if("Blue".equals(color)){ return new Blue(); }else { return null; } } public Shape getShape(String shape) { return null; }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | public class AbstractFactoryPatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ShapeFactory shapeFactory = new ShapeFactory(); ColorFactory colorFactory = new ColorFactory(); Shape square = shapeFactory.getShape("Square"); Shape circle = shapeFactory.getShape("Circle"); Color red = colorFactory.getColor("Red"); Color blue = colorFactory.getColor("Blue"); square.draw(); circle.draw(); red.fill(); blue.fill(); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 | // 输出结果Inside Square::draw() method.Inside Circle::draw() method.Inside Red::fill() method.Inside Blue::fill() method. |
3.单例模式(Singleton Pattern)
单例模式是Java中最简单的设计模式之一。
这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
单例模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类负责创建自己的对象,同时确保只有单个对象被创建。这个类提供了一种访问其唯一的对象的方式,可以直接访问,不需要实例化该类的对象。
注意:
单例类只能有一个实例
单例类必须自己创建自己的唯一实例
单例类必须给所有其他对象提供这一实例
实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class SingleObject { // 构造函数为私有的,该类就不会被实例化 private SingleObject(){}; // 自己创建自己的唯一实例 private static SingleObject singleObject = new SingleObject(); // 获取唯一可用的对象 public static SingleObject getSingleObject(){ return singleObject; } public void show(){ System.out.println("SingleObject.show()"); }} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | public class SingletonPatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 编译期报错 // SingleObject singleObject = new SingleObject(); SingleObject singleObject = SingleObject.getSingleObject(); singleObject.show(); }} |
1 2 | // 代码执行结果SingleObject.show() |
懒汉式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | // 懒汉式单例public class LazySingletonPattern { // 私有的无参构造方法 private LazySingletonPattern(){} // 默认不实例化,什么时候用什么时候实例化 private static LazySingletonPattern lazySingletonPattern = null; // 获取唯一可用的对象 public static LazySingletonPattern getLazySingletonPattern(){ if(lazySingletonPattern == null){ lazySingletonPattern = new LazySingletonPattern(); } return lazySingletonPattern; }} |
饿汉式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | // 饿汉式单例public class HungrySingletonPattern { // 无参构造方法私有化 private HungrySingletonPattern (){} <br> // 直接实例化 private static final HungrySingletonPattern hungrySingletonPattern = new HungrySingletonPattern(); <br> // 获取唯一可用的对象 public static HungrySingletonPattern getHungrySingletonPattern(){ return hungrySingletonPattern; }} |
4.建造者模式(Builder Pattern)
建造者模式,使用多个简单的对象一步一步构建成一个复杂的对象。
一个Builder类会一步一步构造最终的对象。该Builder类是独立于其他的对象。
5.原型模式(Prototype Pattern)
原型模式,用于创建重复的对象,又可以保证性能。
原型模式是实现了一个原型接口,该接口用于创建当前对象的克隆。当直接创建对象代价比较大时,使用这种模式。
例如:一个对象需要在一个高代价的数据库操作之后创建。我们可以先缓存该对象,在下一个请求时返回他的克隆,在需要的时候更新数据库,以此来减少数据库的调用。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 29 期(2025年3.1-3.9)
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异