深度优先算法和Ncurses - 迷宫
前言:
阅读此篇文章要求读者具有一些基础的ncurses库了解
深度优先算法是将各种情况分配一定的优先级,然后在某个问题出现的时候,选择优先级高的情况进行处理,特定情况下进行回退,选择优先级次之的情况进行尝试. 点击这里可以得到源码
我这里没有考虑没有出口的情况下,深度优先算法的行为结果。之后会有专门的研究文章。
程序主体思路
过程
- 创建一个迷宫
- 创建一个人
- 把人放到迷宫的入口
- 深度优先算法控制人,走到出口。
- 退出
代码
#include <ncurses.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
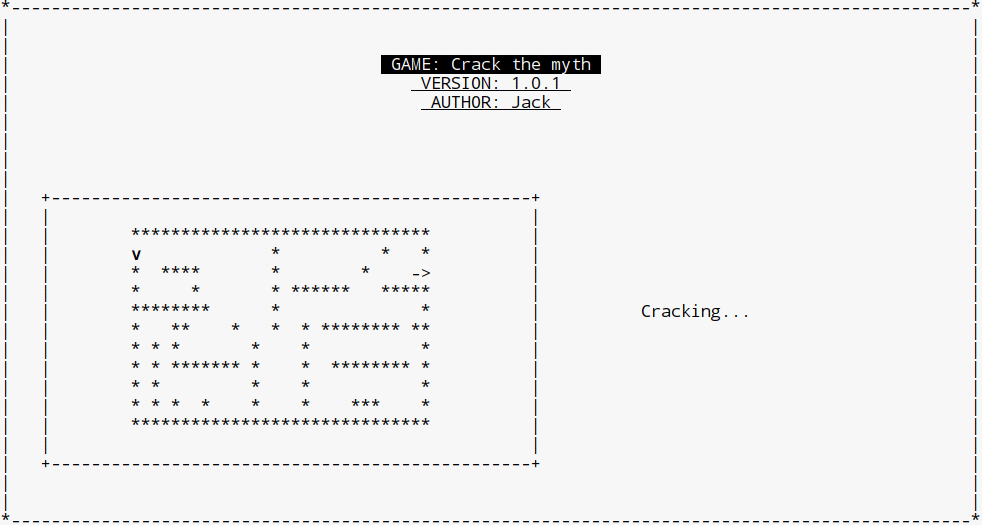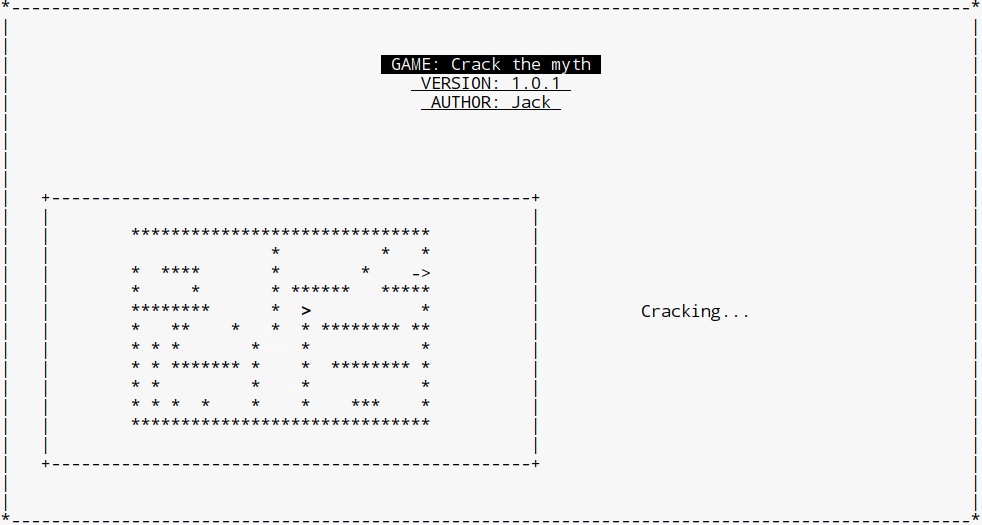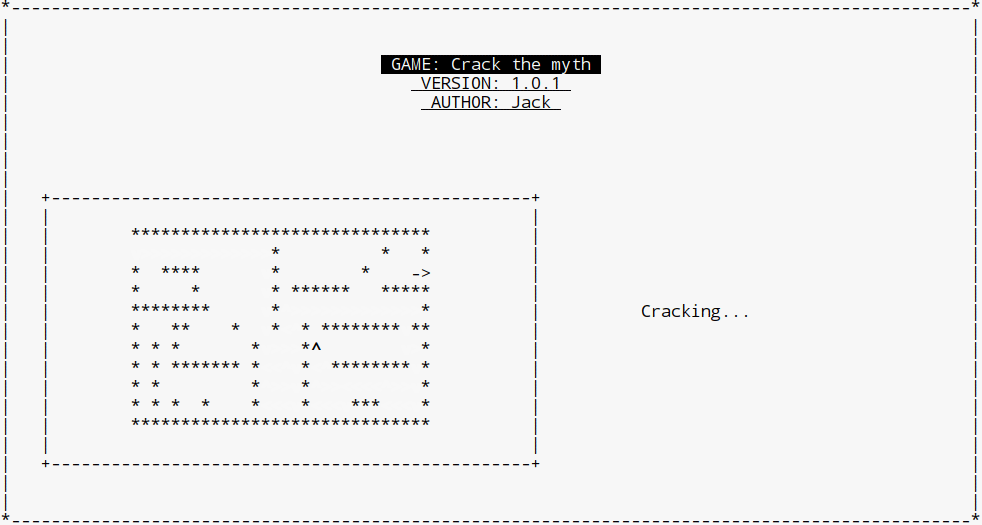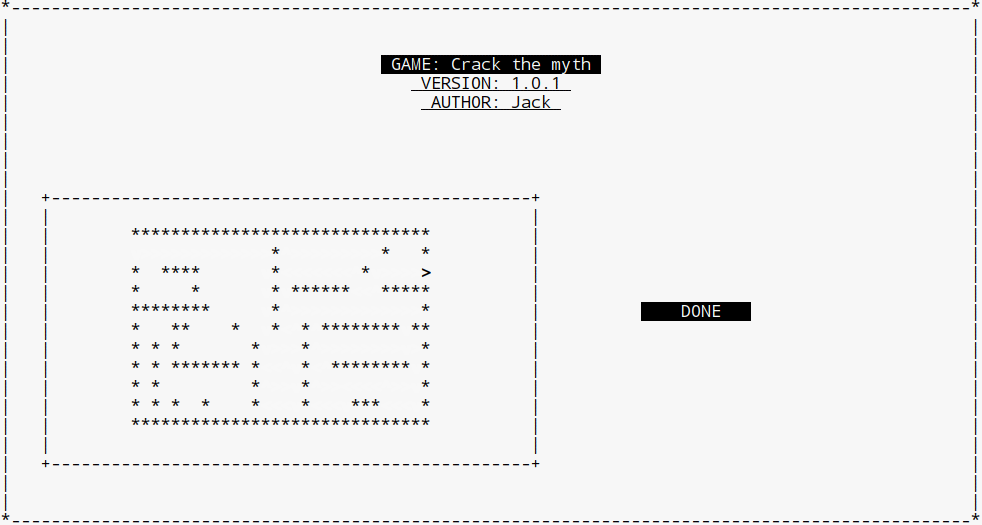
// this is the myth map.
char myth[][31] = {
"******************************",
" * * *",
"* **** * * ->",
"* * * ****** *****",
"******** * *",
"* ** * * * ******** **",
"* * * * * *",
"* * ******* * * ******** *",
"* * * * *",
"* * * * * * *** *",
"******************************"
};
这里用一个字符数组来存储迷宫的信息
char book[12][30] = {0};
book数组负责这个点有没有走过的标记
int myth_starty = 0;
int myth_startx = 0;
myth_starty, myth_startx 分别负责在myth WINDOW里面的迷宫左上角起点坐标的y和x, 因为在ncurses里面,的坐标和我们的迷宫数组下标之间需要一个翻译。
// this is a person struct.
typedef struct _person
{
int x;
int y;
int step;
}Person;
这是一个结构体,来存放player的信息
// this a struct for a point in game.
typedef struct _loc
{
int x, y;
}MLoc;
一个包装了y和x两个int值的结构体, 没怎么用
// this function handle the person's moving.
void moveTo(WINDOW *w, Person *p, int y, int x);
这个函数负责把一个Person移动到某个窗口w的y行x列
// this function return a person pointer.
Person* con_person();
这个函数负责construct一个person,返回Person指针
// this function destroy a person.
void destroy_person(Person *p);
这个函数释放Person指针p指向的堆内存
// this funcion creates a myth in the middle of the target window.
int create_myth(WINDOW *target);
这个函数负责打印迷宫到窗口target的中心
//
void go_through(WINDOW *, Person *);
这个函数就是负责让小人走出迷宫
int main()
{
// preparation for this program.
initscr();
clear();
curs_set(0); // hide the cursor
noecho(); // no echo.
cbreak(); // close the line buffer.
ncurses程序初始化准备部分
init_pair(1, COLOR_RED, COLOR_BLACK);
init_pair(2, COLOR_BLACK, COLOR_WHITE);
颜色效果不太好,然后就取消掉了。这两行代码无用
// make a border for the standred screen.
wborder(stdscr, '|', '|', '-', '-', '*', '*', '*', '*');
refresh();
给标准屏幕添加一个边框
// two var for the max size of the stdscr.
int scry, scrx;
getmaxyx(stdscr, scry, scrx);
// 把标准屏幕的宽度和高度存放在scrx,scry里面
// use a LOC var for an area. y stands for height, x stands for width.
MLoc title_part;
title_part.y = (scry-15)/2 + 4;
title_part.x = (scrx-50)/2;
// 计算出title_part的大小, 用来存放一些程序信息
/* print some game info */
char *title = " GAME: Crack the myth ";
char *author = " AUTHOR: Jack ";
char *version = " VERSION: 1.0.1 ";
attron(A_REVERSE);
mvprintw((title_part.y - 3)/2, (scrx-strlen(title))/2, "%s", title);
attroff(A_REVERSE);
attron(A_UNDERLINE);
mvprintw((title_part.y - 3)/2 + 1, (scrx-strlen(version))/2, "%s", version);
mvprintw((title_part.y - 3)/2 + 2, (scrx-strlen(author))/2, "%s", author);
attroff(A_UNDERLINE);
refresh();
把名称、作者信息、版本号打印在游戏界面中
// myth is a window for the myth map.
WINDOW *w_myth = newwin(15, 50, (scry-15)/2 + 4, (scrx-50)/2 - 20);
// we called the function which we defined to show the myth map
create_myth(w_myth);
wborder(w_myth, '|', '|', '-', '-', '+', '+', '+', '+');
//
mvwprintw(stdscr, (scry-15)/2 + 4 + 6, (scrx-50)/2 - 20 + 60, "Cracking...");
refresh();
wrefresh(w_myth);
创建一个窗口来存放迷宫地图,并且给其添加边界
// put a person on myth.
Person *player = con_person();
moveTo(w_myth, player, 1, 0);
getchar();
随便得到一个字符之后,开始进行寻路
go_through(w_myth, player);
// get a character then exit.
getchar();
endwin();
return 0;
}
以上就是程序的全部流程,不难 对吗?
深度优先算法
过程
我们测试每一个点,如果当前位置在终点位置上,那么我们就直接结束程序。或者我们就来计算下一个点的坐标。下一个点的坐标可以是右边的、下边的、左边的、上边的、(东南西北),我们在这里用一个next二维数组来处理,如果是下一个点是邻接的右边的点,那么y坐标不变,x坐标+1, 所以在next数组里面对应的是{0, 1} ( {y, x} ) 这样。
在后面用for循环遍历每一种情况的时候,会用到这个next数组。
代码
void go_through(WINDOW *w, Person *p)
{
int cy, cx;
int ny, nx;
if ( p->y == 2 && p->x == 29)
{
attron(A_REVERSE);
mvwprintw(stdscr, (LINES-15)/2 + 4 + 6, (COLS-50)/2 - 20 + 60, " DONE ");
attroff(A_REVERSE);
wrefresh(stdscr);
wrefresh(stdscr);
getchar();
endwin();
exit(0);
}
int next[4][2] =
{
{0, 1},
{1, 0},
{0, -1},
{-1, 0},
};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
// 计算下一个点的坐标
ny = p->y + next[i][0];
nx = p->x + next[i][1];
// 保存当前坐标
cy = p->y;
cx = p->x;
// 如果下个坐标值非法(越界),那么就跳过这个尝试
// 在这里,每个循环代表的是每个方向上的尝试
if (ny > 10 || ny < 0 || nx > 29 || nx < 0)
{
continue;
}
// 如果下一个坐标没有走过,并且不是墙
if (book[ny][nx] == 0 && myth[ny][nx] != '*')
{
// 标记走过了这个点
book[ny][nx] = 1;
// 移动Person p走到这个点
moveTo(w, p, ny, nx);
// 睡100毫秒
usleep(100000);
// 以新的点作为起点进行尝试, 这就是递归算法。
go_through(w, p);
// 尝试结束后(可能是尝试失败的情况下), 退回来。 在for循环的下一次循环中尝试其他方向
moveTo(w, p, cy, cx);
// book[ny][nx] = 0;
}
}
return ;
}
总结
学习算法总是: 纸上得来终觉浅, 绝知此事要躬行。 另外,这个程序只是寻找一条路,而不是寻找最短路径。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号