图 题解
一、题目:

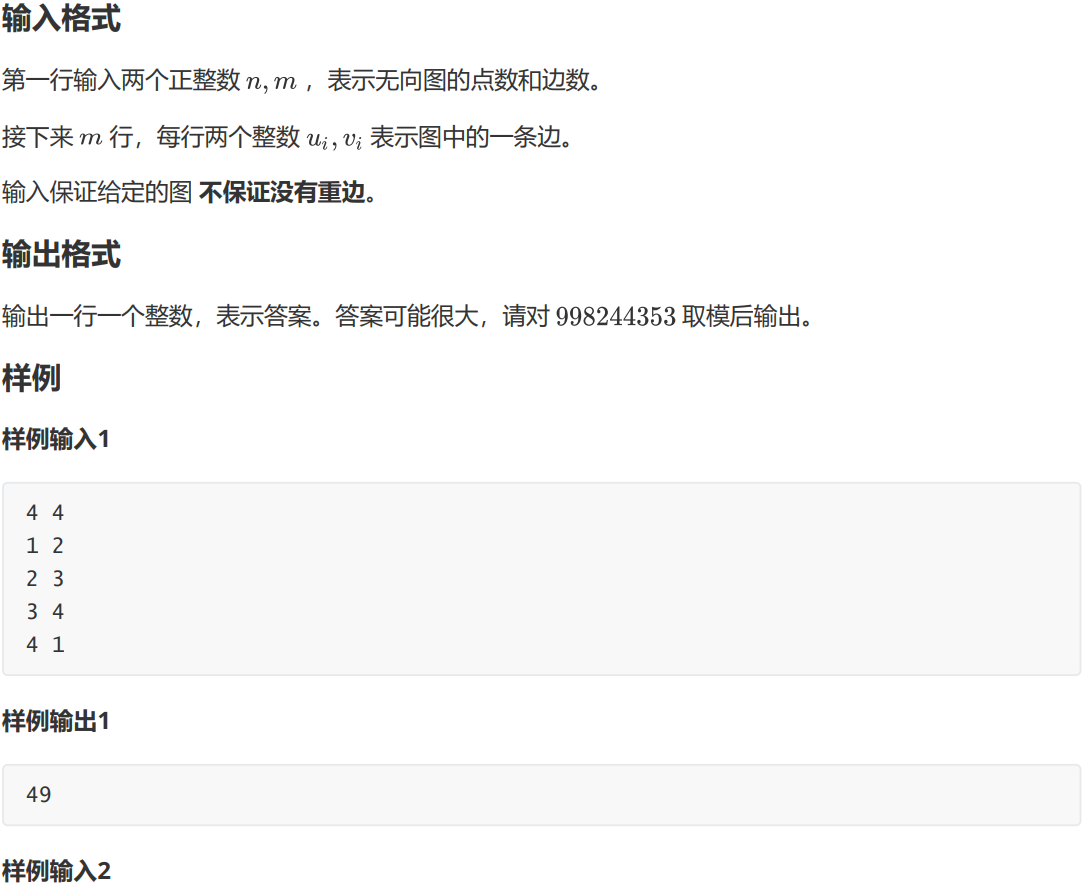
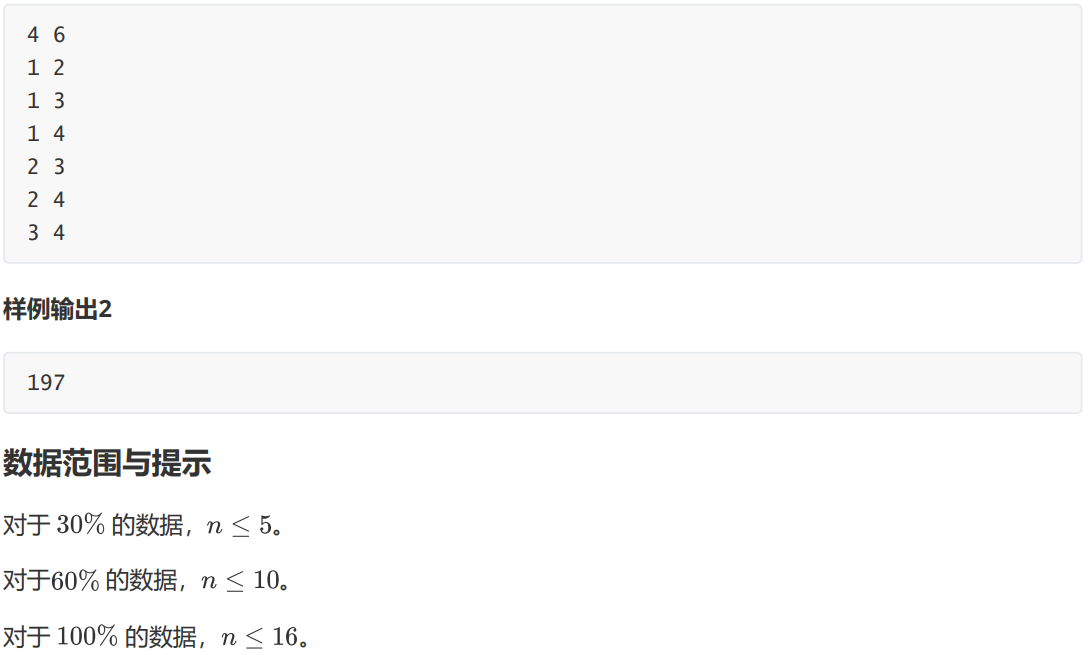
二、思路:
容易看出,本题的意思是说,保留一张图的一些边,图就会被分割成很多个联通块。新的图至多只能有一个环。每种情况的贡献是所有联通块大小的乘积。
我们首先可以用这道题的思路,预处理出\(circle(s)\),表示由\(s\)这个集合中的点可以组成几个环。
考虑\(O(2^n)\)枚举当前要保留哪个环。设当前环中的所有点的集合是\(s\)。将\(s\)缩点,设缩成的大点是\(S\)。建立一个虚拟节点\(T\),从虚拟节点向剩下的每个节点连一条无向边。特别地,从\(T\)向\(S\)连\(|s|\)条边。
然后,用矩阵树定理处理出当前图的生成树个数。然后我们惊奇地发现,当前图的生成树个数就等于所有可能的联通块大小之积的总和。这个很容易证明,用映射的思想想一想就可以发现它是对的。重点是需要记住这一个重要的转化。
然后别忘了乘上形成\(s\)环的方案数。
所以矩阵树定理+状压DP即可解决本题。
三、代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#define FILEIN(s) freopen(s".in", "r", stdin)
#define FILEOUT(s) freopen(s".out", "w", stdout)
#define mem(s, v) memset(s, v, sizeof s)
using namespace std;
inline int read(void) {
int x = 0, f = 1; char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }
return f * x;
}
const int maxn = 18, mod = 998244353;
int n, m;
long long circle[1 << maxn], f[maxn][1 << maxn];
long long mat[maxn][maxn], ans;
int G[maxn][maxn];
#define call(s, i) ((s >> i) & 1)
inline int lowbit(int x) { return x & (-x); }
inline int count(int s) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) {
if (call(s, i)) ++ res;
}
return res;
}
inline long long power(long long a, long long b) {
long long res = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1) {
if (b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
a = a * a % mod;
}
return res;
}
inline void init(void) {
for (int x = 0; x < n; ++ x) f[x][1 << x] = 1;
for (int s = 0; s < (1 << n); ++ s) {
for (int x = 0; x < n; ++ x) {
if (!call(s, x)) continue;
for (int y = 0; y < n; ++ y) {
if (!G[x][y]) continue;
if (lowbit(s) > (1 << y)) continue;
if (lowbit(s) == (1 << y)) (circle[s] += f[x][s]) %= mod;
else if (!call(s, y)) (f[y][s | (1 << y)] += f[x][s]) %= mod;
}
}
}
for (int s = 0; s < (1 << n); ++ s) {
if (count(s) <= 2) circle[s] = 0;
else (circle[s] *= (mod + 1) / 2) %= mod;
}
}
inline long long Gauss(long long a[maxn][maxn], int n) {
long long res = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) {
int mx = i;
for (int j = i; j < n; ++ j) {
if (a[j][i] != 0) { mx = j; break; }
}
if (!a[mx][i]) return 0;
if (mx != i) swap(a[mx], a[i]), res = -res;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++ j) {
long long r = a[j][i] * power(a[i][i], mod - 2) % mod;
for (int k = i; k < n; ++ k) {
(a[j][k] -= r * a[i][k] % mod) %= mod;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) {
(res *= a[i][i]) %= mod;
}
if (res < 0) res += mod;
return res;
}
inline void prepare(int s) {
mem(mat, 0);
int represent = log2(lowbit(s));
for (int x = 0; x < n; ++ x) {
for (int y = 0; y < n; ++ y) {
if (call(s, x) && call(s, y)) continue;
if (call(s, x) && !call(s, y))
(mat[represent][y] -= G[x][y]) %= mod,
(mat[represent][represent] += G[x][y]) %= mod;
if (!call(s, x) && call(s, y))
(mat[x][represent] -= G[x][y]) %= mod,
(mat[x][x] += G[x][y] % mod) %= mod;
if (!call(s, x) && !call(s, y))
(mat[x][y] -= G[x][y]) %= mod,
(mat[x][x] += G[x][y]) %= mod;
}
}
for (int x = 0; x < n; ++ x) {
if (x == represent) {
int cnt = count(s);
mat[x][n] -= cnt % mod;
mat[x][n] %= mod;
mat[n][x] -= cnt % mod;
mat[n][x] %= mod;
mat[x][x] += cnt % mod;
mat[x][x] %= mod;
mat[n][n] += cnt % mod;
mat[n][n] %= mod;
} else {
mat[x][n] --;
mat[n][x] --;
mat[x][x] ++;
mat[n][n] ++;
}
}
}
int main() {
FILEIN("graph"); FILEOUT("graph");
n = read(); m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i) {
int x = read(), y = read();
-- x; -- y;
G[x][y] = G[y][x] = 1;
}
init();
for (int x = 0; x < n; ++ x)
for (int y = 0; y < n; ++ y) {
mat[x][y] -= G[x][y];
mat[x][x] += G[x][y];
}
for (int x = 0; x < n; ++ x) {
-- mat[x][n];
-- mat[n][x];
++ mat[x][x];
++ mat[n][n];
}
(ans += Gauss(mat, n)) %= mod;
for (int s = 0; s < (1 << n); ++ s) {
if (count(s) <= 2) continue;
if (!circle[s]) continue;
prepare(s);
(ans += Gauss(mat, n) * circle[s]) %= mod;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}


