P1827 [USACO3.4]美国血统 American Heritage 题解
一、已知前序+中序,求后序
(1)、二叉树的遍历,就是一个深度优先搜索的过程:
前序
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
//树的结构体+存储数组
struct Node {
int id; // 当前结点ID
int left; // 左结点ID
int right;// 右结点ID
} t[N];
int n;
void pre_order(int x){
printf("%d\n",x);
if(t[x].left) pre_order(t[x].left);
if(t[x].right) pre_order(t[x].right);
}
中序
void in_order(int x){
if(t[x].left) in_order(t[x].left);
printf("%d\n",x);
if(t[x].right) in_order(t[x].right);
}
后序
void post_order(int x){
if(t[x].left) post_order(t[x].left);
if(t[x].right) post_order(t[x].right);
printf("%d\n",x);
}
说白了,套路基本一样,就是三步:输出当前结点,递归左子树,递归右子树。根据输出顺序不同,产生了三种遍历方式。
算法步骤:
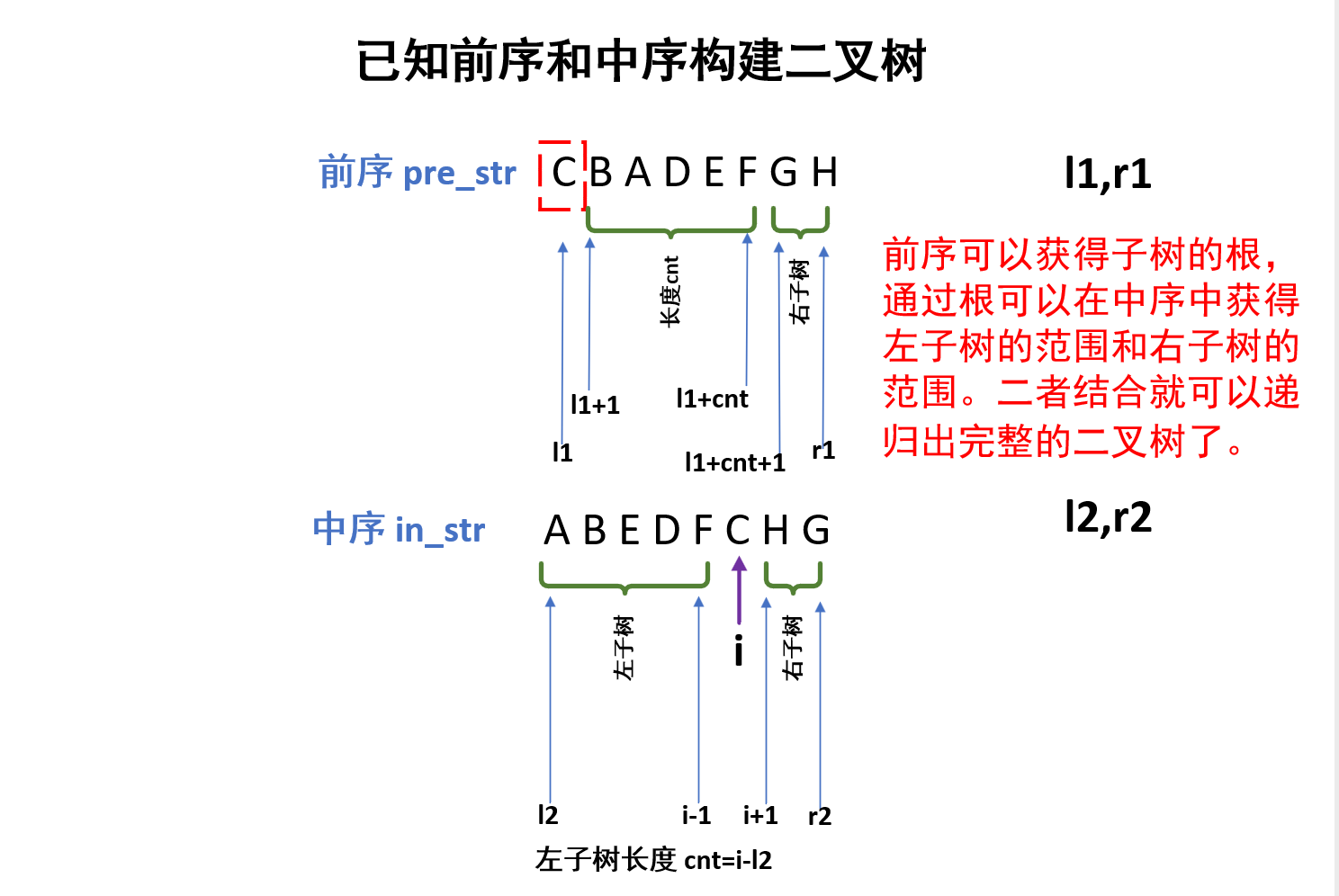
(1)给出一个前序遍历的字符串,那么首字母一定是子树的根。
(2)另外再给出同样子树的中序遍历字符串,那么通过上面查找到的首字母在中序遍历字符串中找到它,它的左边就是左子树,右边就是右子树。
(3)利用中序字符串左子树的范围和右子树的范围,就可以确定在前序字符串中左子树的范围和右子树的范围,通过递归就可以继续遍历左右子树。
很多二叉树的题目,不需要真正的还原创建出二叉树,只是根据字符串,不断的递归子串,在递归过程中输出想要的结果,这样更轻量一些,代码更短。当然,想要还原真正的二叉树也是完全可以的。
代码原理:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string pre_str; //前序
string in_str; //中序
/**
* 功能:对二叉树进行后序遍历.根据四个参数,(1)确定子树的根,(2)确定左右子树的大小范围,(3)按后序进行输出递归
* @param l1 前序遍历的起点
* @param r1 前序遍历的终点
* @param l2 中序遍历的起点
* @param r2 中序遍历的终点
*/
void dfs(int l1, int r1, int l2, int r2) {
if (l1 > r1 || l2 > r2) return;//规定边界条件
int i = in_str.find(pre_str[l1]); //利用根左右的特性来在中序队列中查找
int cnt = i - l2;//左子树的节点个数
//前序:l1是根,左子树是从l1+1开始,到l1+cnt结束
//中序:l2开始,到i-1结束
dfs(l1 + 1, l1 + cnt, l2, i - 1); //递归左子树
dfs(l1 + cnt + 1, r1, i + 1, r2); //递归右子树
cout << pre_str[l1]; //输出根结点
}
/**
ABEDFCHG
CBADEFGH
参考结果:AEFDBHGC
*/
int main() {
//输入中序遍历,前序遍历字符串
cin >> in_str >> pre_str;
int right = in_str.size() - 1; //right索引:因为是0开始,所以要-1
//递归构建还原二叉树
//本题,并没有真正的进行构建二叉树,只是根据二叉树的特点,不断查找过程中,输出后序遍历的字符串
dfs(0, right, 0, right);//每个字符串有两个指针指向头和尾
return 0;
}
二、已知后序+中序,求前序
P1030 [NOIP2001 普及组] 求先序排列
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1030
姊妹题: https://www.cnblogs.com/littlehb/p/15088998.html
三、已知前序+后序,求中序个数
P1229 遍历问题
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P1229
https://www.cnblogs.com/littlehb/p/15099843.html



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!
2018-08-02 mysql备份与还原
2017-08-02 PostgreSQL9.6.3的REDIS测试