第二题 题解
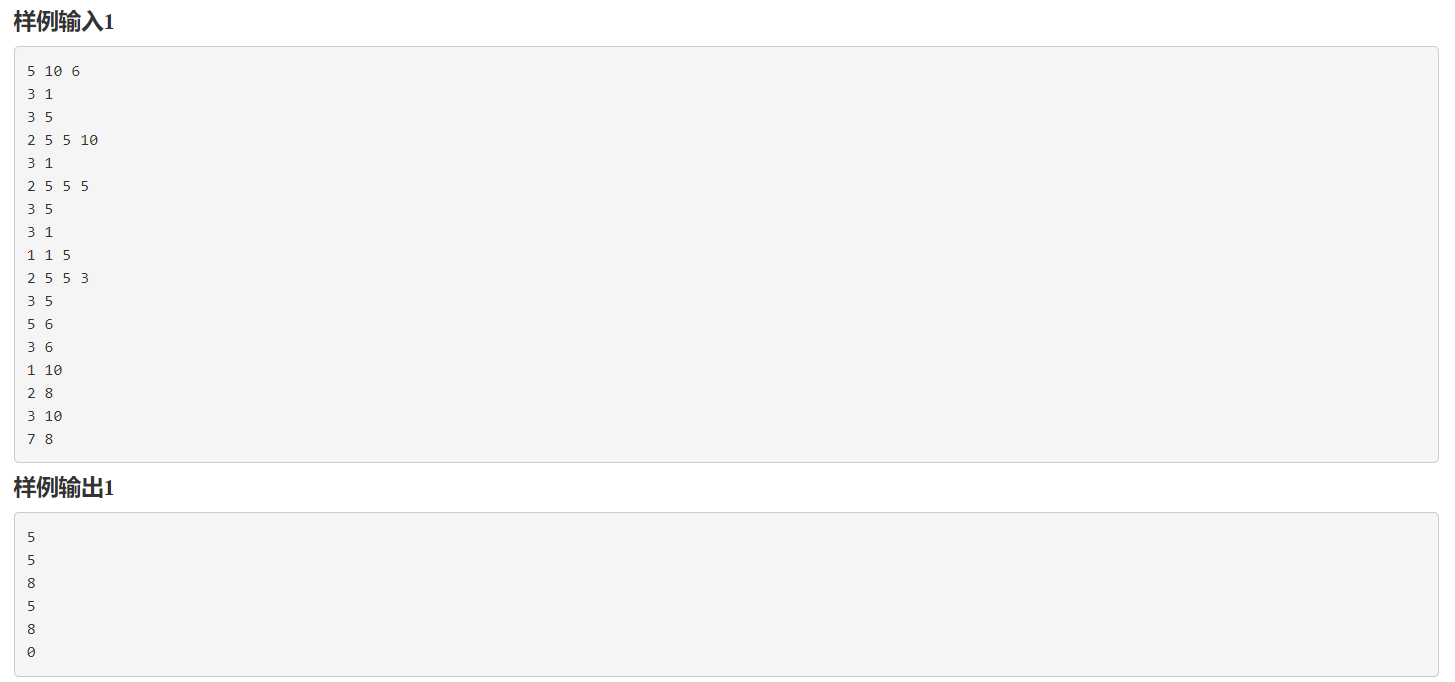
一、题目:


二、思路:
这道题的思路也非常的巧妙。
为了方便叙述,我们将操作 3 称作“小询问”,将需要输出答案的询问称为“大询问”。
将操作按照时刻从大到小排序,依次扫描每个操作,并将大询问 \([l,r]\) 挂在对应的 \(l\) 上。维护以下数据结构。
- 对每个位置维护一个 vector 数组,数组中存储一些小询问的出现时刻。
- 一个 set,维护非空的 vector 数组的下标。
- 一个树状数组,以时刻为下标,存储小询问的答案。
对当前扫描到的操作类型分类讨论,时刻为 \(t\)。
-
当前操作是一个对位置 \(x\) 的一个小询问。
将时刻 \(t\) 存到位置 \(x\) 的 vector 数组中。实时维护好 set。
-
当前操作是对区间 \([L,R]\) 的覆盖,覆盖的值为 \(v\)。
将 set 中处于 \([L,R]\) 的那些 vector 中存储的时刻取出来,对于每个时刻,在树状数组中单点修改成 \(v\)。
然后将这些 vector 清空,并将 set 维护好。
-
当前操作是交换 \((x,y)\)。
直接将 \(x\) 的 vector 和 \(y\) 的 vector 进行交换。并维护好 set 即可。
对于挂在当前时刻的所有询问。直接在树状数组上查询区间和。
考虑这样做为什么是对的。
我们可以发现,对于一个出现在时刻 \(t\)、对位置 \(x\) 的小询问,只有距离 \(t\) 最近的区间覆盖可以成为这个小询问的答案。所以我们倒序扫描每个操作,在每个区间覆盖之后立即清空所有可以覆盖到的 vector 数组。
树状数组的作用只是快速维护前缀和。
三、代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define FILEIN(s) freopen(s, "r", stdin)
#define FILEOUT(s) freopen(s, "w", stdout)
#define mem(s, v) memset(s, v, sizeof s)
inline int read(void) {
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
return f * x;
}
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 5;
int n, m, Q;
LL tr[MAXN], ans[MAXN];
struct Operation {
int opt, l, r, x;
}ope[MAXN];
vector<pair<int, int> >query[MAXN];
vector<int>vec[MAXN];
set<int>S;
set<int>::iterator it;
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
inline void add(int p, int x) {
for (; p <= m; p += lowbit(p))
tr[p] += x;
}
inline LL sum(int p) {
LL res = 0;
for (; p; p -= lowbit(p))
res += tr[p];
return res;
}
int main() {
n = read(); m = read(); Q = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i) {
ope[i].opt = read();
if (ope[i].opt == 1) {
ope[i].l = read(); ope[i].r = read();
}
else if (ope[i].opt == 2) {
ope[i].l = read(); ope[i].r = read(); ope[i].x = read();
}
else if (ope[i].opt == 3) {
ope[i].x = read();
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; ++ i) {
int l = read(), r = read();
query[l].push_back({ r, i });
}
for (int i = m; i >= 1; -- i) {
if (ope[i].opt == 3) {
int x = ope[i].x;
if (S.find(x) == S.end()) S.insert(x);
vec[x].push_back(i);
}
else if (ope[i].opt == 2) {
int l = ope[i].l, r = ope[i].r, v = ope[i].x;
while (true) {
it = S.lower_bound(l);
if (it == S.end() || (*it) > r) break;
for (auto &t : vec[*it]) {
add(t, v);
}
vec[*it].clear();
S.erase(it);
}
}
else {
int x = ope[i].l, y = ope[i].r;
if (x != y) {
if (S.find(x) != S.end()) S.erase(x);
if (S.find(y) != S.end()) S.erase(y);
swap(vec[x], vec[y]);
if (vec[x].size()) S.insert(x);
if (vec[y].size()) S.insert(y);
}
}
for (auto &p : query[i]) {
ans[p.second] = sum(p.first);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= Q; ++ i) {
printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
}
return 0;
}



