01-Vue.js基础
一、Vue基础
1、介绍
Vue是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架。Vue的核心库只关注视图层,不仅容易上手,还便于与第三方库或既有的项目整合。兼容性:Vue 不支持 IE8 及以下版本,因为 Vue 使用了 IE8 无法模拟的 ECMAScript 5 特性。但它支持所有兼容 ECMAScript 5 的浏览器。Vue.js 不支持 IE8 及其以下 IE 版本。
2、Vue.js安装
安装有三种方式,一种直接下载开发版本,第二种CDN链接,国外有比较稳定的两个CDN,第三种官方命令工具,可用于快速搭建大型单页应用。开发学习还是建议第一种,Vue.js 的官网上直接下载 vue.min.js 并用 <script> 标签引入。
unpkg:https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js, 会保持和 npm 发布的最新的版本一致。
cdnjs : https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/vue/2.1.8/vue.min.js
第三种安装就是利用淘宝npm(大于3.0)镜像下载:
升级淘宝镜像:
npm install cnpm -g #升级cnpm或者安装 cnpm install npm -g #升级npm npm -v #查看版本
cnpm install vue #安装最新版本
第四种命令行工具,可以用于快速搭建大型单页应用
cnpm install --global vue-cli # 全局安装 vue-cli vue init webpack my-project # 创建一个基于 webpack 模板的新项目 这里需要进行一些配置,默认回车即可
进入项目,安装依赖包并运行:
cd my-project
cnpm install
cnpm run dev
3、Vue.js目录结构
build 项目构建(webpack)相关代码
config 配置目录,包括端口号等。我们初学可以使用默认的
node_modules npm 加载的项目依赖模块
src 我们要开发的目录,基本上要做的事情都在这个目录里。里面包含了几个目录及文件 assets: 放置一些图片,如logo等。components: 目录里面放了一个组件文件,可以不用。App.vue: 项目入口文件,我们也可以直接将组件写这里,而不使用 components 目录。main.js: 项目的核心文件
static 静态资源目录,如图片、字体等
test 初始测试目录,可删除
index.html 首页入口文件,你可以添加一些 meta 信息或统计代码啥的
package.json 项目配置文件
.xxxx文件 这些是一些配置文件,包括语法配置,git配置等
src/APP.vue:
<!-- 展示模板 -->
<template> <div id="app"> <img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png"> <HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/> </div> </template> //导入组件 <script> import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue' export default { name: 'app', components: { HelloWorld } } </script> //样式代码 <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } </style>
初始化项目,将src/components/HelloWorld.vue修改为以下代码:

<template> <div class="hello"> <h1>{{ msg }}</h1> <p> For a guide and recipes on how to configure / customize this project,<br> check out the <a href="https://cli.vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">vue-cli documentation</a>. </p> <h3>Installed CLI Plugins</h3> <ul> <li><a href="https://github.com/vuejs/vue-cli/tree/dev/packages/%40vue/cli-plugin-babel" target="_blank" rel="noopener">babel</a></li> <li><a href="https://github.com/vuejs/vue-cli/tree/dev/packages/%40vue/cli-plugin-eslint" target="_blank" rel="noopener">eslint</a></li> </ul> <h3>Essential Links</h3> <ul> <li><a href="https://vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Core Docs</a></li> <li><a href="https://forum.vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Forum</a></li> <li><a href="https://chat.vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Community Chat</a></li> <li><a href="https://twitter.com/vuejs" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Twitter</a></li> <li><a href="https://news.vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">News</a></li> </ul> <h3>Ecosystem</h3> <ul> <li><a href="https://router.vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">vue-router</a></li> <li><a href="https://vuex.vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">vuex</a></li> <li><a href="https://github.com/vuejs/vue-devtools#vue-devtools" target="_blank" rel="noopener">vue-devtools</a></li> <li><a href="https://vue-loader.vuejs.org" target="_blank" rel="noopener">vue-loader</a></li> <li><a href="https://github.com/vuejs/awesome-vue" target="_blank" rel="noopener">awesome-vue</a></li> </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'HelloWorld', data() { return { msg: '欢迎来到前端世界!' } } } </script> <!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only --> <style scoped> h3 { margin: 40px 0 0; } ul { list-style-type: none; padding: 0; } li { display: inline-block; margin: 0 10px; } a { color: #42b983; } </style>

4、Vue.js起步
使用vue.js实现HelloWorld,在使用之前我们先用dom实现hello world:(index.html)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Hello World</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"></div> <script> var dom = document.getElementById("app"); dom.innerHTML = "Hello World!" </script> </body> </html>

接下来用Vue.js实现同样的目标:index.html:
<meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Hello World</title> <!-- 引入vue.js的库 --> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app">{{content}}</div> <script> // var dom = document.getElementById("app"); // dom.innerHTML = "Hello World!" // 创建Vue实例,接受参数 var app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { content:'Hello World!!!' } }) </script> </body> </html>

如果想要让它延时2秒在显示出来,那么我们用dom应该怎样操作呢?
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Hello World</title> <!-- 引入vue.js的库 --> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app">{{content}}</div> <script> var dom = document.getElementById("app"); dom.innerHTML = "Hello World!"; setTimeout(function() { dom.innerHTML = "Bye Bye World!"; },2000) // 创建Vue实例,接受参数 // var app = new Vue({ // el: '#app', // data: { // content:'Hello World!!!' // } // }) </script> </body> </html>
用Vue实现:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Hello World</title> <!-- 引入vue.js的库 --> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app">{{content}}</div> <script> // 创建Vue实例,接受参数 var app = new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { content:'Hello World!!!' } }); setTimeout(function() { app.$data.content = "Bye Bye World!" },2000) </script> </body> </html>
这样书写vue的代码不再关注dom操作对象啦,而是关注数据操作。
5、使用vue.js实现todoList
v-for实现遍历:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList</title> <!-- 引入vue.js的库 --> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text"/> <button>提交</button> <!-- v_for遍历数组 --> <ul> <li v-for="item in list">{{item}}</li> </ul> </div> <script> var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data: { list: ['第一课的内容','第二课的内容','第三课的内容'] } }) </script> </body> </html>
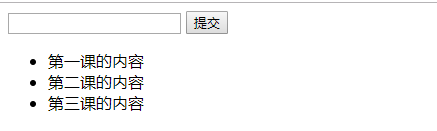
现在将数组清空,变成空数组,这样来运行:
button绑定事件 :
数据都没有啦,现在我们的目的就是在输入框输入数据,然后数据在下面的li标签中显示,那么现在就来利用vue来实现代码(button绑定事件):

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList</title> <!-- 引入vue.js的库 --> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text"/> <!-- 在标签中绑定点击事件,有个方法,方法一定要写在vue实例中,有个叫methods的键值对里 --> <button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button> <!-- v_for遍历数组 --> <ul> <li v-for="item in list">{{item}}</li> </ul> </div> <script> var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data: { list: [] }, methods: { handleBtnClick: function() { alert('click'); } } }) </script> </body> </html>
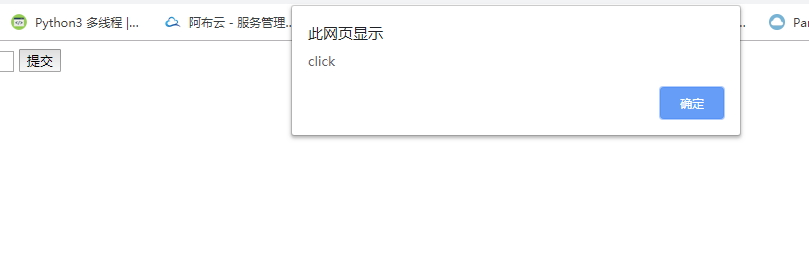
v-model数据的双向绑定:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList</title> <!-- 引入vue.js的库 --> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <!-- v-model数据的双向绑定,在浏览器控制台对app.$data.inputValue进行赋值,然后浏览器的输入框也会显示一样的值 --> <input type="text" v-model="inputValue"/> <!-- 在标签中绑定点击事件,有个方法,方法一定要写在vue实例中,有个叫methods的键值对里 --> <button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button> <!-- v_for遍历数组 --> <ul> <li v-for="item in list">{{item}}</li> </ul> </div> <script> var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data: { list: [], inputValue: '', }, methods: { handleBtnClick: function() { // list中是空值,因此向list中添加值,添加的值是输入框的内容 this.list.push(this.inputValue) // 提交将输入框的值弹出来 // alert(this.inputValue); // 每次点击按钮,都将input框的值赋值为空 this.inputValue = "" } } }) </script> </body> </html>

我们操作的都不是dom对象,都是对数据进行操作,这种操作被称为MVVM模式,
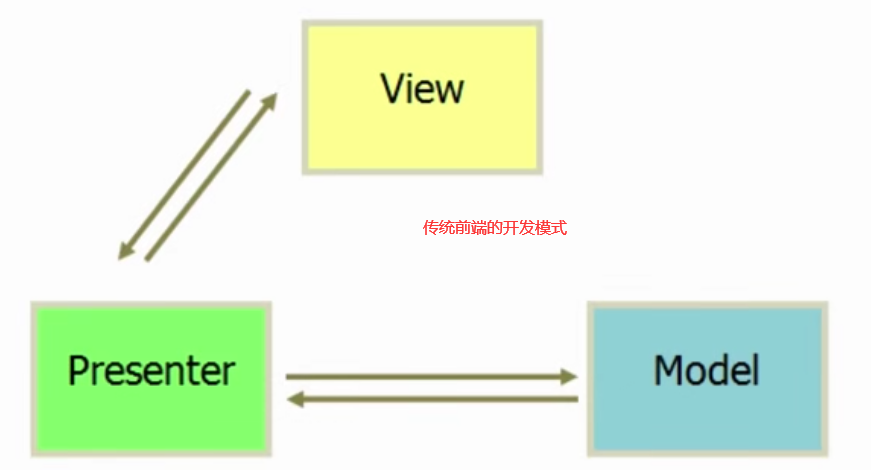
传统的开发模式MVP模式:Model层:数据层。Presenter层:呈现层,View层:视图层接下来利用Jquery实现MPV开发模式的TodoList。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList Jquery</title> <script src="./jquery.js"></script> </head> <body> <!-- V层 视图 --> <div> <input type="text" id="input" /> <button id="btn">提交</button> <ul id="list"></ul> </div> <script> // MPV模式 // P层 控制器通过控制dom操作改变视图,控制ajax请求 M层这里没有,就是操作ajax数据层 function Page() { } $.extend(Page.prototype, { init: function() { this.bindEvents() }, bindEvents: function() { var btn = $('#btn'); btn.on('click', $.proxy(this.handleBtnClick,this)) }, handleBtnClick: function() { var inputElem = $("#input"); var inputValue =inputElem.val(); var ulElem = $("#list"); ulElem.append('<li>'+ inputValue +'</li>'); inputElem.val(""); } }) var page = new Page(); page.init(); </script> </body> </html>
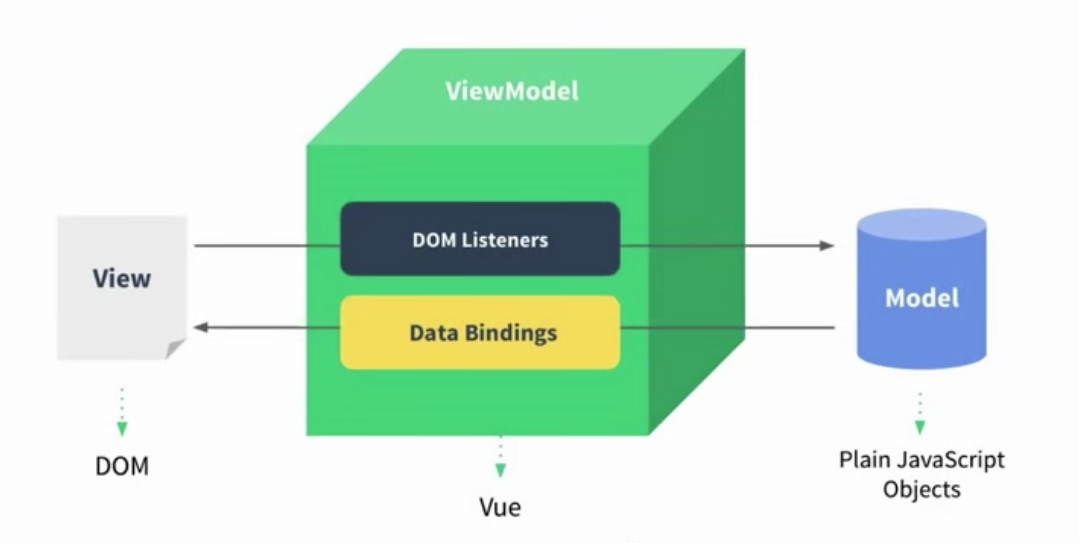
MVVM设计模式图:我们不用关心dom是如何实现的,我们只需要关注View层以及Model层。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList</title> <!-- 引入vue.js的库 --> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <!-- V层 --> <div id="app"> <!-- v-model数据的双向绑定,在浏览器控制台对app.$data.inputValue进行赋值,然后浏览器的输入框也会显示一样的值 --> <input type="text" v-model="inputValue"/> <!-- 在标签中绑定点击事件,有个方法,方法一定要写在vue实例中,有个叫methods的键值对里 --> <button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button> <!-- v_for遍历数组 --> <ul> <li v-for="item in list">{{item}}</li> </ul> </div> <script> // MVVM设计模式 // VM层实现数据变化,标签的显示也发生变化,自动实现。 // M层,对数据进行操作 我们基本需要关注M层 面向数据进行编程 var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data: { list: [], inputValue: '', }, methods: { handleBtnClick: function() { // list中是空值,因此向list中添加值,添加的值是输入框的内容 this.list.push(this.inputValue) // 提交将输入框的值弹出来 // alert(this.inputValue); // 每次点击按钮,都将input框的值赋值为空 this.inputValue = "" } } }) </script> </body> </html>
6、前端组件化
前端组件化,就是将整个部分是由每一个组件拼接起来的,这样的便于维护。有点像我们生活中拼积木一样,将一个一个的积木拼接起来,组件化就像我们的积木一样,拼接成一个大型项目。
7、使用组件化思想修改TodoList
全局组件:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="inputValue"/> <button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button> <ul> <todo-item v-bind:content="item" v-for="item in list"> </todo-item> </ul> </div> <script> Vue.component("TodoItem", { // 组件化 props: ["content"], template: "<li>{{content}}</li>", }); var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', data: { list: [], inputValue: '', }, methods: { handleBtnClick: function() { this.list.push(this.inputValue); this.inputValue = "" } } }) </script> </body> </html>
组件化与绑定值,这是Vue提供的全局组件,将item与content绑定起来,然后必须将props绑定的值添加到列表中,最后用组件template模板键值对对应需要添加的值。
局部组件:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="inputValue"/> <button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button> <ul> <todo-item v-bind:content="item" v-for="item in list"> </todo-item> </ul> </div> <script> // Vue.component("TodoItem", { // props: ["content"], // template: "<li>{{content}}</li>", // }); var TodoItem = { props: ["content"], template: "<li>{{content}}</li>", } var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', components: { TodoItem: TodoItem }, data: { list: [], inputValue: '', }, methods: { handleBtnClick: function() { this.list.push(this.inputValue); this.inputValue = "" } } }) </script> </body> </html>
对比一下全局组件,局部组件需要将组件注册到Vue实例中去,这样也能实现全局组件的功能。
8、简单的组件间传值
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>TodoList</title> <script src="./vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model="inputValue"/> <button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">提交</button> <ul> <!-- 副组件 --> <todo-item :content="item" v-bind:index="index" v-for="(item,index) in list" @delete="handleItemDelete"> </todo-item> </ul> </div> <script> // Vue.component("TodoItem", { // props: ["content"], // template: "<li>{{content}}</li>", // }); // 子组件 var TodoItem = { props: ["content","index"], template: "<li @click='handleItemClick'>{{content}}</li>", methods: { handleItemClick: function() { this.$emit("delete",this.index); } } } var app = new Vue({ el:'#app', components: { TodoItem: TodoItem }, data: { list: [], inputValue: '', }, methods: { handleBtnClick: function() { this.list.push(this.inputValue); this.inputValue = "" }, handleItemDelete: function(index) { this.list.splice(index,1); }, } }) </script> </body> </html>
副组件传过来的index就会被子组件的props接受,子组件被点击的时候,触发delete事件,同时把this.index作为参数传给副组件,副组件正好监听delete事件,他就会去执行handleItemDelete这个方法,这个方法就会拿到子组件传递过来的值。




