Java实验报告(三)及总结
实验三 String类的应用
一、 实验目的
(1) 掌握类String类的使用;
(2) 学会使用JDK帮助文档;
二、 实验内容
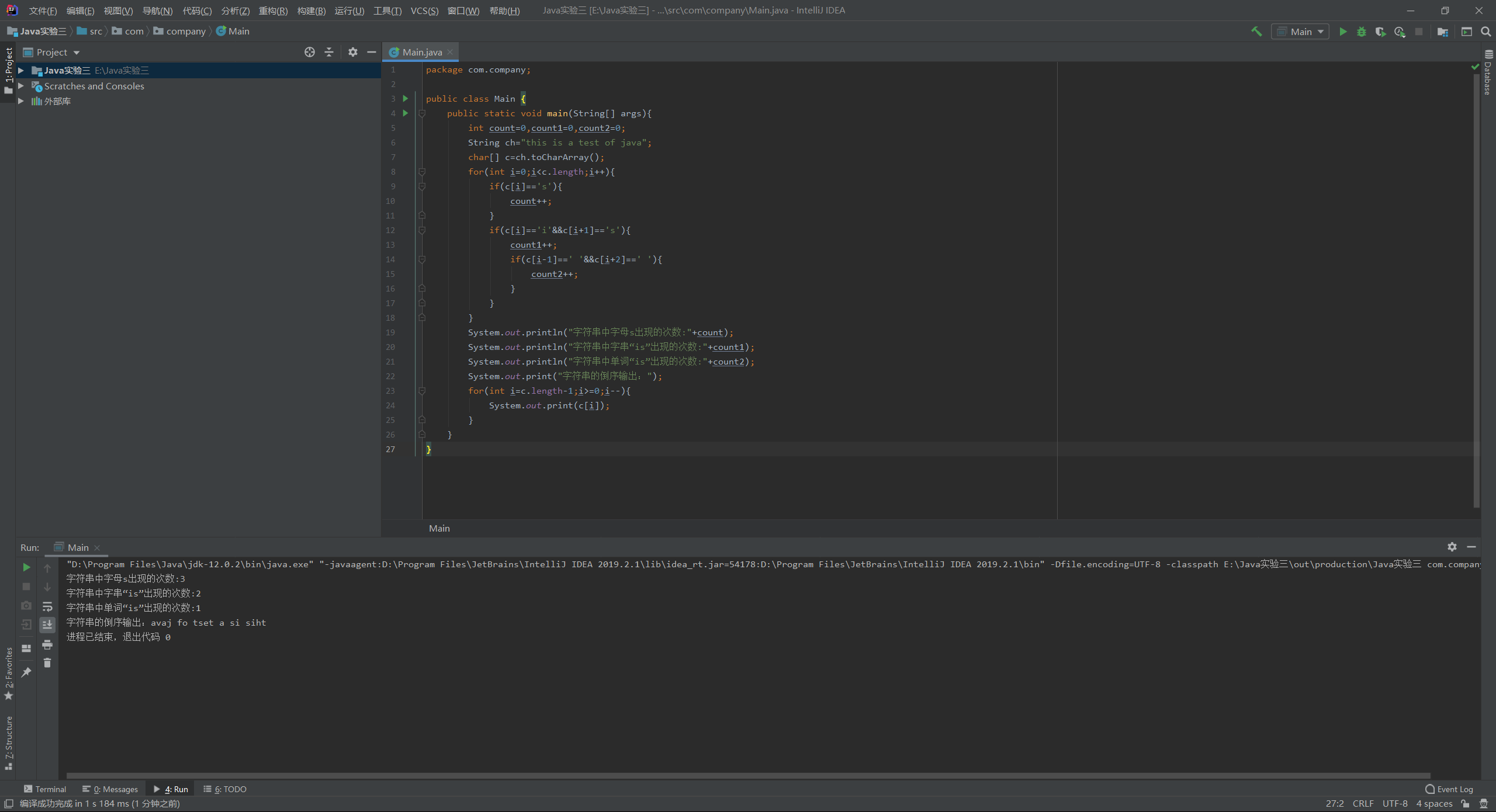
1.已知字符串:"this is a test of java".按要求执行以下操作:(要求源代码、结果截图。)
① 统计该字符串中字母s出现的次数。
② 统计该字符串中子串“is”出现的次数。
③ 统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数。
④ 实现该字符串的倒序输出。
实验代码:
package com.company; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ int count=0,count1=0,count2=0; String ch="this is a test of java"; char[] c=ch.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++){ if(c[i]=='s'){ count++; } if(c[i]=='i'&&c[i+1]=='s'){ count1++; if(c[i-1]==' '&&c[i+2]==' '){ count2++; } } } System.out.println("字符串中字母s出现的次数:"+count); System.out.println("字符串中字串“is”出现的次数:"+count1); System.out.println("字符串中单词“is”出现的次数:"+count2); System.out.print("字符串的倒序输出:"); for(int i=c.length-1;i>=0;i--){ System.out.print(c[i]); } } }
输出结果:
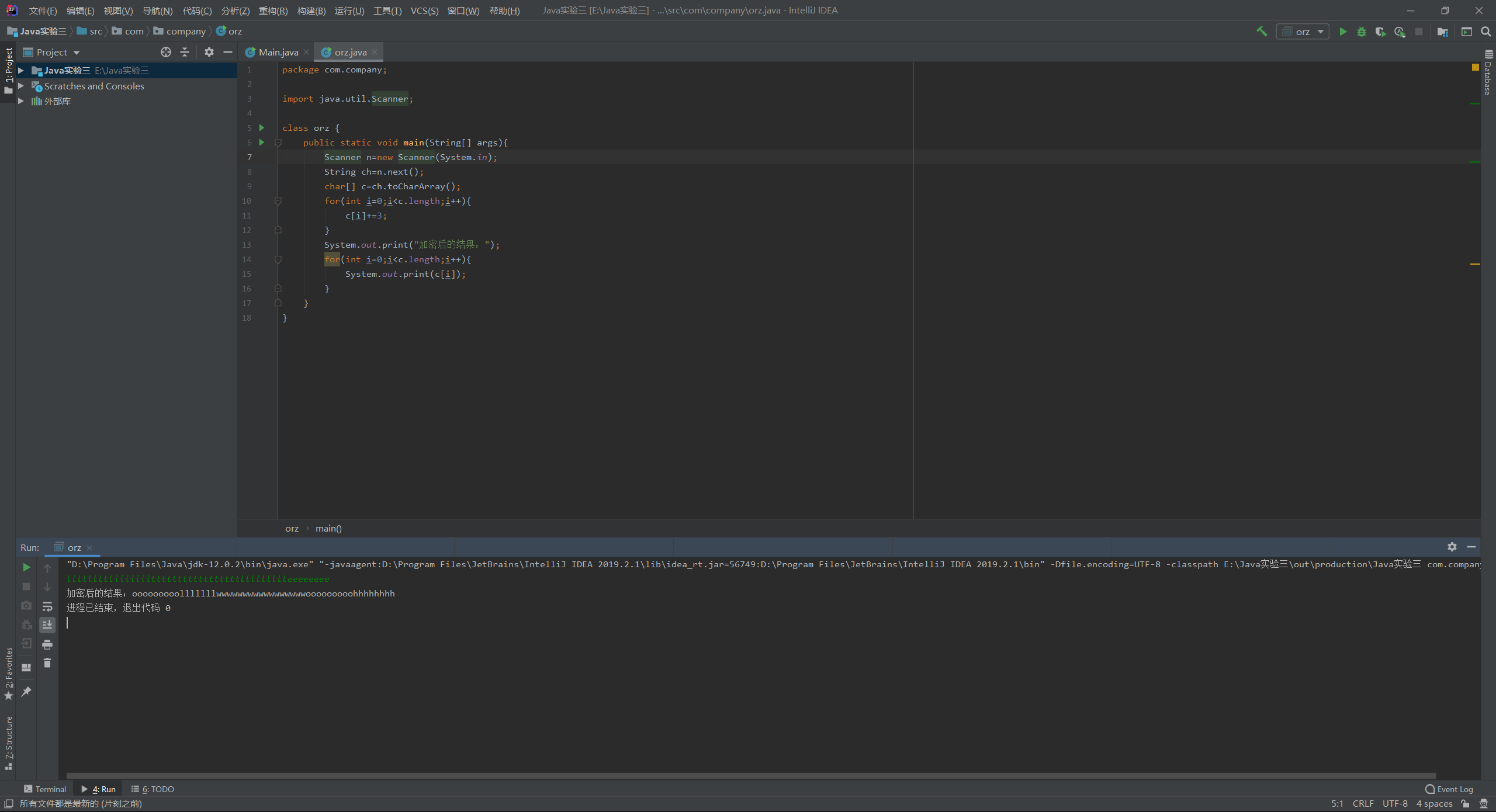
2.请编写一个程序,使用下述算法加密或解密用户输入的英文字串。要求源代码、结果截图。
实验代码:
package com.company;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner n=new Scanner(System.in);
String ch=n.next();
char[] c=ch.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++){
c[i]+=3;
}
System.out.print("加密后的结果:");
for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++){
System.out.print(c[i]);
}
}
}
实验结果:
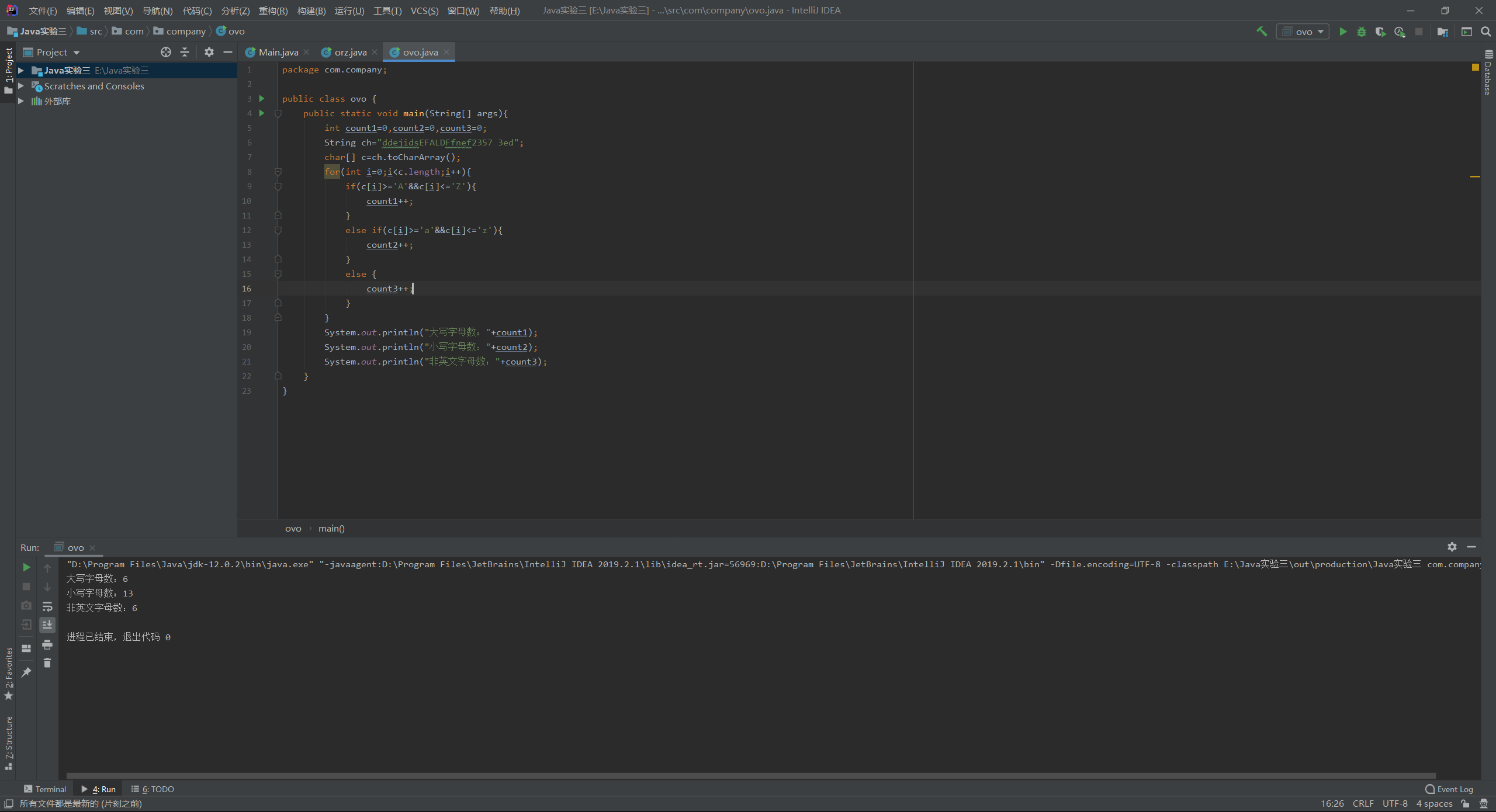
3.已知字符串“ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed”。输出字符串里的大写字母数,小写英文字母数,非英文字母数。
实验代码:
package com.company; public class ovo { public static void main(String[] args){ int count1=0,count2=0,count3=0; String ch="ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed"; char[] c=ch.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<c.length;i++){ if(c[i]>='A'&&c[i]<='Z'){ count1++; } else if(c[i]>='a'&&c[i]<='z'){ count2++; } else { count3++; } } System.out.println("大写字母数:"+count1); System.out.println("小写字母数:"+count2); System.out.println("非英文字母数:"+count3); } }
实验结果:
小结:
final关键字是我们经常使用的关键字之一,它的用法有很多,但是并不是每一种用法都值得我们去广泛使用。它的主要用法有以下四种:
1、用来修饰数据,包括成员变量和局部变量,该变量只能被赋值一次且它的值无法被改变。对于成员变量来讲,我们必须在声明时或者构造方法中对它赋值;
2、用来修饰方法参数,表示在变量的生存期中它的值不能被改变;
3、修饰方法,表示该方法无法被重写;
4、修饰类,表示该类无法被继承。
上面的四种方法中,第三种和第四种方法需要谨慎使用,因为在大多数情况下,如果是仅仅为了一点设计上的考虑,我们并不需要使用final来修饰方法和类。



