ansible之数据提取与Juniper实例演示
一、Ansible列表两种表达方式
基于YAML的列表
my_list: - a - b - c - d
基于Json格式的列表
{"my_list":[
"a",
"b",
"c",
]
}
二、Ansible列表数据的提取方式
正向列表索引取值
每个列表里的元素,都存在位置,即索引号,可根据列表变量名[索引号]提取,如:my_list[2],取第3个元素,索引号从0开始
反向列表索引取值
每个列表里的元素,都存在位置,即索引号,反向取值可根据列表变量名[-索引号]提取,如:my_list[-2],取倒数第2个元素,反向索引号从-1开始,即代表最后一个元素
正反向切片取值
根据my_list[索引1:索引2],可取到索引1到索引2范围的元素,索引1不填则表示从索引0开始;索引2不填则默认取到最后一个元素 如:my_list=['a','b','c','d','e'] my_list[2:3] #结果:['c','d'],从第3个元素开始,到第4个元素结尾,不包含第4个元素 my_list[:2] #结果:['a','b','c'],从第1个元素开始,到第3个元素,不包含第3个元素 my_list[2:] #结果:['c','d','e'],从第3个元素开始,到最后一个元素,包含最后一个元素 my_list[2:-1] #结果:['c','d','e'],从第3个元素开始,到最后一个元素,不包含最后一个元素
三、Ansible字符串数据提取方式
字符串提取方法与上面列表一样
四、playbook两种方法输出dict字典内容
基于Jinja2格式输出
my_dict.key, 如my_dict={"a":'a1',"b":"b1"}
my_dict.a #输出a1值
基于Python格式输出
my_dict[key], 如my_dict={"a":'a1',"b":"b1"}
my_dict["a"] #输出值a1
五、案例
5.1 Juniper收集设备信息以及数据处理
 1.juniper初始化配置
1.juniper初始化配置2.ansible主控端:nano group_vars/junos.yaml
---
ansible_connection: local
ansible_network_os: junos
ansible_user: admin
ansible_ssh_pass: juniper123
3.ansible主控端:nano test_host文件
[junos]
junipervsrx junos_host=192.168.xx.xx
4.ansible主控端: nano 3_8_3_filter_junos_facts.yaml剧本
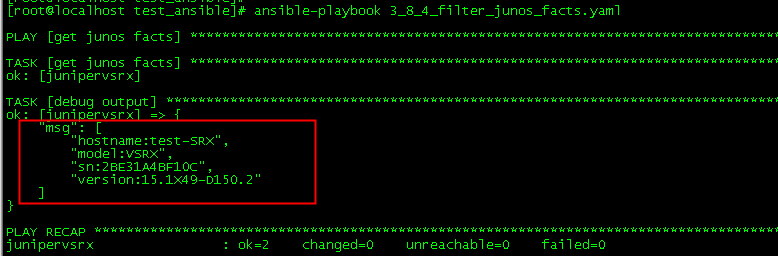
--- - name: get junos facts hosts: junipervsrx gather_facts: no roles: - Juniper.junos tasks: - name: get junos facts juniper_junos_facts: host: "{{junos_host}}" register: facts_result - name: debug output debug: msg: "hostname:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.hostname }}, model:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.model }}, sn:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.serialnumber }}, version:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.version }}"
结果:


- name: debug output debug: msg: - "hostname:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.hostname }}" - "model:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.model }}" - "sn:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.serialnumber }}" - "version:{{ facts_result.ansible_facts.junos.version }}"
结果2:
5.2 Juniper路由表信息收集

juniper初始化配置: 1.root%界面下输入cli 2.root>界面下输入configure,进入配置模式 3.root#界面下输入如下配置 delete system autoinstallation set system host-name test-SRX set system root-authentication plain-text-password回车 #设置root密码 输入密码juniper123 set system login user admin class super-user #新增用户admin,并具有所有权限 set system login user admin authentication plain-text-password 输入密码juniper123 set system services ssh root-login allow #开启ssh服务 set system services netconf ssh port 830 #开启netconf服务承载在ssh,端口830 set interfaces fxp0 unit 0 family inet address 192.168.3.20/24 #配置带外管理口fxp0地址 commit #提交变更
2.ansible主控端:nano group_vars/junos.yaml
---
ansible_connection: local
ansible_network_os: junos
ansible_user: admin
ansible_ssh_pass: juniper123
3.ansible主控端:nano test_host文件
[junos]
junipervsrx junos_host=192.168.xx.xx
4.ansible主控端: nano 3_8_3_filter_junos_facts.yaml剧本
--- - name: get junos routing table hosts: junos gather_facts: no roles: - Juniper.junos tasks: - name: get junos routes juniper_junos_command: commands: - "show route table inet.0" host: "{{junos_host}}" register: route_result - name: debug output debug: msg: "The subnet is {{route_result.stdout_lines[5][0:15]}}, and the host route is: {{route_result.stdout_lines[7][0:16]}}"




