Interstellar 题解
一、题目:

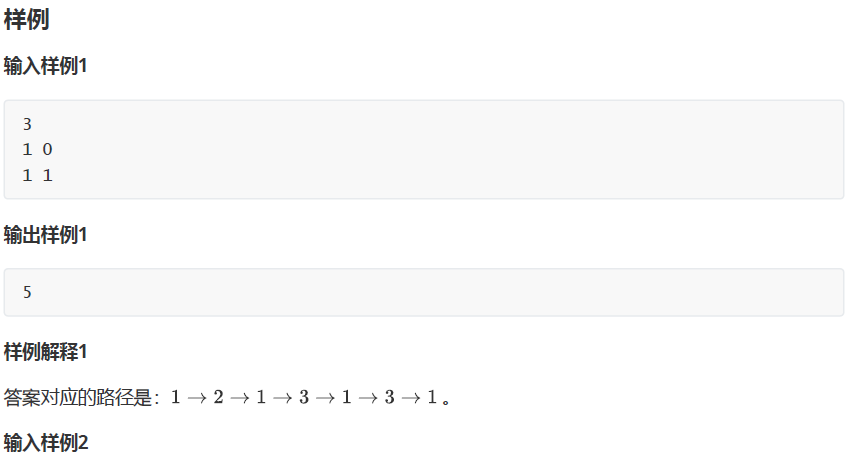
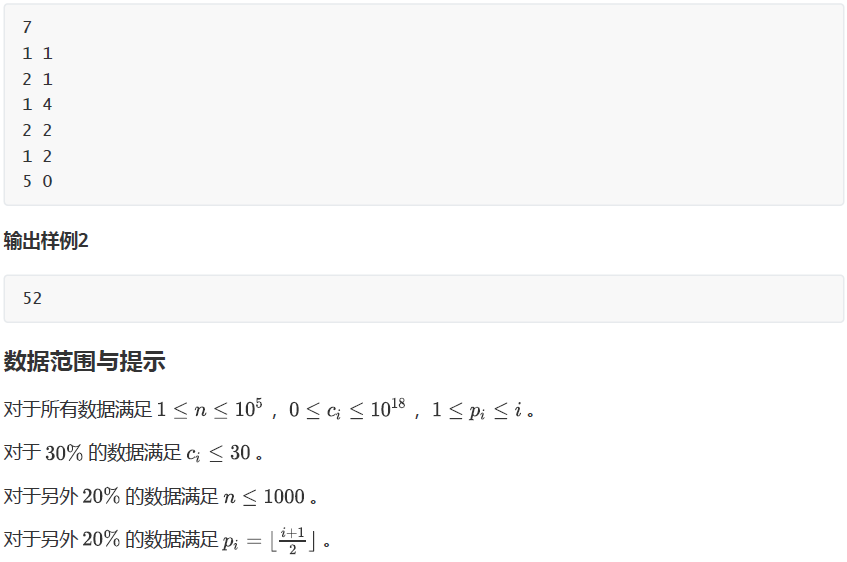
二、思路:
在没看数据范围之前,这道题有一个十分显然的树形DP做法。
设 \(dp(x)\) 表示 \(x\) 及其子树内所能获得的最大代价(题目为什么要使代价最大化呢?),于是有转移方程
\[dp(x)=\max_{y\in son(x)}\{dp(y)+w(x,y)\}+\sum_{y\in son(x)} (dp(y)+w(x,y))
\]
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\),这题不就解决了吗?
然后看到数据范围 \(0\leq c_i\leq 10^{18}\),也就是说每条边的权值最大可以是 \(2^{10^{18}}\),当场去世。
于是考虑用 set 维护每条边的权值中有哪几个2的幂次。加法和比较大小都类似于高精度。
考虑这样的复杂度为什么是对的,因为每条边至多只会贡献一个2的幂次,而且加法每进一位都会少一个1,所以每次均摊复杂度是 \(O(1)\) 的。如果我们再用启发式合并,那总的复杂度就是 \(O(n\log^2 n)\)的。比较大小也一样。
再考虑我们还要取出最大的数进行累加,这时候相当于对一个数乘2,也就是每一个2的幂次都会左移。暴力移肯定不行,考虑使用懒标记。
然后呢?然后就没了。
三、启示:
其实这样的做法很容易想到,这启发我们需要认真分析复杂度,而且当不方便实时维护的时候一定要想到懒标记,有时候能解决很多问题。
四、代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define FILEIN(s) freopen(s".in", "r", stdin)
#define FILEOUT(s) freopen(s".out", "w", stdout)
inline long long read(void) {
long long x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
return f * x;
}
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5, mod = 998244353;
int n, tot = 1, head[maxn];
long long ans[maxn];
struct Edge {
int y, next;
long long w;
Edge() {}
Edge(int _y, int _next, long long _w) : y(_y), next(_next), w(_w) {}
}e[maxn << 1];
struct Node {
set<long long>S;
long long tag;
inline void insert(long long p) {
p -= tag;
while (S.find(p) != S.end()) {
S.erase(p);
++ p;
}
S.insert(p);
}
inline friend bool operator <(const Node&a, const Node&b) {
if (b.S.size() == 0) return 0;
if (a.S.size() == 0) return 1;
set<long long>::iterator i1 = a.S.end(), i2 = b.S.end();
-- i1; -- i2;
while ((*i1) + a.tag == (*i2) + b.tag) {
if (i2 == b.S.begin()) return 0;
if (i1 == a.S.begin()) return 1;
-- i1; -- i2;
}
return (*i1) + a.tag < (*i2) + b.tag;
}
}dp[maxn];
inline long long power(long long a, long long b) {
long long res = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1) {
if (b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
inline void connect(int x, int y, long long w) {
e[++ tot] = Edge(y, head[x], w);
head[x] = tot;
}
void dfs(int x, int fa) {
int mx = -1;
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int y = e[i].y;
if (y == fa) continue;
dfs(y, x);
ans[y] += power(2, e[i].w);
dp[y].insert(e[i].w);
if (mx == -1 || dp[mx] < dp[y]) mx = y;
}
if (mx != -1) {
++ dp[mx].tag;
(ans[mx] *= 2) %= mod;
}
for (int i = head[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int y = e[i].y;
if (y == fa) continue;
if (dp[y].S.size() > dp[x].S.size()) swap(dp[y], dp[x]);
for (set<long long>::iterator it = dp[y].S.begin(); it != dp[y].S.end(); ++ it) {
dp[x].insert(*it + dp[y].tag);
}
(ans[x] += ans[y]) %= mod;
}
}
int main() {
FILEIN("a"); FILEOUT("a");
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++ i) {
int p = read(); long long w = read();
connect(i + 1, p, w);
connect(p, i + 1, w);
}
dfs(1, 0);
printf("%lld\n", ans[1]);
return 0;
}


