腾讯云文字识别API提取表格数据并生成Excel文件
本文主要介绍了利用腾讯云表格文字识别API提取图片表格数据并生成Excel文件。主要涉及的知识点有:腾讯云API的调用、json文件的处理以及Excel文件的生成。
背景
在工作中,各种电子文件和纸质文件满天飞,穿梭于各个用户终端之间。有时,我们需要将纸质版数据电子化,往往需要耗费大量的人力,从而增加工作负担。一种被称为OCR的技术的发明,在一定程度上解决了这个问题。文字识别技术已经发展的十分成熟,我们熟知的软件,如QQ等,都可以进行文字识别。但是支持结构化的表格文字识别的工具不多,即使有,大多数也是收费的——目前我们还没有养成付费使用的习惯。
鉴于上述情况,本文利用腾讯云提供的表格文字提取API,结合python,实现了表格文字批量提取的功能,避免了手动录入的尴尬,减轻了工作负担。
使用工具及python包介绍
- 腾讯API
国内大型互联网公司都提供云服务,如阿里、百度、腾讯等。本文选择腾讯云服务,是因为提供的API说明比较详细,看一遍就能用。更良心的是,提供了在线测试的功能,基本不用写代码也能够测试效果。
-
Python包
-
pandas 数据分析必备包,用来对二维表数据进行分析整合。
-
os 更改系统配置信息,如列出工作目录的文件,更改工作目录等。
-
json 用来处理json数据,或者把字符串等其他格式的数据转化为json数据。
-
base64 用来对图片进行base64编码,这是根据API的要求做的。
-
xlwings 用来与Excel进行交互,几乎可以取代VBA,容易学习。
-
tencentcloud 腾讯云服务,提供了很多功能,值得探索。
-
re 正则表达式包,用来处理字符串中的空格等。
-
必要的准备工作
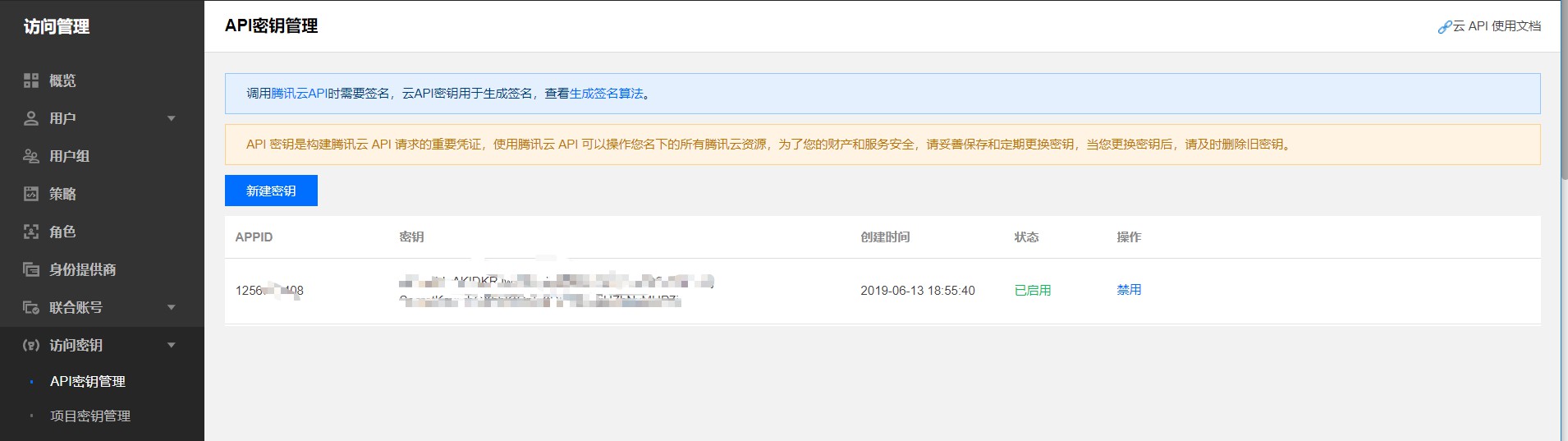
- 注册腾讯云,获取SecretID和SecretKey.
在控制台新建一个API秘钥,获取SecretID和SecretKey.
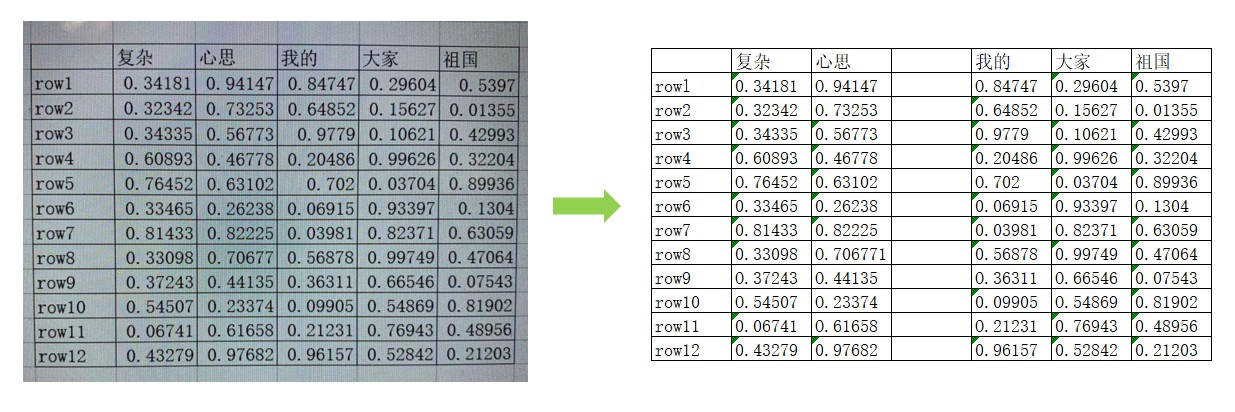
- 准备几张较为清晰的截图
代码实现
# from PIL import Image
# import pytesseract
##导入通用包
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import json
import re
import base64
import xlwings as xw
##导入腾讯AI api
from tencentcloud.common import credential
from tencentcloud.common.profile.client_profile import ClientProfile
from tencentcloud.common.profile.http_profile import HttpProfile
from tencentcloud.common.exception.tencent_cloud_sdk_exception import TencentCloudSDKException
from tencentcloud.ocr.v20181119 import ocr_client, models
#定义函数
def excelFromPictures(picture,SecretId,SecretKey):
try:
with open(picture,"rb") as f:
img_data = f.read()
img_base64 = base64.b64encode(img_data)
cred = credential.Credential(SecretId, SecretKey) #ID和Secret从腾讯云申请
httpProfile = HttpProfile()
httpProfile.endpoint = "ocr.tencentcloudapi.com"
clientProfile = ClientProfile()
clientProfile.httpProfile = httpProfile
client = ocr_client.OcrClient(cred, "ap-shanghai", clientProfile)
req = models.TableOCRRequest()
params = '{"ImageBase64":"' + str(img_base64, 'utf-8') + '"}'
req.from_json_string(params)
resp = client.TableOCR(req)
# print(resp.to_json_string())
except TencentCloudSDKException as err:
print(err)
##提取识别出的数据,并且生成json
result1 = json.loads(resp.to_json_string())
rowIndex = []
colIndex = []
content = []
for item in result1['TextDetections']:
rowIndex.append(item['RowTl'])
colIndex.append(item['ColTl'])
content.append(item['Text'])
##导出Excel
##ExcelWriter方案
rowIndex = pd.Series(rowIndex)
colIndex = pd.Series(colIndex)
index = rowIndex.unique()
index.sort()
columns = colIndex.unique()
columns.sort()
data = pd.DataFrame(index = index, columns = columns)
for i in range(len(rowIndex)):
data.loc[rowIndex[i],colIndex[i]] = re.sub(" ","",content[i])
writer = pd.ExcelWriter("../tables/" + re.match(".*\.",f.name).group() + "xlsx", engine='xlsxwriter')
data.to_excel(writer,sheet_name = 'Sheet1', index=False,header = False)
writer.save()
#xlwings方案
# wb = xw.Book()
# sht = wb.sheets('Sheet1')
# for i in range(len(rowIndex)):
# sht[rowIndex[i],colIndex[i]].value = re.sub(" ",'',content[i])
# wb.save("../tables/" + re.match(".*\.",f.name).group() + "xlsx")
# wb.close()
if not ('tables') in os.listdir():
os.mkdir("./tables/")
os.chdir("./pictures/")
pictures = os.listdir()
for pic in pictures:
excelFromPictures(pic,"YoungID","YourKey")
print("已经完成" + pic + "的提取.")
datascience.org.cn


