民科吧编程赛 题解
评:没几个人做呀,是因为我的知名度不如小梦,还是出的太难了?
1.选择题
【题目简介】
只允许使用四则运算,求出任意正数 的自然对数
【思路&解答】
由于无法使用 函数,所以普通的方法,如二分法,牛顿法等依托原函数的迭代法无法使用。
考虑到 的特殊性质 ,可以使用积分方法求出。
自适应辛普森法(推导过程不再给出)
递归计算精度是否满足要求,具体过程不再给出。
值得点出的是, 当 时,要 从开始进行正积分,当 时,要从 开始进行负积分,否则误差会很大。
注意不要使用 和近似公式来完成这道题。因为为了用这个你可能还得写上上百行代码,而且亲测使用近似公式的话即使在取到也会有的偏差。
代码如下:
填空题
这道题是被骂的最狠的一道。因为导数太毒瘤。
此题难点在于 函数的四则运算表达和函数最值的计算。
可以通过公式 和二倍角公式 进行计算。
函数计算代码如下:
开平方函数四则运算计算方法不再赘述。
观察函数,下面恒>0,上面的函数很容易看出来
再看分母,当很大时函数基本为0,所以可以使用爬山法求最值。
爬山法:
随机取一点,判断该点处是上坡还是下坡,上坡则将该点往前进,下坡则往后退,多次迭代后可求出最值。
为了防止出现该点卡在题图中给出的双峰函数比较小的峰上,可以多次随机取点得到最大值。
本题当然也可使用快速傅里叶变换,但很显然为了这么简单一道题用这么复杂的算法很不值得……
注意玄学错误:l和r会卡在两个相对山峰上出不来,这时候得判一判
不过还是建议使用一个变量
双变量代码
单变量代码(还没优化……容易被卡):
3.解答题
这次民科吧大赛出的最失败的一道题,本来想的只能用模拟退火写的题被左茂雄老师一个质心公式秒掉……
题目灵感源于: [JSOI2004]平衡点 / 吊打XXX
1.质心公式法:
$ x_{ \sigma} = \dfrac { \sum { i=1 } ^ { n } x_i m_i}{ \sum {i=1}^{n}m_i} $
$ y_{ \sigma} = \dfrac { \sum { i=1 }^{n}y_i m_i}{\sum^{n}m_i} $
2.模拟退火:
1.随机出来一个质心并通过该质心得到各质点矢径
2.计算各质点对质心的贡献向量并相加。
3.向着加和方向走一点点
4.迭代回到第二步,直到无路可走,该点为质心。
代码如下:
__EOF__

本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/little-red/p/13394404.html
关于博主:评论和私信会在第一时间回复。或者直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
声援博主:如果您觉得文章对您有帮助,可以点击文章右下角【推荐】一下。您的鼓励是博主的最大动力!

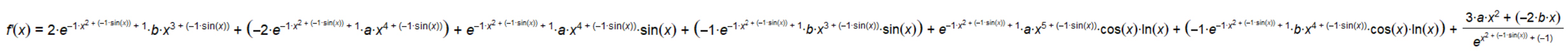


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)