java反射机制
6、反射机制
动态语言:动态语言是一种在运行时可以改变其结构的语言。
而java是一种静态语言,但是java的反射机制使得java更加灵活,于是Java也是一种“准动态语言”。
反射:反射就像照镜子一样,通过镜子可以看到所有信息。java种通过反射可以获取一个类的所有内部信息。反射虽然灵活,但是也损失了运行速度
反射通过Class对象来实现,每个类只有一个Class实例对象,包括接口,注解,枚举类等都存在Class对象。
获取class对象的方式:
student s=new student();
Class c1=Class.forName("包名");//通过包名获取
Class c2=person.class; //通过类命获取
Class c3=s.getClass();//通过对象名
Class类:
对于每个类,JRE都为其保留了一个不变的class类的对象,通过这个对象可以获取该类的属性、方法、构造器、实现的接口等。一个Class类对象包含了特定某个结构的有关信息(class/interface/enum/annotation/primitive type/void/[])
---->Class本身是一个类
---->Class对象只能由系统创建
---->一个加载的类在JVM中只有一个Class实例
---->一个Class对象对应了一个加载到JVM中的class文件
---->通过Class可以完整地得到一个类所加载的结构
---->Class是reflection的根源,对于想要动态加载和运行的类,只有先获得相应的Class对象
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException,ClassNotFoundException {
//每个类都只有一个class,所以同一个类的多个对象他们的class一样。
student s=new student();
Class c1=Class.forName("com.company.reflection.person");//通过包名获取
Class c2=person.class; //通过类命获取
Class c3=s.getClass();//通过对象名
System.out.println(c3.getConstructors());
System.out.println(c3.getMethods());
Class c4=c3.getSuperclass(); //通过子类的Class对象
Class c5=int[].class; //数组
Class c6=Runnable.class;//接口
Class c7=void.class;
Class c8=Integer.TYPE;//int与Integer的Class是一样的
Class c9=int.class;
Class c10= Target.class;//注解
Class c12= ElementType.class;//枚举类
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
System.out.println(c8);
System.out.println(c9);
System.out.println(c10);
System.out.println(c12);
//只要类型和维度一样,Class就是一样的
//每种类型都只有一个Class实例
int[] a=new int[10];
int[] b=new int[20];
int[][] c=new int[2][4];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(c.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
class person{
String name;
public person(){
this.name="王琴";
}
}
class student extends person{
int id;
public student(){
this.name="wq";
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
7、通过反射获取类的运行时结构
这个过程通过类的Class对象进行获取
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
//类的主动引用:通过new关键字,调用类的静态成员和静态方法,通过反射调用,
//customer cs=new customer();//通过new 关键字初始化customer
//user us=new user(1,"wq"); //通过new 关键字初始化user
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("com.company.reflection.customer");//反射会引起子类和父类的初始化
//customer.print();//类调用静态方法或成员会初始化类
System.out.println(c1.getName());//获取包名+类名
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName());//获取简单类名
System.out.println(c1.getSuperclass());//获取父类全路径名
//Constructor constructor = c1.getConstructor(int.class);//获取public的指定构造器
Constructor declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class);//获取任意的指定的构造器,不管是public还是private
Constructor[] constructors = c1.getConstructors();//获取所有的public构造器
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = c1.getDeclaredConstructors();//获取所有构造器
//System.out.println(constructor);
System.out.println(declaredConstructor);
for (Constructor constructor1 : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor1);
}
for (Constructor declaredConstructor1 : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(declaredConstructor1);
}
Method method = c1.getMethod("print",null);//获取指定的public 方法
//Method[] methods = c1.getMethods();//获取该类和父类的所有public方法
Method sb = c1.getDeclaredMethod("sb", null);//获取任意指定的方法
//Method[] declaredMethods = c1.getDeclaredMethods();//获取本类的所有方法
System.out.println(method);
System.out.println(sb);
// for (Method method1 : methods) {
// System.out.println(method1);
// }
// for (Method declaredMethod : declaredMethods) {
// System.out.println(declaredMethod);
// }
System.out.println("===============================");
Field p = c1.getField("p");//获取pulic字段
System.out.println(p);
Field declaredField = c1.getDeclaredField("cId");//获取任意指定字段
System.out.println(declaredField);
System.out.println("===============================");
Field[] fields = c1.getFields();//获取本类和父类的public字段
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
System.out.println("===============================");
Field[] declaredFields = c1.getDeclaredFields();//获取本类的所有字段
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(field);
}
}
8、通过反射动态创建对象
//通过反射动态创建对象
public class test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1=Class.forName("com.company.reflection.user");
ClassLoader classLoader = c1.getClassLoader();
//通过Class对象创建实例,只能调用无参构造方法创建
user us = (user) c1.newInstance();
//通过构造器创建实例
Constructor constructor=c1.getConstructor(int.class,String.class);
user us2= (user) constructor.newInstance(12,"wq");
System.out.println(us2);
//通过反射获取方法,然后操作方法
Method setId = c1.getMethod("setId", int.class);//(方法名,参数类型)
setId.invoke(us,14);//激活方法invoke(所属对象,方法要传入的参数值)
System.out.println(us.getId());
//获取属性
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);//关闭权限检查
name.set(us,"王琴");//设置属性的值
System.out.println(us);
}
}
9、类加载器
public class test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
Class c1=Class.forName("com.company.reflection.user");
ClassLoader classLoader = c1.getClassLoader();
//获取系统类加载器------>我们自己定义的类的加载器都是系统加载器
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader);
//获取系统类加载器的父类--->扩展类加载器
ClassLoader parent = systemClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(parent);
//获取扩展类加载器的父类----->根加载器(c/c++编写),java核心类库的加载器获取,无法
ClassLoader parent1 = parent.getParent();
//"java.lang.String"类在java核心类库----在rt.jar包中,所以无法获取
ClassLoader classLoader1 = Class.forName("java.lang.String").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(parent1);
System.out.println(classLoader);
System.out.println(classLoader1);
}
结果:
jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@63947c6b
jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$PlatformClassLoader@7ef20235
null
jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@63947c6b
null
10、反射调用性能比较
public class performance {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException {
test01();
test02();
test03();
}
//普通方式调用
public static void test01(){
user us=new user();
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
us.getName();
}
long stop=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("普通方式耗时"+(stop-start));
}
//反射方式调用
public static void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
user us=new user();
Class c=us.getClass();
Method m = c.getDeclaredMethod("getName");
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
m.invoke(us);
}
long stop=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射方式耗时"+(stop-start));
}
//反射方式调用,关闭权限检查
public static void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
user us=new user();
Class c=us.getClass();
Method m = c.getDeclaredMethod("getName");
m.setAccessible(true);
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
m.invoke(us);
}
long stop=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("关闭权限检查方式耗时"+(stop-start));
}
}
结果分析:反射机制确实耗时很大,其中权限检查消耗一半的时间,如果反射调用很多最好关闭权限检查。
我是user
我是无参构造方法
普通方式耗时4
我是无参构造方法
反射方式耗时2329
我是无参构造方法
关闭权限检查方式耗时1104
11、获取泛型信息
public class test05 {
public Map<String,user> a(Map<String,user> map){
return map;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Class c=test05.class;
Method a = c.getDeclaredMethod("a", Map.class);
//获取参数类型
Type[] genericParameterTypes = a.getGenericParameterTypes();
for (Type t:genericParameterTypes) {
System.out.println(t);
if(t instanceof ParameterizedType){//如果泛型是参数化类型
Type[] actualType=((ParameterizedType) t).getActualTypeArguments();//获取真实类型
for (Type type : actualType) {
System.out.println(type);
}
}
}
//获取参数类型
Type genericReturnType = a.getGenericReturnType();
System.out.println(genericReturnType);
if(genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
Type[] actualType=((ParameterizedType) genericReturnType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type type : actualType) {
System.out.println(type);
}
}
}
}
12、通过反射获取注解
//通过反射操作注解
public class test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c = Class.forName("com.company.reflection.student2");
//获取类上的注解
Annotation[] annotations = c.getDeclaredAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
//获取注解的值
Table table= (Table)c.getAnnotation(Table.class);
System.out.println(table.value());
//先获取字段,通过字段获取字段上的注解,再获取注解上的值
Field name = c.getDeclaredField("name");
Filed annotation = name.getAnnotation(Filed.class);
System.out.println(annotation.columnName());
System.out.println(annotation.length());
System.out.println(annotation.type());
}
}
@Table("db_student")
class student2{
@Filed(columnName = "db_id",type = "int",length = 10)
private int id;
@Filed(columnName = "db_age",type = "int",length = 4)
private int age;
@Filed(columnName = "db_name",type = "varchar",length = 5)
private String name;
public student2() {
}
public student2(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Table{
String value();
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Filed{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}
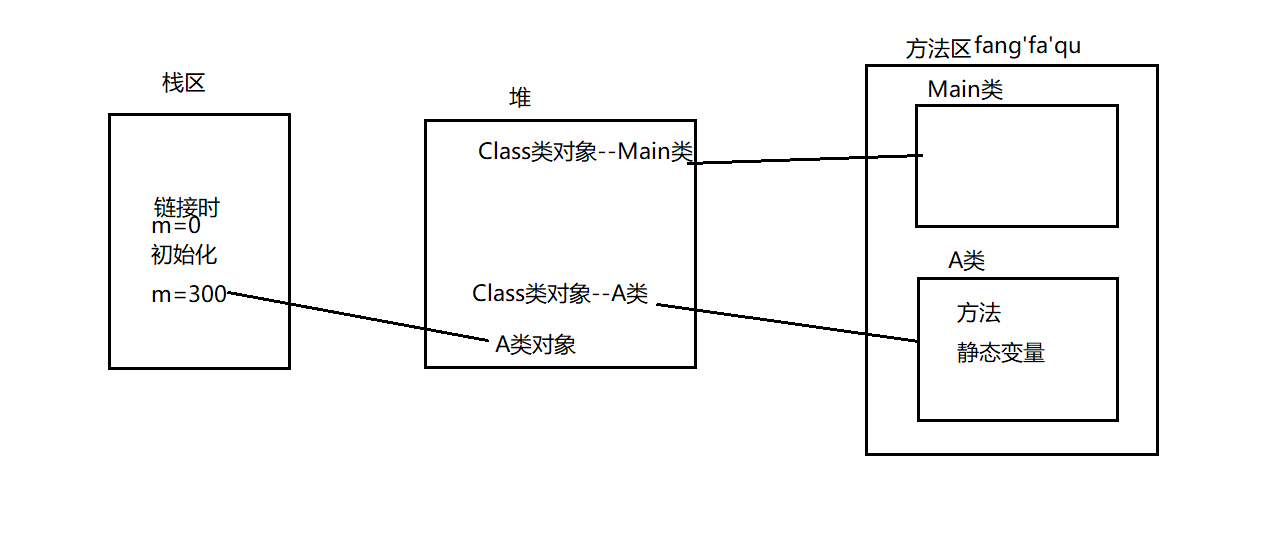
13、类的内存分析
-
加载:将class文件加载到内存中,生成Class对象
-
链接:将java的字节码文件合并到JVM中,静态变量初始化
-
初始化:将类变量的赋值动作与静态代码块合并
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write your code here
//获取cpu核数
//cpu密集型 I/O密集型
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
A a=new A();
}
}
class A{
static {
m=100;
}
private static int m=300;
public A(){
System.out.println(m);
}
}
内存分析:






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧