java-IO-字符流
一 概述
字符流主要是来处理中文的,比如:一篇文章出现了多少个好字,判断好字的个数
字节流操作的是字节数组,字符流操作的是字符数组
1.1 编码表
1,ascii 一个字节的7位数可以表示,对应的字节都是正数
2.iso8859-1 拉丁码表,用了一个字节的8位数,1-xxxxxxx 负数
3,GB2312 简体中文码表,6,7 千,两个字节表示.两个字节都是负数
GBK 目前是两万多字和符号,用两个字节表示,一部分文字,第一个字节开头是1,第二个字节开头是0
4,unicode 国际标准码表,无论是什么文字,都用两个字节存储,java中的char就是用的这个码表,
占两个字节.在java中,字符串按照系统默认的码表来解析的,简体中文版的码表的GBK
5,UTF-8基于unicode ,一个字节就可以存储数据,不要两个字节存储,而且这个码表更加的标准,在每个表头加入了编码信息.
文字--->二进制:数字 编码
二进制---->文字, 解码
二 FileRead
public class CharStreamDemo { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /* * 需求1:通过流写一个篇文章,里面有中文。"你好你好"。indexOf('好'); */ // writeCNText(); /* * 需求2:一篇文章中出现了多少个好字。读取数据。判断好字并计数。 * 思路:读取一个文本,获取内容判断好字。 */ readCNText(); /* * 解决需求2问题: * 使用FileReader。 * */ System.out.println("-----------读取字符-------------"); readCNTextByReader(); } public static void readCNTextByReader() throws IOException { //创建一个读取字符文件的读取流对象。FileReader。 FileReader fr = new FileReader("tempfile\\cn.txt");//这个流的底层使用的是FileInputStream // int ch = fr.read(); // System.out.println("读取一个字符:"+ch); // int ch1 = fr.read();//一次读取一个中文,读取多个字节查表转成中文。 // System.out.println("读取一个字符:"+(char)ch1); int ch = 0; int count = 0; while((ch=fr.read())!=-1){ if(ch=='好'){ count++; } } System.out.println("count="+count); fr.close(); } public static void readCNText() throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("tempfile\\cn.txt"); //一次读一个字节。这样对中文是无法判断。怎么解决呢?一个中文默认是两个字节。 //读取所有的字节,存储起来(字节数组),变成字符串。然后找指定的字符。 // byte[] buf = new byte[4]; // int len = 0; // while((len=fis.read(buf))!=-1){ // String str = new String(buf,0,len); // System.out.println(str); // } // int ch = 0; // while((ch=fis.read())!=-1){ // System.out.println(ch); // } int ch = fis.read(); System.out.println("读取一个字节:"+ch); int ch1 = fis.read(); System.out.println("读取一个字节:"+ch1); fis.close(); } public static void writeCNText() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("tempfile\\cn.txt"); fos.write("你好你好".getBytes()); fos.close(); } }
三 FileWrite
public class FileWriterDemo { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //演示FileWriter 用于操作文件的便捷类。 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("tempfile\\fw.txt"); fw.write("你好谢谢再见");//这些文字都要先编码。都写入到了流的缓冲区中。 fw.flush(); fw.close(); /* * flush()和close()的区别? * * flush():将流中的缓冲区缓冲的数据刷新到目的地中,刷新后,流还可以继续使用。 * close():关闭资源,但在关闭前会将缓冲区中的数据先刷新到目的地,否则丢失数据,然后在关闭流。流不可以使用。 * * 如果写入数据多,一定要一边写一边刷新,最后一次可以不刷新,由close完成刷新并关闭。 * * */ } }
四 按照指定编码读写中文
1.正因为识别中文码表不唯一,涉及到了编码解码的问题;
2.转换流和子类的区别
public class TransStreamDemo { /** * @param args * @throws IOException * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // writeCN(); readCN(); /* 总结: 发现继承关系是这样的。 OutputStreamWriter: |--FileWriter: InputStreamReader: |--FileReader; 父类和子类的功能有什么区别呢? OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader是字符和字节的桥梁:也可以称之为字符转换流。 字符转换流原理:字节流+编码表。 FileWriter和FileReader:作为子类,仅作为操作字符文件的便捷类存在。 当操作的字符文件,使用的是默认编码表时可以不用父类,而直接用子类就完成操作了,简化了代码。 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));//默认字符集。 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("a.txt"),"GBK");//指定GBK字符集。 FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt"); 这三句代码的功能是一样的,其中第三句最为便捷。 注意:一旦要指定其他编码时,绝对不能用子类,必须使用字符转换流。 什么时候用子类呢? 条件: 1,操作的是文件。 2,使用默认编码。 字节--->字符 : 看不懂的--->看的懂的。 需要读。输入流。 InputStreamReader 字符--->字节 : 看的懂的--->看不懂的。 需要写。输出流。 OutputStreamWriter */ } public static void readCN() throws IOException { //创建InputStreamReader对象。 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("tempfile\\u8cn.txt"),"UTF-8"); char[] buf = new char[1024]; int len = isr.read(buf); System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len)); isr.close(); } //读取中文。 public static void readCN_no() throws IOException { // 使用FileReader没出来,因为文件是UTF-8编码。读取UTF-8字节时,用该指定用UTF-8解码。 // 说明需要指定码表。那就需要使用InputStreamReader。 FileReader fr = new FileReader("tempfile\\u8cn.txt"); // int ch = (char)fr.read(); // System.out.println((char)ch); char[] buf = new char[1024]; int len = fr.read(buf); System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));//浣犲ソ fr.close(); } public static void writeCN() throws Exception { //需求:既然识别中文的码表有两个,GBK UTF-8 //能不能将中文数据按照utf-8的方式进行文件的存储呢? //还能使用FileWriter吗?不能使用了,因为FileWriter中默认的是GBK //通过FileWriter的api描述,要指定编码表这些值,需要使用OutputStreamWriter //OutputStreamWriter 是字符流通向字节流的桥梁:可使用指定的 charset 将要写入流中的字符编码成字节。 //它的作用的就是,将字符串按照指定的编码表转成字节,在使用字节流将这些字节写出去。 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("tempfile\\u8cn.txt"),"utf-8"); osw.write("你好");//写入缓冲区。 osw.close(); } }
图解
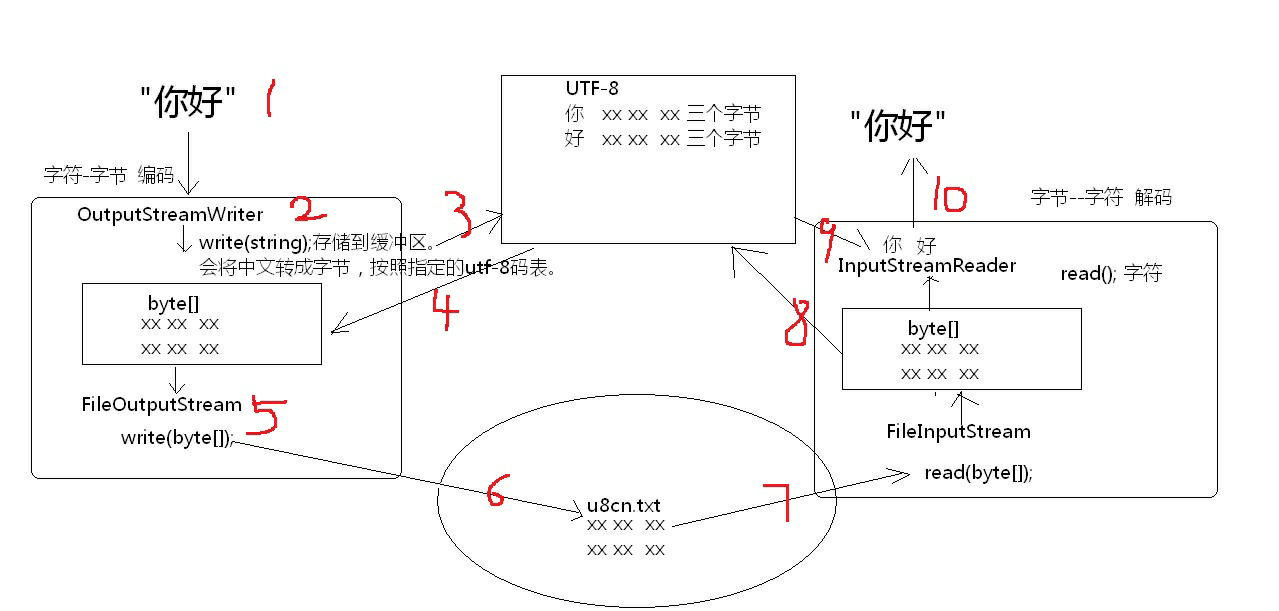
五 复制文本文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /* * 练习:复制文本文件。 * 思路: * 1,既然是文本涉及编码表。需要用字符流。 * 2,操作的是文件。涉及硬盘。 * 3,有指定码表吗?没有,默认就行。 * 操作的是文件,使用的 默认码表。使用哪个字符流对象。直接使用字符流操作文件的便捷类。FileReader FileWriter */ copyTextFile(); } public static void copyTextFile() throws IOException { //1,明确源和目的。 FileReader fr = new FileReader("Test24.java"); FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("tempfile\\test24_copy.txt"); //2,为了提高效率。自定义缓冲区数组。字符数组。 char[] buf = new char[1024]; int len = 0; while((len=fr.read(buf))!=-1){ fw.write(buf,0,len); } //2,循环读写操作。效率低。 // int ch = 0; // while((ch=fr.read())!=-1){ // fw.write(ch); // } //3,关闭资源。 fw.close(); fr.close(); }
六 对象复制文本文件
public class CharStreamBufferedTest { /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /* * 字符流中是否有提供缓冲区中。 * 注意:其实自定义数组就可以解决问题缓冲区问题并提高效率。 * 为什么还要使用流中的缓冲区对象呢?因为缓冲区对象中除了封装数组以外, * 还提供了更多的操作缓冲区数据的方法。 * BufferedReader BufferedWriter * * 讲解字符流缓冲区中的特有方法。 * 操作字符数据时,有一个文本特有的表形实行 :行(hang) * 操作行的方法。 * BufferedReader:readLine():一次读取一行。 * BufferedWriter: */ copyTextByBuffer(); // readText(); // writeText(); } public static void writeText() throws IOException { BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("tempfile\\test24_buf.txt")); for(int x=1; x<=4; x++){ bufw.write(x+"-itcast"); bufw.newLine(); bufw.flush(); } bufw.close(); } public static void readText() throws IOException { BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Test24.java")); String line = null; while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(line); } // String line = bufr.readLine(); // System.out.println("-"+line+"-"); // String line1 = bufr.readLine(); // System.out.println("-"+line1+"-"); bufr.close(); } public static void copyTextByBuffer() throws IOException { BufferedReader bufr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Test24.java")); BufferedWriter bufw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("tempfile\\test24_bufcopy.txt")); //循环读写一行数据。 String line = null; while((line=bufr.readLine())!=null){ bufw.write(line); bufw.newLine(); bufw.flush(); } bufw.close(); bufr.close(); } }
作者:8亩田
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接.
本文如对您有帮助,还请多帮 【推荐】 下此文。
如果喜欢我的文章,请关注我的公众号
如果有疑问,请下面留言
学而不思则罔 思而不学则殆


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号