uvm及sv中的plusargs使用
1. uvm cmdline的用法
<1> 使用uvm_cmdline_processor可以从脚本层级,从外部向仿真环境传递参数.
program automatic test; import uvm_pkg::*; class hello_world extends uvm_test; uvm_cmdline_processor clp; int arg_value; string arg; `uvm_component_utils(hello_world); function new (string name, uvm_component parent); super.new(name, parent); clp=new(); if(clp.get_arg_value("+arg_value=",this.arg)) begin this.arg_value=this.arg.atoi(); `uvm_info("test_arg", $sformatf("input value = %d", arg_value), UVM_DEBUG); end else begin `uvm_info("test_arg", "no input arg_value", UVM_DEBUG); end endfunction endclass initial begin run_test(); end endprogram
运行:
./simv +UVM_TESTNAME=hello_world +UVM_VERBOSITY=UVM_DEBUG +arg_value=100
结果:
UVM_INFO hello.sv(19) @ 0: uvm_test_top [test_arg] input value = 100
<2> 使用uvm_cmdline_processor可以从脚本层级,从外部指定uvm的virtual sequence
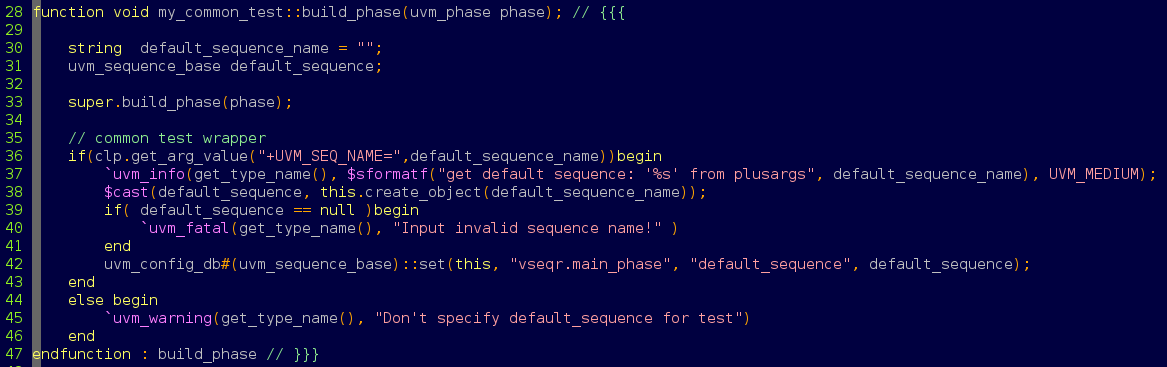
通过plargs指定virtual sequence

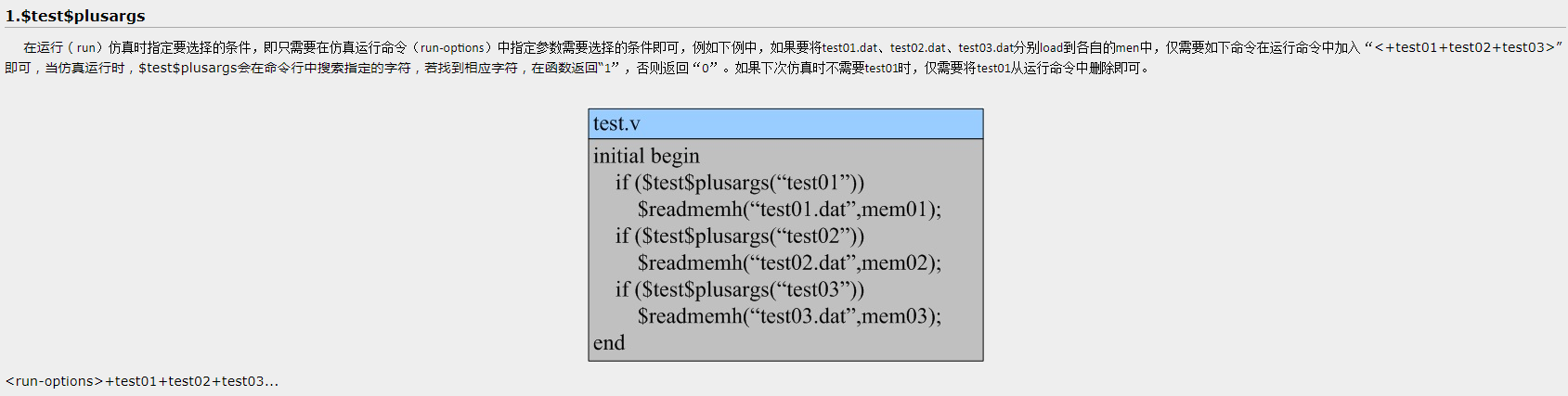
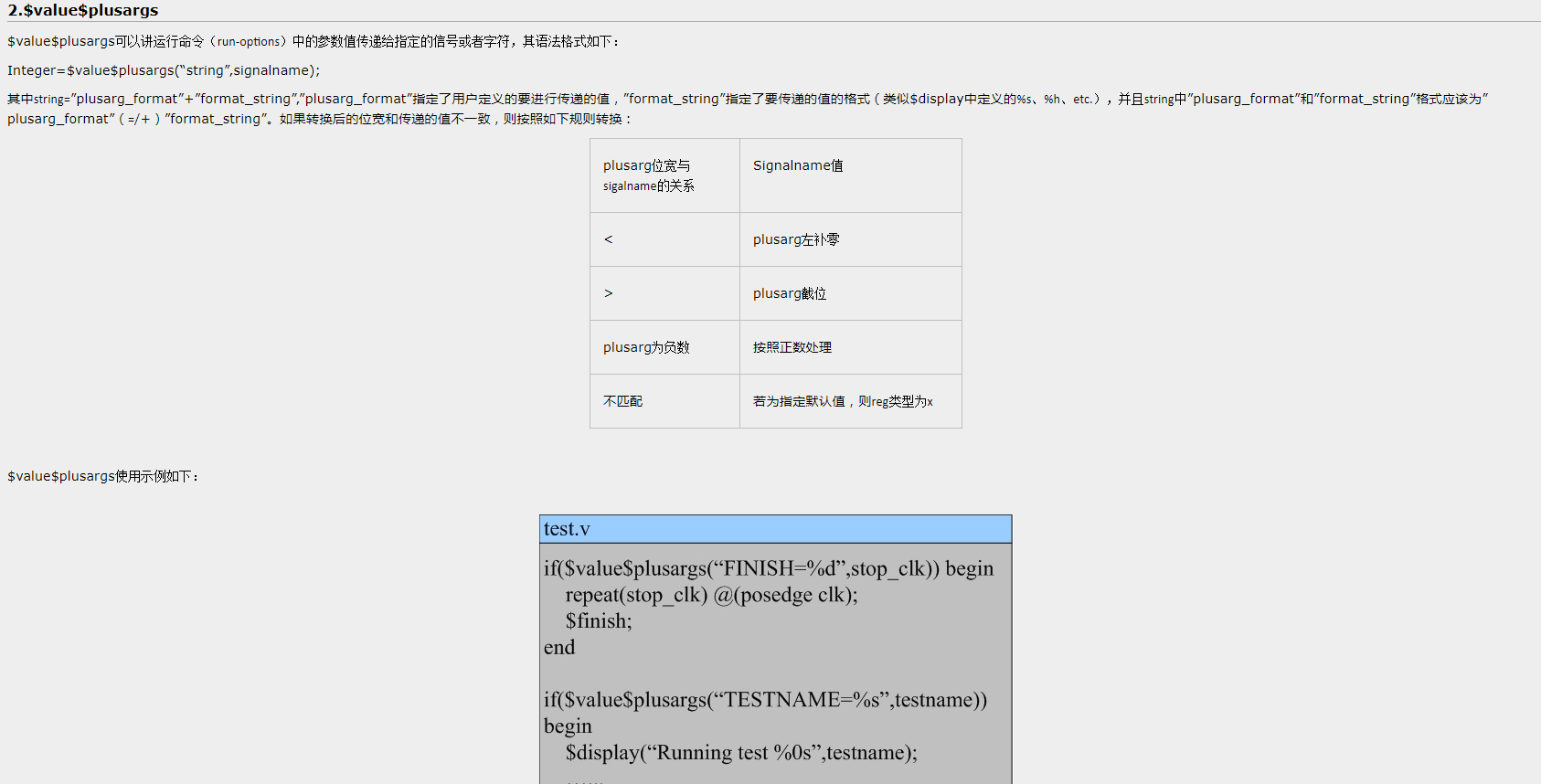
2. SV中$test$plusargs及$value$plusargs
和编译中通过宏进行区分的主要区别是

3.总结
使用$value$plusargs 可以设定不同的运算参数,如吃的文件的位置,时钟频率等。
使用$test$plusargs 则选取不同的分支进行执行。
和编译中的define的区别:define要求在编译前将变量定义好,编译后变量值已经固定了,但是假如我们希望编译后通过simv+AAA可以执行不同的分支,就需要使用上面两种方式

所以在plusargs命名时最好前缀不要一样。
本文来自博客园,作者:hematologist,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/littleMa/p/9478860.html
posted on 2018-08-14 23:45 hematologist 阅读(1994) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报



